neutralizing antibodies – NIH Director's Blog (original) (raw)
How COVID-19 Immunity Holds Up Over Time
Posted on March 1st, 2022 by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.
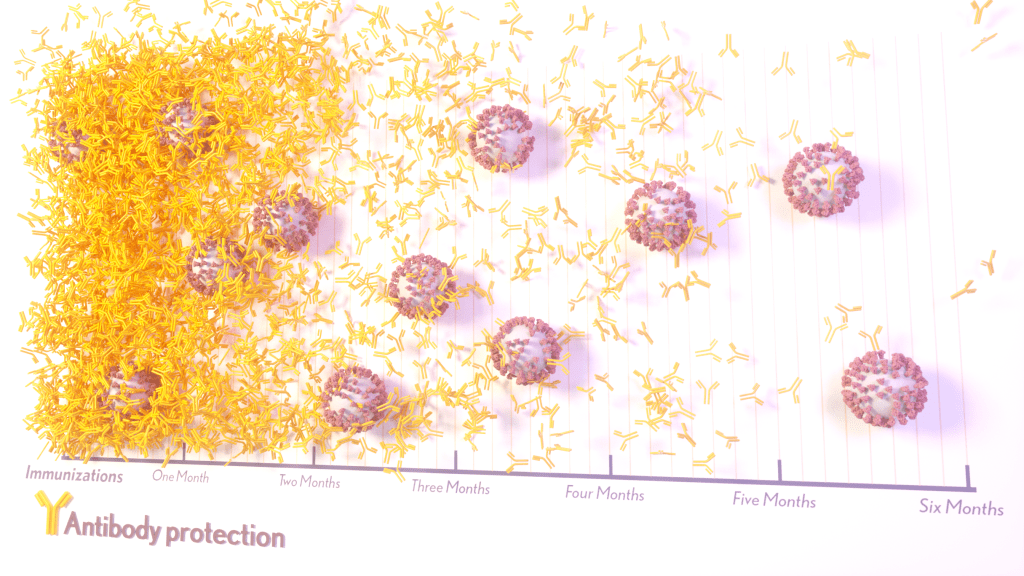
More than 215 million people in the United States are now fully vaccinated against the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19 [1]. More than 40 percent—more than 94 million people—also have rolled up their sleeves for an additional, booster dose. Now, an NIH-funded study exploring how mRNA vaccines are performing over time comes as a reminder of just how important it will be to keep those COVID-19 vaccines up to date as coronavirus variants continue to circulate.
The results, published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, show that people who received two doses of either the Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccines did generate needed virus-neutralizing antibodies [2]. But levels of those antibodies dropped considerably after six months, suggesting declining immunity over time.
The data also reveal that study participants had much reduced protection against newer SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Delta and Omicron. While antibody protection remained stronger in people who’d also had a breakthrough infection, even that didn’t appear to offer much protection against infection by the Omicron variant.
The new study comes from a team led by Shan-Lu Liu at The Ohio State University, Columbus. They wanted to explore how well vaccine-acquired immune protection holds up over time, especially in light of newly arising SARS-CoV-2 variants.
This is an important issue going forward because mRNA vaccines train the immune system to produce antibodies against the spike proteins that crown the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. These new variants often have mutated, or slightly changed, spike proteins compared to the original one the immune system has been trained to detect, potentially dampening the immune response.
In the study, the team collected serum samples from 48 fully vaccinated health care workers at four key time points: 1) before vaccination, 2) three weeks after the first dose, 3) one month after the second dose, and 4) six months after the second dose.
They then tested the ability of antibodies in those samples to neutralize spike proteins as a correlate for how well a vaccine works to prevent infection. The spike proteins represented five major SARS-CoV-2 variants. The variants included D614G, which arose very soon after the coronavirus first was identified in Wuhan and quickly took over, as well as Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529).
The researchers explored in the lab how neutralizing antibodies within those serum samples reacted to SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses representing each of the five variants. SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses are harmless viruses engineered, in this case, to bear coronavirus spike proteins on their surfaces. Because they don’t replicate, they are safe to study without specially designed biosafety facilities.
At any of the four time points, antibodies showed a minimal ability to neutralize the Omicron spike protein, which harbors about 30 mutations. These findings are consistent with an earlier study showing a significant decline in neutralizing antibodies against Omicron in people who’ve received the initial series of two shots, with improved neutralizing ability following an additional booster dose.
The neutralizing ability of antibodies against all other spike variants showed a dramatic decline from 1 to 6 months after the second dose. While there was a marked decline over time after both vaccines, samples from health care workers who’d received the Moderna vaccine showed about twice the neutralizing ability of those who’d received the Pfizer vaccine. The data also suggests greater immune protection in fully vaccinated healthcare workers who’d had a breakthrough infection with SARS-CoV-2.
In addition to recommending full vaccination for all eligible individuals, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) now recommends everyone 12 years and up should get a booster dose of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines at least five months after completing the primary series of two shots [3]. Those who’ve received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine should get a booster at least two months after receiving the initial dose.
While plenty of questions about the durability of COVID-19 immunity over time remain, it’s clear that the rapid deployment of multiple vaccines over the course of this pandemic already has saved many lives and kept many more people out of the hospital. As the Omicron threat subsides and we start to look forward to better days ahead, it will remain critical for researchers and policymakers to continually evaluate and revise vaccination strategies and recommendations, to keep our defenses up as this virus continues to evolve.
References:
[1] COVID-19 vaccinations in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. February 27, 2022.
[2] Neutralizing antibody responses elicited by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination wane over time and are boosted by breakthrough infection. Evans JP, Zeng C, Carlin C, Lozanski G, Saif LJ, Oltz EM, Gumina RJ, Liu SL. Sci Transl Med. 2022 Feb 15:eabn8057.
[3] COVID-19 vaccine booster shots. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Feb 2, 2022.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Shan-Lu Liu (The Ohio State University, Columbus)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Cancer Institute; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
Posted In: News
Tags: antibodies, booster shot, CDC, coronavirus, COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccine, Delta variant, immunity, Moderna, Moderna vaccine, mRNA vaccines, neutralizing antibodies, Omicron variant, pandemic, Pfizer, Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, pseudovirus, SARS-CoV-2, vaccines, variants
Latest on Omicron Variant and COVID-19 Vaccine Protection
Posted on December 14th, 2021 by Dr. Francis Collins
Credit: Adapted from Pfizer, Dec. 8, 2021
There’s been great concern about the new Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. A major reason is Omicron has accumulated over 50 mutations, including about 30 in the spike protein, the part of the coronavirus that mRNA vaccines teach our immune systems to attack. All of these genetic changes raise the possibility that Omicron could cause breakthrough infections in people who’ve already received a Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccine.
So, what does the science show? The first data to emerge present somewhat encouraging results. While our existing mRNA vaccines still offer some protection against Omicron, there appears to be a significant decline in neutralizing antibodies against this variant in people who have received two shots of an mRNA vaccine.
However, initial results of studies conducted both in the lab and in the real world show that people who get a booster shot, or third dose of vaccine, may be better protected. Though these data are preliminary, they suggest that getting a booster will help protect people already vaccinated from breakthrough or possible severe infections with Omicron during the winter months.
Though Omicron was discovered in South Africa only last month, researchers have been working around the clock to learn more about this variant. Last week brought the first wave of scientific data on Omicron, including interesting work from a research team led by Alex Sigal, Africa Health Research Institute, Durban, South Africa [1].
In lab studies working with live Omicron virus, the researchers showed that this variant still relies on the ACE2 receptor to infect human lung cells. That’s really good news. It means that the therapeutic tools already developed, including vaccines, should generally remain useful for combatting this new variant.
Sigal and colleagues also tested the ability of antibodies in the plasma from 12 fully vaccinated individuals to neutralize Omicron. Six of the individuals had no history of COVID-19. The other six had been infected with the original variant in the first wave of infections in South Africa.
As expected, the samples showed very strong neutralization against the original SARS-CoV-2 variant. However, antibodies from people who’d been previously vaccinated with the two-dose Pfizer vaccine took a significant hit against Omicron, showing about a 40-fold decline in neutralizing ability.
This escape from immunity wasn’t complete. Indeed, blood samples from five individuals showed relatively good antibody levels against Omicron. All five had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in addition to being vaccinated. These findings add to evidence on the value of full vaccination for protecting against reinfections in people who’ve had COVID-19 previously.
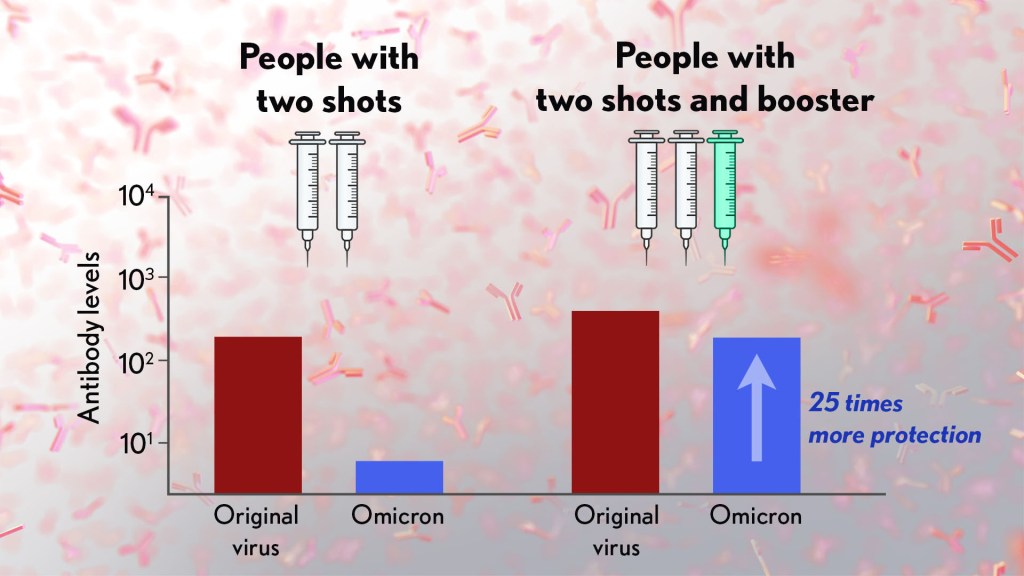
Also of great interest were the first results of the Pfizer study, which the company made available in a news release [2]. Pfizer researchers also conducted laboratory studies to test the neutralizing ability of blood samples from 19 individuals one month after a second shot compared to 20 others one month after a booster shot.
These studies showed that the neutralizing ability of samples from those who’d received two shots had a more than 25-fold decline relative to the original virus. Together with the South Africa data, it suggests that the two-dose series may not be enough to protect against breakthrough infections with the Omicron variant.
In much more encouraging news, their studies went on to show that a booster dose of the Pfizer vaccine raised antibody levels against Omicron to a level comparable to the two-dose regimen against the original variant (as shown in the figure above). While efforts already are underway to develop an Omicron-specific COVID-19 vaccine, these findings suggest that it’s already possible to get good protection against this new variant by getting a booster shot.
Very recently, real-world data from the United Kingdom, where Omicron cases are rising rapidly, are providing additional evidence for how boosters can help. In a preprint [3], Andrews et. al showed the effectiveness of two shots of Pfizer mRNA vaccine trended down after four months to about 40 percent. That’s not great, but note that 40 percent is far better than zero. So, clearly there is some protection provided.
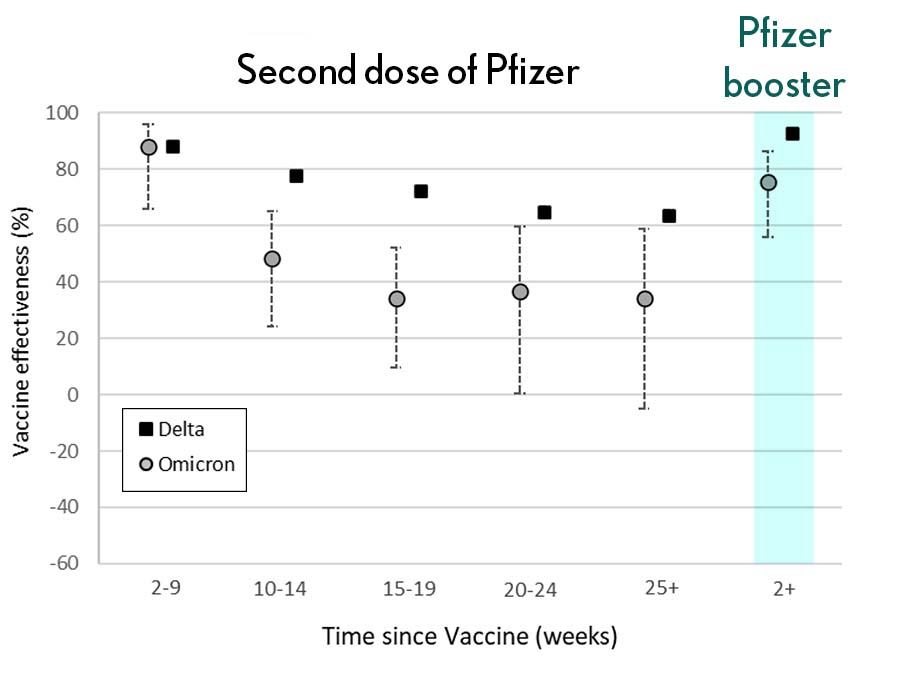
Credit: Andrews N, et al., KHub.net 2021
Most impressively (as shown in the figure from Andrews N, et al.) a booster substantially raised that vaccine effectiveness to about 80 percent. That’s not quite as high as for Delta, but certainly an encouraging result. Once again, these data show that boosting the immune system after a pause produces enhanced immunity against new viral variants, even though the booster was designed from the original virus. Your immune system is awfully clever. You get both quantitative and qualitative benefits.
It’s also worth noting that the Omicron variant mostly doesn’t have mutations in portions of its genome that are the targets of other aspects of vaccine-induced immunity, including T cells. These cells are part of the body’s second line of defense and are generally harder for viruses to escape. While T cells can’t prevent infection, they help protect against more severe illness and death.
It’s important to note that scientists around the world are also closely monitoring Omicron’s severity While this variant appears to be highly transmissible, and it is still early for rigorous conclusions, the initial research indicates this variant may actually produce milder illness than Delta, which is currently the dominant strain in the United States.
But there’s still a tremendous amount of research to be done that could change how we view Omicron. This research will take time and patience.
What won’t change, though, is that vaccines are the best way to protect yourself and others against COVID-19. (And these recent data provide an even-stronger reason to get a booster now if you are eligible.) Wearing a mask, especially in public indoor settings, offers good protection against the spread of all SARS-CoV-2 variants. If you’ve got symptoms or think you may have been exposed, get tested and stay home if you get a positive result. As we await more answers, it’s as important as ever to use all the tools available to keep yourself, your loved ones, and your community happy and healthy this holiday season.
References:
[1] SARS-CoV-2 Omicron has extensive but incomplete escape of Pfizer BNT162b2 elicited neutralization and requires ACE2 for infection. Sandile C, et al. Sandile C, et al. medRxiv preprint. December 9, 2021.
[2] Pfizer and BioNTech provide update on Omicron variant. Pfizer. December 8, 2021.
[3] Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant of concern. Andrews N, et al. KHub.net preprint. December 10, 2021.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Sigal Lab (Africa Health Research Institute, Durban, South Africa)
Posted In: News
Tags: ACE2, booster shot, breakthrough infections, COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccine, Delta variant, mRNA vaccines, mutations, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, Omicron, Omicron variant, pandemic, Pfizer, Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, SARS-CoV-2, South Africa, spike protein, T cells, vaccination, variants
Accelerating COVID-19 Vaccine Testing with ‘Correlates of Protection’
Posted on December 7th, 2021 by Dr. Francis Collins

With Omicron now on so many people’s minds, public health officials and virologists around the world are laser focused on tracking the spread of this concerning SARS-CoV-2 variant and using every possible means to determine the effectiveness of our COVID-19 vaccines against it. Ultimately, the answer will depend on what happens in the real world. But it will also help to have a ready laboratory means for gauging how well a vaccine works, without having to wait many months for the results in the field.
With this latter idea in mind, I’m happy to share results of an NIH-funded effort to understand the immune responses associated with vaccine-acquired protection against SARS-CoV-2 [1]. The findings, based on the analysis of blood samples from more than 1,000 people who received the Moderna mRNA vaccine, show that antibody levels do correlate, albeit somewhat imperfectly, with how well a vaccine works to prevent infection.
Such measures of immunity, known as “correlates of protection,” have potential to support the approval of new or updated vaccines more rapidly. They’re also useful to show how well a vaccine will work in groups that weren’t represented in a vaccine’s initial testing, such as children, pregnant women, and those with certain health conditions.
The latest study, published in the journal Science, comes from a team of researchers led by Peter Gilbert, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle; David Montefiori, Duke University, Durham, NC; and Adrian McDermott, NIH’s Vaccine Research Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
The team started with existing data from the Coronavirus Efficacy (COVE) trial. This phase 3 study, conducted in 30,000 U.S. adults, found the Moderna vaccine was safe and about 94 percent effective in protecting people from symptomatic infection with SARS-CoV-2 [2].
The researchers wanted to understand the underlying immune responses that afforded that impressive level of COVID-19 protection. They also sought to develop a means to measure those responses in the lab and quickly show how well a vaccine works.
To learn more, Gilbert’s team conducted tests on blood samples from COVE participants at the time of their second vaccine dose and again four weeks later. Two of the tests measured concentrations of binding antibodies (bAbs) that latch onto spike proteins that adorn the coronavirus surface. Two others measured the concentration of more broadly protective neutralizing antibodies (nAbs), which block SARS-CoV-2 from infecting human cells via ACE2 receptors found on their surfaces.
Each of the four tests showed antibody levels that were consistently higher in vaccine recipients who did not develop COVID-19 than in those who did. That is consistent with expectations. But these data also allowed the researchers to identify the specific antibody levels associated with various levels of protection from disease.
For those with the highest antibody levels, the vaccine offered an estimated 98 percent protection. Those with levels about 1,000 times lower still were well protected, but their vaccine efficacy was reduced to about 78 percent.
Based on any of the antibodies tested, the estimated COVID-19 risk was about 10 times lower for vaccine recipients with antibodies in the top 10 percent of values compared to those with antibodies that weren’t detectable. Overall, the findings suggest that tests for antibody levels can be applied to make predictions about an mRNA vaccine’s efficacy and may be used to guide modifications to the current vaccine regimen.
To understand the significance of this finding, consider that for a two-dose vaccine like Moderna or Pfizer, a trial using such correlates of protection might generate sufficient data in as little as two months [3]. As a result, such a trial might show whether a vaccine was meeting its benchmarks in 3 to 5 months. By comparison, even a rapid clinical trial done the standard way would take at least seven months to complete. Importantly also, trials relying on such correlates of protection require many fewer participants.
Since all four tests performed equally well, the researchers say it’s conceivable that a single antibody assay might be sufficient to predict how effective a vaccine will be in a clinical trial. Of course, such trials would require subsequent real-world studies to verify that the predicted vaccine efficacy matches actual immune protection.
It should be noted that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) would need to approve the use of such correlates of protection before their adoption in any vaccine trial. But, to date, the totality of evidence on neutralizing antibody responses as correlates of protection—for which this COVE trial data is a major contributor—is impressive.
Neutralizing antibody levels are also now being considered for use in future coronavirus vaccine trials. Indeed, for the EUA of Pfizer’s mRNA vaccine for 5-to-11-year-olds, the FDA accepted pre-specified success criteria based on neutralizing antibody responses in this age group being as good as those observed in 16- to 25-year-olds [4].
Antibody levels also have been taken into consideration for decisions about booster shots. However, it’s important to note that antibody levels are not precise enough to help in deciding whether or not any particular individual needs a COVID-19 booster. Those recommendations are based on how much time has passed since the original immunization.
Getting a booster is a really good idea heading into the holidays. The Delta variant remains very much the dominant strain in the U.S., and we need to slow its spread. Most experts think the vaccines and boosters will also provide some protection against the Omicron variant—though the evidence we need is still a week or two away. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a COVID-19 booster for everyone ages 18 and up at least six months after your second dose of mRNA vaccine or two months after receiving the single dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine [5]. You may choose to get the same vaccine or a different one. And, there is a place near you that is offering the shot.
References:
[1] Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial.
Gilbert PB, Montefiori DC, McDermott AB, Fong Y, Benkeser D, Deng W, Zhou H, Houchens CR, Martins K, Jayashankar L, Castellino F, Flach B, Lin BC, O’Connell S, McDanal C, Eaton A, Sarzotti-Kelsoe M, Lu Y, Yu C, Borate B, van der Laan LWP, Hejazi NS, Huynh C, Miller J, El Sahly HM, Baden LR, Baron M, De La Cruz L, Gay C, Kalams S, Kelley CF, Andrasik MP, Kublin JG, Corey L, Neuzil KM, Carpp LN, Pajon R, Follmann D, Donis RO, Koup RA; Immune Assays Team§; Moderna, Inc. Team§; Coronavirus Vaccine Prevention Network (CoVPN)/Coronavirus Efficacy (COVE) Team§; United States Government (USG)/CoVPN Biostatistics Team§. Science. 2021 Nov 23:eab3435.
[2] Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, Diemert D, Spector SA, Rouphael N, Creech CB, McGettigan J, Khetan S, Segall N, Solis J, Brosz A, Fierro C, Schwartz H, Neuzil K, Corey L, Gilbert P, Janes H, Follmann D, Marovich M, Mascola J, Polakowski L, Ledgerwood J, Graham BS, Bennett H, Pajon R, Knightly C, Leav B, Deng W, Zhou H, Han S, Ivarsson M, Miller J, Zaks T; COVE Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 4;384(5):403-416.
[3] A government-led effort to identify correlates of protection for COVID-19 vaccines. Koup RA, Donis RO, Gilbert PB, Li AW, Shah NA, Houchens CR. Nat Med. 2021 Sep;27(9):1493-1494.
[4] Evaluation of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in children 5 to 11 years of age. Walter EB, Talaat KR, Sabharwal C, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, Paulsen GC, Barnett ED, Muñoz FM, Maldonado Y, Pahud BA, Domachowske JB, Simões EAF, Sarwar UN, Kitchin N, Cunliffe L, Rojo P, Kuchar E, Rämet M, Munjal I, Perez JL, Frenck RW Jr, Lagkadinou E, Swanson KA, Ma H, Xu X, Koury K, Mather S, Belanger TJ, Cooper D, Türeci Ö, Dormitzer PR, Şahin U, Jansen KU, Gruber WC; C4591007 Clinical Trial Group. N Engl J Med. 2021 Nov 9:NEJMoa2116298.
[5] COVID-19 vaccine booster shots. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Nov 29, 2021.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Combat COVID (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services)
Peter Gilbert (Fred Hutchison Cancer Research Center)
David Montefiori (Duke University, Durham, NC)
Adrian McDermott (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/NIH)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Posted In: News
Tags: ACE2, antibodies, clinical trial, Coronavirus Efficacy Trial, correlates of protection, COVE, COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccine, immunity, Johnson & Johnson vaccine, Moderna vaccine, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, Omicron variant, pandemic, Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, SARS-CoV-2, spike protein
Breakthrough Infections Occur in Those with Lower Antibody Levels, Israeli Study Shows
Posted on October 26th, 2021 by Dr. Francis Collins
To see how COVID-19 vaccines are working in the real world, Israel has provided particularly compelling data. The fact that Israel is relatively small, keeps comprehensive medical records, and has a high vaccination rate with a single vaccine (Pfizer) has contributed to its robust data collection. Now, a new Israeli study offers some insight into those relatively uncommon breakthrough infections. It confirms that breakthrough cases, as might be expected, arise most often in individuals with lower levels of neutralizing antibodies.
The findings reported in The New England Journal of Medicine focused on nearly 1,500 of about 11,500 fully vaccinated health care workers at Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel [1]. All had received two doses of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine. But, from December 19, 2020 to April 28, 2021, they were tested for a breakthrough infection due to a known exposure to someone with COVID-19 or possible symptoms of the disease.
Just 39 confirmed breakthrough cases were found, indicating a breakthrough infection rate of just 0.4 percent. That’s consistent with rates reported in previous studies. Most in the Israeli study who tested positive for COVID-19 had mild or no symptoms and none required hospitalization.
In the new study, researchers led by Gili Regev-Yochay at Sheba Medical Center’s Infection Control and Prevention Unit, characterized as many breakthrough infections as possible among the health care workers. Almost half of the infections involved members of the hospital nursing staff. But breakthrough cases also were found in hospital administration, maintenance workers, doctors, and other health professionals.
The average age of someone with a breakthrough infection was 42, and it’s notable that only one person was known to have a weakened immune system. The most common symptoms were respiratory congestion, muscle aches (myalgia), and loss of smell or taste. Most didn’t develop a fever. At six weeks after diagnosis, 19 percent reported having symptoms of Long COVID syndrome, including prolonged loss of smell, persistent cough, weakness, and fatigue. About a quarter stayed home from work for longer than the required 10 days, and one had yet to return to work at six weeks.
For 22 of the 39 people with a breakthrough infection, the researchers had results of neutralizing antibody tests from the week leading up to their positive COVID-19 test result. To look for patterns in the antibody data, they matched those individuals to 104 uninfected people for whom they also had antibody test results. These data showed that those with a breakthrough infection had consistently lower levels of neutralizing antibodies circulating in their bloodstream to SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. In general, higher levels of neutralizing antibodies are associated with greater protection and lower infectivity—though other aspects of the immune system (memory B cells and cell-mediated immunity) also contribute.
Importantly, in all cases for which there were relevant data, the source of the breakthrough infection was thought to be an unvaccinated person. In fact, more than half of those who developed a breakthrough infection appeared to have become infected from an unvaccinated member of their own household.
Other cases were suspected to arise from exposure to an unvaccinated coworker or patient. Contact tracing found no evidence that any of the 39 health care workers with a breakthrough infection passed it on to anyone else.
The findings add to evidence that full vaccination and associated immunity offer good protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe illness. Understanding how SARS-CoV-2 immunity changes over time is key for charting the course of this pandemic and making important decisions about COVID-19 vaccine boosters.
Many questions remain. For instance, it’s not clear from the study whether lower neutralizing antibodies in those with breakthrough cases reflect waning immunity or, for reasons we don’t yet understand, those individuals may have had a more limited immune response to the vaccine. Also, this study was conducted before the Delta variant became dominant in Israel (and now in the whole world).
Overall, these findings provide more reassurance that these vaccines are extremely effective. Breakthrough infections, while they can and do occur, are a relatively uncommon event. Here in the U.S., the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recently estimated that infection is six times less likely for vaccinated than unvaccinated persons [2]. That those with immunity tend to have mild or no symptoms if they do develop a breakthrough case, however, is a reminder that these cases could easily be missed, and they could put vulnerable populations at greater risk. It’s yet another reason for all those who can to get themselves vaccinated as soon as possible or consider a booster shot when they become eligible.
References:
[1] Covid-19 breakthrough infections in vaccinated health care workers. Bergwerk M, Gonen T, Lustig Y, Amit S, Lipsitch M, Cohen C, Mandelboim M, Levin EG, Rubin C, Indenbaum V, Tal I, Zavitan M, Zuckerman N, Bar-Chaim A, Kreiss Y, Regev-Yochay G. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 14;385(16):1474-1484.
[2] Rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths by vaccination status, COVID Data Tracker, Centers for Disease and Prevention. Accessed October 25, 2021.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Sheba Medical Center (Ramat Gan, Israel)
Posted In: News
Tags: booster shot, breakthrough infections, coronavirus, COVID-19, COVID-19 infections, COVID-19 recovery, COVID-19 vaccine, Delta variant, health care, Israel, Long COVID syndrome, neutralizing antibodies, pandemic, Pfizer, Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, SARS-CoV-2
Studies Confirm COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Safe, Effective for Pregnant Women
Posted on June 1st, 2021 by Dr. Francis Collins
Credit: GettyImages/bogdankosanovic
Clinical trials have shown that COVID-19 vaccines are remarkably effective in protecting those age 12 and up against infection by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. The expectation was that they would work just as well to protect pregnant women. But because pregnant women were excluded from the initial clinical trials, hard data on their safety and efficacy in this important group has been limited.
So, I’m pleased to report results from two new studies showing that the two COVID-19 mRNA vaccines now available in the United States appear to be completely safe for pregnant women. The women had good responses to the vaccines, producing needed levels of neutralizing antibodies and immune cells known as memory T cells, which may offer more lasting protection. The research also indicates that the vaccines might offer protection to infants born to vaccinated mothers.
In one study, published in JAMA [1], an NIH-supported team led by Dan Barouch, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, wanted to learn whether vaccines would protect mother and baby. To find out, they enrolled 103 women, aged 18 to 45, who chose to get either the Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna mRNA vaccines from December 2020 through March 2021.
The sample included 30 pregnant women,16 women who were breastfeeding, and 57 women who were neither pregnant nor breastfeeding. Pregnant women in the study got their first dose of vaccine during any trimester, although most got their shots in the second or third trimester. Overall, the vaccine was well tolerated, although some women in each group developed a transient fever after the second vaccine dose, a common side effect in all groups that have been studied.
After vaccination, women in all groups produced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Importantly, those antibodies neutralized SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. The researchers also found those antibodies in infant cord blood and breast milk, suggesting that they were passed on to afford some protection to infants early in life.
The other NIH-supported study, published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology, was conducted by a team led by Jeffery Goldstein, Northwestern’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago [2]. To explore any possible safety concerns for pregnant women, the team took a first look for any negative effects of vaccination on the placenta, the vital organ that sustains the fetus during gestation.
The researchers detected no signs that the vaccines led to any unexpected damage to the placenta in this study, which included 84 women who received COVID-19 mRNA vaccines during pregnancy, most in the third trimester. As in the other study, the team found that vaccinated pregnant women showed a robust response to the vaccine, producing needed levels of neutralizing antibodies.
Overall, both studies show that COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are safe and effective in pregnancy, with the potential to benefit both mother and baby. Pregnant women also are more likely than women who aren’t pregnant to become severely ill should they become infected with this devastating coronavirus [3]. While pregnant women are urged to consult with their obstetrician about vaccination, growing evidence suggests that the best way for women during pregnancy or while breastfeeding to protect themselves and their families against COVID-19 is to roll up their sleeves and get either one of the mRNA vaccines now authorized for emergency use.
References:
[1] Immunogenicity of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in pregnant and lactating women. Collier AY, McMahan K, Yu J, Tostanoski LH, Aguayo R, Ansel J, Chandrashekar A, Patel S, Apraku Bondzie E, Sellers D, Barrett J, Sanborn O, Wan H, Chang A, Anioke T, Nkolola J, Bradshaw C, Jacob-Dolan C, Feldman J, Gebre M, Borducchi EN, Liu J, Schmidt AG, Suscovich T, Linde C, Alter G, Hacker MR, Barouch DH. JAMA. 2021 May 13.
[2] Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination in pregnancy: Measures of immunity and placental histopathology. Shanes ED, Otero S, Mithal LB, Mupanomunda CA, Miller ES, Goldstein JA. Obstet Gynecol. 2021 May 11.
[3] COVID-19 vaccines while pregnant or breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Barouch Laboratory (Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston)
Jeffery Goldstein (Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Cancer Institute, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering
Posted In: News
Tags: breast milk, breastfeeding, cord blood, COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccine, gynecology, infants, Moderna vaccine, mRNA vaccine, neutralizing antibodies, obstetrics, pandemic, Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, placenta, pregnancy, pregnancy complications, SARS-CoV-19 variants, SARS-CoV-2, T cells, women's health
Caught on Camera: Neutralizing Antibodies Interacting with SARS-CoV-2
Posted on December 3rd, 2020 by Dr. Francis Collins

Caption: Illustration showing the binding regions for the four classes of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. They bind to a part of the virus’s spike protein called the receptor binding domain (gray). Credit: Christopher Barnes, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena
As this long year enters its final month, there is good reason to look ahead to 2021 with optimism that the COVID-19 pandemic will finally be contained. The Food and Drug Administration is now reviewing the clinical trial data of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines to ensure their safety and efficacy. If all goes well, emergency use authorization could come very soon, allowing immunizations to begin.
Work also continues on developing better therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Though we’ve learned a great deal about this coronavirus in a short time, structural biologists continue to produce more detailed images that reveal more precisely where and how to target SARS-CoV-2. This research often involves neutralizing antibodies that circulate in the blood of most people who’ve recovered from COVID-19. The study of such antibodies and how they interact with SARS-CoV-2 offers critical biological clues into how to treat and prevent COVID-19.
A recent study in the journal Nature brings more progress, providing the most in-depth analysis yet of how human neutralizing antibodies physically grip SARS-CoV-2 to block it from binding to our cells [1]. To conduct this analysis, a team of NIH-supported structural biologists, led by postdoc Christopher Barnes and Pamela Björkman, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, used the power of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to capture complex molecular interactions at near-atomic scale.
People infected with SARS-CoV-2 (or any foreign substance, for that matter) generate thousands of different versions of attack antibodies. Some of these antibodies are very good at sticking to the coronavirus, while others attach only loosely. Barnes used cryo-EM to capture highly intricate pictures of eight different human neutralizing antibodies bound tightly to SARS-CoV-2. Each of these antibodies, which had been isolated from patients a few weeks after they developed symptoms of COVID-19, had been shown in lab tests to be highly effective at blocking infection.
The researchers mapped all physical interactions between several human neutralizing antibodies and SARS-CoV-2’s spike protein that stud its surface. The virus uses these spiky extensions to infect a human cell by grabbing on to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. The molecular encounter between the coronavirus and ACE2 takes place via one or more of a trio of three protein domains, called receptor-binding domains (RBDs), that jut out from its spikes. RBDs flap up and down in the fluid surrounding cells, “reaching up” to touch and enter, or “laying down” to hide from an infected person’s antibodies and immune cells. Only an “up” RBD can attach to ACE2 and get into a cell.
Taken together with other structural information known about SARS-CoV-2, Barnes’ cryo-EM snapshots revealed four different types of shapes, or classes, of antibody-spike combinations. These high-resolution molecular views show that human neutralizing antibodies interact in many different ways with SARS-CoV-2: blocking access to either one or more RBDs in their “up” or “down” positions.
These results tell us a number of things, including underscoring why strategies that combine multiple types of antibodies in an “antibody cocktail” might likely offer broader protection against infection than using just a single type of antibody. Indeed, that approach is currently being tested in patients with COVID-19.
The findings also provide a molecular guide for custom-designing synthetic antibodies in the lab to foil SARS-CoV-2. As one example, Barnes and his team observed that one antibody completely locked all three RBDs into closed (“down”) positions. As you might imagine, scientists might want to copy that antibody type when designing an antibody-based drug or vaccine.
It is tragic that hundreds of thousands of people have died from this terrible new disease. Yet the immune system helps most to recover. Learning as much as we possibly can from those individuals who’ve been infected and returned to health should help us understand how to heal others who develop COVID-19, as well as inform precision design of additional vaccines that are molecularly targeted to this new foe.
While we look forward to the arrival of COVID-19 vaccines and their broad distribution in 2021, each of us needs to remember to practice the three W’s: Wear a mask. Watch your distance (stay 6 feet apart). Wash your hands often. In parallel with everyone adopting these critical public health measures, the scientific community is working harder than ever to meet this moment, doing everything possible to develop safe and effective ways of treating and preventing COVID-19.
Reference:
[1] SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies. Barnes CO, Jette CA, Abernathy ME, et al. Nature. 2020 Oct 12. [Epub ahead of print].
Links:
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
Combat COVID (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, D.C.)
Freezing a Moment in Time: Snapshots of Cryo-EM Research (National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH)
Björkman Lab (California Institute of Technology, Pasadena)
NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Posted In: News
Tags: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor, antibodies, basic research, coronavirus, COVID-19, cryo-electron microscopy, cryo-EM, drug design, imaging, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, pandemic, RBD, receptor binding domain, SARS-CoV-2, structural biology, treatments, vaccine
Researchers Publish Encouraging Early Data on COVID-19 Vaccine
Posted on July 16th, 2020 by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit: NIH
People all around the globe are anxiously awaiting development of a safe, effective vaccine to protect against the deadly threat of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Evidence is growing that biomedical research is on track to provide such help, and to do so in record time.
Just two days ago, in a paper in the New England Journal of Medicine [1], researchers presented encouraging results from the vaccine that’s furthest along in U.S. human testing: an innovative approach from NIH’s Vaccine Research Center (VRC), in partnership with Moderna Inc., Cambridge, MA [1]. The centerpiece of this vaccine is a small, non-infectious snippet of messenger RNA (mRNA). Injecting this mRNA into muscle will spur a person’s own body to make a key viral protein, which, in turn, will encourage the production of protective antibodies against SARS-CoV-2—the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
While it generally takes five to 10 years to develop a vaccine against a new infectious agent, we simply don’t have that time with a pandemic as devastating as COVID-19. Upon learning of the COVID-19 outbreak in China early this year, and seeing the genome sequence of SARS-CoV-2 appear on the internet, researchers with NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) carefully studied the viral instructions, focusing on the portion that codes for a spike protein that the virus uses to bind to and infect human cells.
Because of their experience with the original SARS virus back in the 2000s, they thought a similar approach to vaccine development would work and modified an existing design to reflect the different sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Literally within days, they had created a vaccine in the lab. They then went on to work with Moderna, a biotech firm that’s produced personalized cancer vaccines. All told, it took just 66 days from the time the genome sequence was made available in January to the start of the first-in-human study described in the new peer-reviewed paper.
In the NIH-supported phase 1 human clinical trial, researchers found the vaccine, called mRNA-1273, to be safe and generally well tolerated. Importantly, human volunteers also developed significant quantities of neutralizing antibodies that target the virus in the right place to block it from infecting their cells.
Conducted at Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, Seattle; and Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, the trial led by Kaiser Permanente’s Lisa Jackson involved healthy adult volunteers. Each volunteer received two vaccinations in the upper arm at one of three doses, given approximately one month apart.
The volunteers will be tracked for a full year, allowing researchers to monitor their health and antibody production. However, the recently published paper provides interim data on the phase 1 trial’s first 45 participants, ages 18 to 55, for the first 57 days after their second vaccination. The data revealed:
• No volunteers suffered serious adverse events.
• Optimal dose to elicit high levels of neutralizing antibody activity, while also protecting patient safety, appears to be 100 micrograms. Doses administered in the phase 1 trial were either 25, 100, or 250 micrograms.
• More than half of the volunteers reported fatigue, headache, chills, muscle aches, or pain at the injection site. Those symptoms were most common after the second vaccination and in volunteers who received the highest vaccine dose. That dose will not be used in larger trials.
• Two doses of 100 micrograms of the vaccine prompted a robust immune response, which was last measured 43 days after the second dose. These responses were actually above the average levels seen in blood samples from people who had recovered from COVID-19.
These encouraging results are being used to inform the next rounds of human testing of the mRNA-1273 vaccine. A phase 2 clinical trial is already well on its way to recruiting 600 healthy adults.This study will continue to profile the vaccine’s safety, as well as its ability to trigger an immune response.
Meanwhile, later this month, a phase 3 clinical trial will begin enrolling 30,000 volunteers, with particular focus on recruitment in regions and populations that have been particularly hard hit by the virus.
The design of that trial, referred to as a “master protocol,” had major contributions from the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccine (ACTIV) initiative, a remarkable public-private partnership involving 20 biopharmaceutical companies, academic experts, and multiple federal agencies. Now, a coordinated effort across the U.S. government, called Operation Warp Speed, is supporting rapid conduct of these clinical trials and making sure that millions of doses of any successful vaccine will be ready if the vaccine proves save and effective.
Results of this first phase 3 trial are expected in a few months. If you are interested in volunteering for these or other prevention trials, please check out NIH’s new COVID-19 clinical trials network.
There’s still a lot of work that remains to be done, and anything can happen en route to the finish line. But by pulling together, and leaning on the very best science, I am confident that we will be able rise to the challenge of ending this pandemic that has devastated so many lives.
Reference:
[1] A SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine—Preliminary Report. Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, Ledgerwood JE, Graham BS, Beigel JH, et al. NEJM. 2020 July 14. [Publication ahead of print]
Links:
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/NIH)
Moderna, Inc. (Cambridge, MA)
Safety and Immunogenicity Study of 2019-nCoV Vaccine (mRNA-1273) for Prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19) (ClinicalTrials.gov)
“NIH Launches Clinical Trials Network to Test COVID-19 Vaccines and Other Prevention Tools,” NIAID News Release, NIH, July 8, 2020.
Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) (NIH)
Explaining Operation Warp Speed (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy _and Infectious Disease_s
Posted In: News
Tags: Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines, ACTIV, antibodies, clinical trials, coronavirus, COVID-19, COVID-19 vaccine, COVPN, Kaiser Permanente, Moderna, mRNA, mRNA-1273, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, Operation Warp Speed, pandemic, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, spike protein, vaccine
Study in Primates Finds Acquired Immunity Prevents COVID-19 Reinfections
Posted on July 14th, 2020 by Dr. Francis Collins
There have been rare reports of people recovering from infection with SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, only to test positive a second time. Such results might be explained by reports that the virus can linger in our systems. Yet some important questions remain: Is it possible that people could beat this virus only to get reinfected a short time later? How long does immunity last after infection? And what can we expect about the duration of protection from a vaccine?
A recent study of rhesus macaques, which are among our close primate relatives, offers relevant insights into the first question. In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers found that after macaques recover from mild SARS-CoV-2 infection, they are protected from reinfection—at least for a while.
In work conducted in the lab of Chuan Qin, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, six macaques were exposed to SARS-CoV-2. Following infection, the animals developed mild-to-moderate illness, including pneumonia and evidence of active infection in their respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Twenty-eight days later, when the macaques had cleared the infection and started recovering, four animals were re-exposed to the same strain of SARS-CoV-2. The other two served as controls, with researchers monitoring their continued recovery.
Qin’s team noted that after the second SARS-CoV-2 exposure, the four macaques developed a transient fever that had not been seen after their first infection. No other signs of reinfection were observed or detected in chest X-rays, and the animals tested negative for active virus over a two-week period.
While more study is needed to understand details of the immune responses, researchers did detect a reassuring appearance of antibodies specific to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the macaques over the course of the first infection. The spike protein is what the virus uses to attach to macaque and human cells before infecting them.
Of interest, levels of those neutralizing antibodies were even higher two weeks after the second viral challenge than they were two weeks after the initial exposure. However, researchers note that it remains unclear which factors specifically were responsible for the observed protection against reinfection, and apparently the first exposure was sufficient.
Since the second viral challenge took place just 28 days after the first infection, this study provides a rather limited window into broad landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery. Consequently, it will be important to determine to what extent a first infection might afford protection over the course of months and even years. Also, because the macaques in this study developed only mild-to-moderate COVID-19, more research is needed to investigate what happens after recovery from more severe COVID-19.
Of course, macaques are not humans. Nevertheless, the findings lend hope that COVID-19 patients who develop acquired immunity may be at low risk for reinfection, at least in the short term. Additional studies are underway to track people who came down with COVID-19 in New York during March and April to see if any experience reinfection. By the end of this year, we should have better answers.
Reference:
[1] Primary exposure to SARS-CoV-2 protects against reinfection in rhesus macaques. Deng W, Bao L, Liu J, et al. Science. 2020 Jul 2. [Published online ahead of print].
Links:
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
Qin Lab (Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China)
Posted In: News
Tags: acquired immunity, antibodies, China, coronavirus, COVID-19, COVID-19 reinfection, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, pandemic, primates, reinfection, rhesus macaques, SARS-CoV-2, spike protein, viral challenge
Finding Antibodies that Neutralize SARS-CoV-2
Posted on June 30th, 2020 by Dr. Francis Collins

Caption: Model of three neutralizing antibodies (blue, purple and orange) bound to the spike protein, which allows SARS-CoV-2 attach to our cells. Credit: Christopher Barnes and Pamela Bjorkman, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
It’s now clear that nearly everyone who recovers from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) produces antibodies that specifically target SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes the infection. Yet many critical questions remain. A major one is: just how well do those particular antibodies neutralize the virus to fight off the infection and help someone recover from COVID-19? Fortunately, most people get better—but should the typical antibody response take the credit?
A new NIH-funded study of nearly 150 people who recovered from COVID-19 offers some essential insight. The study, published in the journal Nature, shows that most people, in fact, do produce antibodies that can effectively neutralize SARS-CoV-2. But there is a catch: 99 percent of the study’s participants didn’t make enough neutralizing antibodies to mount an ideal immune response.
The good news is that when researchers looked at individuals who mounted a strong immune response, they were able to identify three antibodies (depicted above) that were extremely effective at neutralizing SARS-CoV-2. By mass-producing copies of these antibodies as so-called monoclonal antibodies, the researchers can now better evaluate their potential as treatments to help people who don’t make strongly neutralizing antibodies, or not enough of them.
These findings come from a team led by Michel Nussenzweig, Paul Bieniasz, and Charles Rice at The Rockefeller University, New York, and Pamela Bjorkman at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. In the Nussenzweig lab, the team has spent years searching for broadly neutralizing antibodies against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In response to the COVID-19 pandemic and its great urgency, Nussenzweig and team shifted their focus recently to look for promising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.
Antibodies are blood proteins that the immune system makes to neutralize viruses or other foreign invaders. The immune system doesn’t make just one antibody to thwart an invader; it makes a whole family of antibodies. But not all antibodies in that family are created equal. They can vary widely in where they latch onto a virus like SARS-CoV-2, and that determines how effective each will be at blocking it from infecting human cells. That’s one reason why people respond differently to infections such as COVID-19.
In early April, Nussenzweig’s team began analyzing samples from volunteer survivors who visited The Rockefeller Hospital to donate plasma, which contains the antibodies. The volunteers had all recovered from mild-to-severe cases of COVID-19, showing their first signs of illness about 40 days prior to their first plasma collection.
Not surprisingly, all volunteers had produced antibodies in response to the virus. To test the strength of the antibodies, the researchers used a special assay that shows how effective each one is at blocking the virus from infecting human cells in lab dishes.
Overall, most of the plasma samples—118 of 149—showed at best poor to modest neutralizing activity. In about one-third of individuals, their plasma samples had below detectable levels of neutralizing activity. It’s possible those individuals just resolved the infection quickly, before more potent antibodies were produced.
More intriguing to the researchers were the results from two individuals that showed an unusually strong ability to neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Among these two “elite responders” and four other individuals, the researchers identified 40 different antibodies that could neutralize SARS-CoV-2. But again, not all antibodies are created equal. Three neutralized the virus even when present at extremely low levels, and they now will be studied further as possible monoclonal antibodies.
The team determined that those strongly neutralizing antibodies bind three distinct sites on the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the coronavirus spike protein. This portion of the virus is important because it allows SARS-CoV-2 to bind and infect human cells. Importantly, when the researchers looked more closely at plasma samples with poor neutralizing ability, they found that they also contained those RBD-binding antibodies, just not in very large numbers.
These findings help not only to understand the immune response to COVID-19, they are also critical for vaccine design, revealing what a strong neutralizing antibody for SARS-CoV-2 should look like to help the immune system win. If a candidate vaccine can generate such strongly neutralizing antibodies, researchers will know that they are on the right track.
While this research showed that there’s a lot of variability in immune responses to SARS-CoV-2, it appears that most of us are inherently capable of producing antibodies to neutralize this devastating virus. That brings more reason for hope that the many vaccines now under study to elicit such neutralizing antibodies in sufficient numbers may afford us with much-needed immune protection.
Reference:
[1] Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Robbiani DF, Gaebler C, Muecksch F, et al. Nature. 2020 Jun 18. [Published online ahead of print].
Links:
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)
Nussenzweig Lab (The Rockefeller University, New York)
Bjorkman Lab (California Institute of Technology, Pasadena)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Posted In: News
Tags: Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines, ACTIV, antibodies, COVID-19, COVID-19 treatment, drug development, elite responders, HIV, immune response, immunity, immunology, monoclonal antibody, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, spike protein, vaccine development
Discussing the Need for Reliable Antibody Testing for COVID-19
Posted on June 4th, 2020 by Dr. Francis Collins

There’s been a great deal of discussion about whether people who recover from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), have neutralizing antibodies in their bloodstream to guard against another infection. Lots of interesting data continue to emerge, including a recent preprint from researchers at Sherman Abrams Laboratory, Brooklyn, NY [1]. They tested 11,092 people for antibodies in May at a local urgent care facility and found nearly half had long-lasting IgG antibodies, a sign of exposure to the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, the cause of COVID-19. The researchers also found a direct correlation between the severity of a person’s symptoms and their levels of IgG antibodies.
This study and others remind us of just how essential antibody tests will be going forward to learn more about this challenging pandemic. These assays must have high sensitivity and specificity, meaning there would be few false negatives and false positives, to tell us more about a person’s exposure to SARS-CoV-2. While there are some good tests out there, not all are equally reliable.
Recently, I had a chance to discuss COVID-19 antibody tests, also called serology tests, with Dr. Norman “Ned” Sharpless, Director of NIH’s National Cancer Institute (NCI). Among his many talents, Dr. Sharpless is an expert on antibody testing for COVID-19. You might wonder how NCI got involved in COVID-19 testing. Well, you’re going to find out. Our conversation took place while videoconferencing, with him connecting from North Carolina and me linking in from my home in Maryland. Here’s a condensed transcript of our chat:
Collins: Ned, thanks for joining me. Maybe we should start with the basics. What are antibodies anyway?
Sharpless: Antibodies are proteins that your body makes as part of the learned immune system. It’s the immunity that responds to a bacterium or a virus. In general, if you draw someone’s blood after an infection and test it for the presence of these antibodies, you can often know whether they’ve been infected. Antibodies can hang around for quite a while. How long exactly is a topic of great interest, especially in terms of the COVID-19 pandemic. But we think most people infected with coronavirus will make antibodies at a reasonably high level, or titer, in their peripheral blood within a couple of weeks of the infection.
Collins: What do antibodies tell us about exposure to a virus?
Sharpless: A lot of people with coronavirus are infected without ever knowing it. You can use these antibody assays to try and tell how many people in an area have been infected, that is, you can do a so-called seroprevalence survey.
You could also potentially use these antibody assays to predict someone’s resistance to future infection. If you cleared the infection and established immunity to it, you might be resistant to future infection. That might be very useful information. Maybe you could make a decision about how to go out in the community. So, that part is of intense interest as well, although less scientifically sound at the moment.
Collins: I have a 3D-printed model of SARS-CoV-2 on my desk. It’s sort of a spherical virus that has spike proteins on its surface. Do the antibodies interact with the virus in some specific ways?
Sharpless: Yes, antibodies are shaped like the letter Y. They have two binding domains at the head of each Y that will recognize something about the virus. We find antibodies in the peripheral blood that recognize either the virus nucleocapsid, which is the structural protein on the inside; or the spikes, which stick out and give coronavirus its name. We know now that about 99 percent of people who get infected with the virus will develop antibodies eventually. Most of those antibodies that you can detect to the spike proteins will be neutralizing, which means they can kill the virus in a laboratory experiment. We know from other viruses that, generally, having neutralizing antibodies is a promising sign if you want to be immune to that virus in the future.
Collins: Are COVID-19 antibodies protective? Are there reports of people who’ve gotten better, but then were re-exposed and got sick again?
Sharpless: It’s controversial. People can shed the virus’s nucleic acid [genetic material], for weeks or even more than a month after they get better. So, if they have another nucleic acid test it could be positive, even though they feel better. Often, those people aren’t making a lot of live virus, so it may be that they never stopped shedding the virus. Or it may be that they got re-infected. It’s hard to understand what that means exactly. If you think about how many people worldwide have had COVID-19, the number of legitimate possible reinfection cases is in the order of a handful. So, it’s a pretty rare event, if it happens at all.
Collins: For somebody who does have the antibodies, who apparently was previously infected, do they need to stop worrying about getting exposed? Can they can do whatever they want and stop worrying about distancing and wearing masks?
Sharpless: No, not yet. To use antibodies to predict who’s likely to be immune, you’ve got to know two things.
First: can the tests actually measure antibodies reliably? I think there are assays available to the public that are sufficiently good for asking this question, with an important caveat. If you’re trying to detect something that’s really rare in a population, then any test is going to have limitations. But if you’re trying to detect something that’s more common, as the virus was during the recent outbreak in Manhattan, I think the tests are up to the task.
Second: does the appearance of an antibody in the peripheral blood mean that you’re actually immune or you’re just less likely to get the virus? We don’t know the answer to that yet.
Collins: Let’s be optimistic, because it sounds like there’s some evidence to support the idea that people who develop these antibodies are protected against infection. It also sounds like the tests, at least some of them, are pretty good. But if there is protection, how long would you expect it to last? Is this one of those things where you’re all set for life? Or is this going to be something where somebody’s had it and might get it again two or three years from now, because the immunity faded away?
Sharpless: Since we have no direct experience with this virus over time, it’s hard to answer. The potential for this cell-based humoral immunity to last for a while is there. For some viruses, you have a long-lasting antibody protection after infection; for other viruses, not so much.
So that’s the unknown thing. Is immunity going to last for a while? Of course, if one were to bring up the topic of vaccines, that’s very important to know, because you would want to know how often one would have to give that vaccine, even under optimal circumstances.
Collins: Yes, our conversation about immunity is really relevant to the vaccines we’re trying to develop right now. Will these vaccines be protective for long periods of time? We sure hope so, but we’ve got to look carefully at the issue. Let’s come back, though, to the actual performance of the tests. The NCI has been right in the middle of trying to do this kind of validation. How did that happen, and how did that experience go?
Sharpless: Yes, I think one might ask: why is the National Cancer Institute testing antibody kits for the FDA? It is unusual, but certainly not unheard of, for NCI to take up problems like this during a time of a national emergency. During the HIV era, NCI scientists, along with others, identified the virus and did one of the first successful compound screens to find the drug AZT, one of the first effective anti-HIV therapies.
NCI’s Frederick National Lab also has a really good serology lab that had been predominantly working on human papillomavirus (HPV). When the need arose for serologic testing a few months ago, we pivoted that lab to a coronavirus serology lab. It took us a little while, but eventually we rounded up everything you needed to create positive and negative reference panels for antibody testing.
At that time, the FDA had about 200 manufacturers making serology tests that hoped for approval to sell. The FDA wanted some performance testing of those assays by a dispassionate third party. The Frederick National Lab seemed like the ideal place, and the manufacturers started sending us kits. I think we’ve probably tested on the order of 20 so far. We give those data back to the FDA for regulatory decision making. They’re putting all the data online.
Collins: How did it look? Are these all good tests or were there some clunkers?
Sharpless: There were some clunkers. But we were pleased to see that some of the tests appear to be really good, both in our hands and those of other groups, and have been used in thousands of patients.
There are a few tests that have sensitivities that are pretty high and specificities well over 99 percent. The Roche assay has a 99.8 percent specificity claimed on thousands of patients, and for the Mt. Sinai assay developed and tested by our academic collaborators in a panel of maybe 4,000 patients, they’re not sure they’ve ever had a false positive. So, there are some assays out there that are good.
Collins: There’s been talk about how there will soon be monoclonal antibodies directed against SARS-CoV-2. How are those derived?
Sharpless: They’re picked, generally, for appearing to have neutralizing activity. When a person makes antibodies, they don’t make one antibody to a pathogen. They make a whole family of them. And those can be individually isolated, so you can know which antibodies made by a convalescent individual really have virus-neutralizing capacity. That portion of the antibody that recognizes the virus can be engineered into a manufacturing platform to make monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal means one kind of antibody. That approach has worked for other infectious diseases and is an interesting idea here too.
Collins: I can say a bit about that, because we are engaged in a partnership with industry and FDA called Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV). One of the hottest ideas right now is monoclonal antibodies, and we’re in the process of devising a master protocol, one for outpatients and one for inpatients.
Janet Woodcock of Operation Warp Speed tells me 21 companies are developing monoclonal antibodies. While doing these trials, we’d love to do comparisons, which is why it’s good to have an organization like ACTIV to bring everybody together, making sure you’re using the same endpoints and the same laboratory measures. I think that, maybe even by late summer, we might have some results. For people who are looking at what’s the next most-hopeful therapeutic option for people who are really sick with COVID-19, so far we have remdesivir. It helps, but it’s not a home run. Maybe monoclonal antibodies will be the next thing that really gives a big boost in survival. That would be the hope.
Ned, let me ask you one final question about herd, or group, immunity. One hears a bit about that in terms of how we are all going to get past this COVID-19 pandemic. What’s that all about?
Sharpless: Herd immunity is when a significant portion of the population is immune to a pathogen, then that pathogen will die out in the population. There just aren’t enough susceptible people left to infect. What the threshold is for herd immunity depends on how infectious the virus is. For a highly infectious virus, like measles, maybe up to 90 percent of the population must be immune to get herd immunity. Whereas for other less-infectious viruses, it may only be 50 percent of the population that needs to be immune to get herd immunity. It’s a theoretical thing that makes some assumptions, such as that everybody’s health status is the same and the population mixes perfectly every day. Neither of those are true.
How well that actual predictive number will work for coronavirus is unknown. The other thing that’s interesting is a lot of that work has been based on vaccines, such as what percentage do you have to vaccinate to get herd immunity? But if you get to herd immunity by having people get infected, so-called natural herd immunity, that may be different. You would imagine the most susceptible people get infected soonest, and so the heterogeneity of the population might change the threshold calculation.
The short answer is nobody wants to find out. No one wants to get to herd immunity for COVID-19 through natural herd immunity. The way you’d like to get there is with a vaccine that you then could apply to a large portion of the population, and have them acquire immunity in a more safe and controlled manner. Should we have an efficacious vaccine, this question will loom large: how many people do we need to vaccinate to really try and protect vulnerable populations?
Collins: That’s going to be a really critical question for the coming months, as the first large-scale vaccine trials get underway in July, and we start to see how they work and how successful and safe they are. But I’m also worried seeing some reports that 1 out of 5 Americans say they wouldn’t take a vaccine. It would be truly a tragedy if we have a safe and effective vaccine, but we don’t get enough uptake to achieve herd immunity. So, we’ve got some work to do on all fronts, that’s for sure.
Ned, I want to thank you for sharing all this information about antibodies and serologies and other things, as well as thank you for your hard work with all your amazing NCI colleagues.
Sharpless: Thanks for having me.
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
At NCI, A Robust and Rapid Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Norman E. Sharpless. Cancer Currents Blog. April 17, 2020 (National Cancer Institute/NIH)
Posted In: Generic
Tags: Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines, ACTIV, antibodies, Brooklyn, coronavirus serology lab, COVID-19, COVID-19 antibody test, COVID-19 vaccine, FDA, Frederick National Lab, herd immunity, HIV, HPV, IgG, immunity, infectious disease, monoclonal antibody, Mt. Sinai asay, natural herd immunity, Ned Sharpless, neutralizing antibodies, novel coronavirus, nucleocapsid, Operation Warp Speed, pandemic, Roche assay, SARS-CoV-2, serology, seroprevalence, spike protein, vaccine