Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance (original) (raw)
The basic building block of Amazon RDS is the DB instance, where you create your databases. You choose the engine-specific characteristics of the DB instance when you create it. You also choose the storage capacity, CPU, memory, and so on of the AWS instance on which the database server runs.
Topics
DB instance prerequisites
The following are prerequisites for creating an RDS DB instance.
Topics
Configure the network for the DB instance
You can create an Amazon RDS DB instance only in a virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon VPC service. Also, it must be in an AWS Region that has at least two Availability Zones. The DB subnet group that you choose for the DB instance must cover at least two Availability Zones. This configuration ensures that you can configure a Multi-AZ deployment when you create the DB instance or easily move to one in the future.
To set up connectivity between your new DB instance and an Amazon EC2 instance in the same VPC, do so when you create the DB instance. To connect to your DB instance from resources other than EC2 instances in the same VPC, configure the network connections manually.
Topics
Configure automatic network connectivity with an EC2 instance
When you create an RDS DB instance, you can use the AWS Management Console to set up connectivity between an EC2 instance and the new DB instance. When you do so, RDS configures your VPC and network settings automatically. The DB instance is created in the same VPC as the EC2 instance so that the EC2 instance can access the DB instance.
The following are requirements for connecting an EC2 instance with the DB instance:
- The EC2 instance must exist in the AWS Region before you create the DB instance.
If no EC2 instances exist in the AWS Region, the console provides a link to create one. - The user who is creating the DB instance must have permissions to perform the following operations:
ec2:AssociateRouteTableec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgressec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngressec2:CreateRouteTableec2:CreateSubnetec2:CreateSecurityGroupec2:DescribeInstancesec2:DescribeNetworkInterfacesec2:DescribeRouteTablesec2:DescribeSecurityGroupsec2:DescribeSubnetsec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttributeec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress
Using this option creates a private DB instance. The DB instance uses a DB subnet group with only private subnets to restrict access to resources within the VPC.
To connect an EC2 instance to the DB instance, choose Connect to an EC2 compute resource in the Connectivity section on the Create database page.

When you choose Connect to an EC2 compute resource, RDS sets the following options automatically. You can't change these settings unless you choose not to set up connectivity with an EC2 instance by choosingDon't connect to an EC2 compute resource.
| Console option | Automatic setting |
|---|---|
| Network type | RDS sets network type to IPv4. Currently, dual-stack mode isn't supported when you set up a connection between an EC2 instance and the DB instance. |
| Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | RDS sets the VPC to the one associated with the EC2 instance. |
| DB subnet group | RDS requires a DB subnet group with a private subnet in the same Availability Zone as the EC2 instance. If a DB subnet group that meets this requirement exists, then RDS uses the existing DB subnet group. By default, this option is set toAutomatic setup. When you chooseAutomatic setup and there is no DB subnet group that meets this requirement, the following action happens. RDS uses three available private subnets in three Availability Zones where one of the Availability Zones is the same as the EC2 instance. If a private subnet isn’t available in an Availability Zone, RDS creates a private subnet in the Availability Zone. Then RDS creates the DB subnet group.When a private subnet is available, RDS uses the route table associated with the subnet and adds any subnets it creates to this route table. When no private subnet is available, RDS creates a route table without internet gateway access and adds the subnets it creates to the route table.RDS also allows you to use existing DB subnet groups. SelectChoose existing if you want to use an existing DB subnet group of your choice. |
| Public access | RDS chooses No so that the DB instance isn't publicly accessible. For security, it is a best practice to keep the database private and make sure it isn't accessible from the internet. |
| VPC security group (firewall) | RDS creates a new security group that is associated with the DB instance. The security group is namedrds-ec2-n, where n is a number. This security group includes an inbound rule with the EC2 VPC security group (firewall) as the source. This security group that is associated with the DB instance allows the EC2 instance to access the DB instance. RDS also creates a new security group that is associated with the EC2 instance. The security group is namedec2-rds-n, where n is a number. This security group includes an outbound rule with the VPC security group of the DB instance as the source. This security group allows the EC2 instance to send traffic to the DB instance. You can add another new security group by choosingCreate new and typing the name of the new security group. You can add existing security groups by choosingChoose existing and selecting security groups to add. |
| Availability Zone | When you choose Single DB instance inAvailability & durability (Single-AZ deployment), RDS chooses the Availability Zone of the EC2 instance. When you choose Multi-AZ DB instance inAvailability & durability (Multi-AZ DB instance deployment), RDS chooses the Availability Zone of the EC2 instance for one DB instance in the deployment. RDS randomly chooses a different Availability Zone for the other DB instance. Either the primary DB instance or the standby replica is created in the same Availability Zone as the EC2 instance. When you choose Multi-AZ DB instance, there is the possibility of cross Availability Zone costs if the DB instance and EC2 instance are in different Availability Zones. |
For more information about these settings, see Settings for DB instances.
If you change these settings after the DB instance is created, the changes might affect the connection between the EC2 instance and the DB instance.
Configure the network manually
To connect to your DB instance from resources other than EC2 instances in the same VPC, configure the network connections manually. If you use the AWS Management Console to create your DB instance, you can have Amazon RDS automatically create a VPC for you. Or you can use an existing VPC or create a new VPC for your DB instance. With any approach, your VPC requires at least one subnet in each of at least two Availability Zones for use with an RDS DB instance.
By default, Amazon RDS creates the DB instance an Availability Zone automatically for you. To choose a specific Availability Zone, you need to change theAvailability & durability setting toSingle DB instance. Doing so exposes anAvailability Zone setting that lets you choose from among the Availability Zones in your VPC. However, if you choose a Multi-AZ deployment, RDS chooses the Availability Zone of the primary or writer DB instance automatically, and the Availability Zone setting doesn't appear.
In some cases, you might not have a default VPC or haven't created a VPC. In these cases, you can have Amazon RDS automatically create a VPC for you when you create a DB instance using the console. Otherwise, do the following:
- Create a VPC with at least one subnet in each of at least two of the Availability Zones in the AWS Region where you want to deploy your DB instance. For more information, see Working with a DB instance in a VPC and Tutorial: Create a VPC for use with a DB instance (IPv4 only).
- Specify a VPC security group that authorizes connections to your DB instance. For more information, see Provide access to your DB instance in your VPC by creating a security group and Controlling access with security groups.
- Specify an RDS DB subnet group that defines at least two subnets in the VPC that can be used by the DB instance. For more information, see Working with DB subnet groups.
If you want to connect to a resource that isn't in the same VPC as the DB instance, see the appropriate scenarios in Scenarios for accessing a DB instance in a VPC.
Additional prerequisites
Before you create your DB instance, consider the following additional prerequisites:
- If you are connecting to AWS using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) credentials, your AWS account must have certain IAM policies. These grant the permissions required to perform Amazon RDS operations. For more information, see Identity and access management for Amazon RDS.
To use IAM to access the RDS console, sign in to the AWS Management Console with your IAM user credentials. Then go to the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/. - To tailor the configuration parameters for your DB instance, specify a DB parameter group with the required parameter settings. For information about creating or modifying a DB parameter group, see Parameter groups for Amazon RDS.
Important
If you are using the BYOL model for Amazon RDS for Db2, before creating a DB instance, you must first create a custom parameter group that contains your IBM Site ID and IBM Customer ID. For more information, see Bring Your Own License for Db2.
- Determine the TCP/IP port number to specify for your DB instance. The firewalls at some companies block connections to the default ports for RDS DB instances. If your company firewall blocks the default port, choose another port for your DB instance. The default ports for Amazon RDS DB engines are:
RDS for Db2 RDS for MariaDB RDS for MySQL RDS for Oracle RDS for PostgreSQL RDS for SQL Server 50000 3306 3306 1521 5432 1433 For RDS for SQL Server, the following ports are reserved, and you can't use them when you create a DB instance: 1234, 1434, 3260, 3343, 3389, 47001,and49152-49156.
Creating a DB instance
You can create an Amazon RDS DB instance using the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
Note
For RDS for Db2, we recommend that you set up items needed for your license model before you create an RDS for Db2 DB instance. For more information, see Amazon RDS for Db2 licensing options.
You can create a DB instance by using the AWS Management Console with Easy create enabled or not enabled. With Easy create enabled, you specify only the DB engine type, DB instance size, and DB instance identifier. Easy create uses the default setting for other configuration options. With Easy create not enabled, you specify more configuration options when you create a database, including ones for availability, security, backups, and maintenance.
Note
In the following procedure, Standard create is enabled, and Easy create isn't enabled. This procedure uses Microsoft SQL Server as an example.
For examples that use Easy create to walk you through creating and connecting to sample DB instances for each engine, see Getting started with Amazon RDS.
To create a DB instance
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/.
- In the upper-right corner of the Amazon RDS console, choose the AWS Region in which you want to create the DB instance.
- In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
- Choose Create database, then chooseStandard create.
- ForEngine type, choose IBM Db2, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL.
Microsoft SQL Server is shown here.
- For Database management type, if you're using Oracle or SQL Server choose Amazon RDS orAmazon RDS Custom.
Amazon RDS is shown here. For more information on RDS Custom, see Amazon RDS Custom. - ForEdition, if you're using Db2, Oracle, or SQL Server, choose the DB engine edition that you want to use.
MySQL has only one option for the edition, and MariaDB and PostgreSQL have none. - For Version, choose the engine version.
- In Templates, choose the template that matches your use case. If you choose Production, the following are preselected in a later step:
- Multi-AZ failover option
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) storage option
- Enable deletion protection option
We recommend these features for any production environment.
Note
Template choices vary by edition. 10. In the Settings section, open Credential Settings. Then do the following:
- (Optional) Change the Master username value.
- Choose either of the following credentials management options:
- Managed in AWS Secrets Manager
In Select the encryption key, choose either a KMS key that Secrets Manager creates or a key that you have created. - Self managed
To specify a password, clear the Auto generate a password check box if it is selected. Enter the same password in Master password and Confirm master password.
- Managed in AWS Secrets Manager
- (Optional) Set up a connection to a compute resource for this DB instance.
You can configure connectivity between an Amazon EC2 instance and the new DB instance during DB instance creation. For more information, see Configure automatic network connectivity with an EC2 instance. - In the Connectivity section under VPC security group (firewall), if you select Create new, a VPC security group is created with an inbound rule that allows your local computer's IP address to access the database.
- For the remaining sections, specify your DB instance settings. For information about each setting, see Settings for DB instances.
- Choose Create database.
If you chose to use an automatically generated password, theView credential details button appears on theDatabases page.
To view the master username and password for the DB instance, chooseView credential details.
To connect to the DB instance as the master user, use the username and password that appear.
Important
You can't view the master user password again. If you don't record it, you might have to change it. If you need to change the master user password after the DB instance is available, modify the DB instance to do so. For more information about modifying a DB instance, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
15. For Databases, choose the name of the new DB instance.
On the RDS console, the details for the new DB instance appear. The DB instance has a status of Creating until the DB instance is created and ready for use. When the state changes toAvailable, you can connect to the DB instance. Depending on the DB instance class and storage allocated, it can take several minutes for the new instance to be available.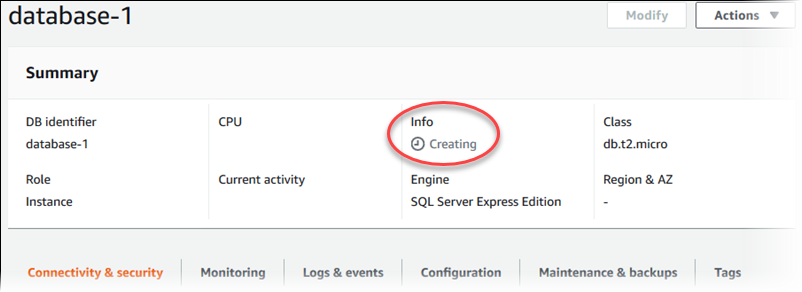
To create a DB instance by using the AWS CLI, call the create-db-instance command with the following parameters:
--db-instance-identifier--db-instance-class--vpc-security-group-ids--db-subnet-group--engine--master-username--master-user-passwordor--manage-master-user-password--allocated-storage--backup-retention-period
For information about each setting, see Settings for DB instances.
This example uses Microsoft SQL Server.
Example
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-instance \
--engine sqlserver-se \
--db-instance-identifier mymsftsqlserver \
--allocated-storage 250 \
--db-instance-class db.t3.large \
--vpc-security-group-ids mysecuritygroup \
--db-subnet-group mydbsubnetgroup \
--master-username masterawsuser \
--manage-master-user-password \
--backup-retention-period 3For Windows:
aws rds create-db-instance ^
--engine sqlserver-se ^
--db-instance-identifier mydbinstance ^
--allocated-storage 250 ^
--db-instance-class db.t3.large ^
--vpc-security-group-ids mysecuritygroup ^
--db-subnet-group mydbsubnetgroup ^
--master-username masterawsuser ^
--manage-master-user-password ^
--backup-retention-period 3This command produces output similar to the following.
DBINSTANCE mydbinstance db.t3.large sqlserver-se 250 sa creating 3 **** n 10.50.2789
SECGROUP default active
PARAMGRP default.sqlserver-se-14 in-syncTo create a DB instance by using the Amazon RDS API, call the CreateDBInstance operation.
For information about each setting, see Settings for DB instances.