Password management with Amazon RDS and AWS Secrets Manager (original) (raw)
Amazon RDS integrates with Secrets Manager to manage master user passwords for your DB instances and Multi-AZ DB clusters.
Topics
- Limitations for Secrets Manager integration with Amazon RDS
- Overview of managing master user passwords with AWS Secrets Manager
- Benefits of managing master user passwords with Secrets Manager
- Permissions required for Secrets Manager integration
- Enforcing RDS management of the master user password in AWS Secrets Manager
- Managing the master user password for a DB instance with Secrets Manager
- Managing the master user password for an RDS for Oracle tenant database with Secrets Manager
- Managing the master user password for a Multi-AZ DB cluster with Secrets Manager
- Rotating the master user password secret for a DB instance
- Rotating the master user password secret for a Multi-AZ DB cluster
- Viewing the details about a secret for a DB instance
- Viewing the details about a secret for a Multi-AZ DB cluster
- Viewing the details about a secret for a tenant database
- Region and version availability
Limitations for Secrets Manager integration with Amazon RDS
Managing master user passwords with Secrets Manager isn't supported for the following features:
- Creating a read replica when the source DB or DB cluster manages credentials with Secrets Manager. This applies to all DB engines except RDS for SQL Server.
- Amazon RDS Blue/Green Deployments
- Amazon RDS Custom
- Oracle Data Guard switchover
Overview of managing master user passwords with AWS Secrets Manager
With AWS Secrets Manager, you can replace hard-coded credentials in your code, including database passwords, with an API call to Secrets Manager to retrieve the secret programmatically. For more information about Secrets Manager, see the AWS Secrets Manager User Guide.
When you store database secrets in Secrets Manager, your AWS account incurs charges. For information about pricing, see AWS Secrets Manager Pricing.
You can specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager for an Amazon RDS DB instance or Multi-AZ DB cluster when you perform one of the following operations:
- Create a DB instance
- Create a Multi-AZ DB cluster
- Create a tenant database in an RDS for Oracle CDB
- Modify a DB instance
- Modify a Multi-AZ DB cluster
- Modify a tenant database (RDS for Oracle only)
- Restore a DB instance from Amazon S3
- Restore a DB instance from a snapshot or to a point in time (RDS for Oracle only)
When you specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager, RDS generates the password and stores it in Secrets Manager. You can interact directly with the secret to retrieve the credentials for the master user. You can also specify a customer managed key to encrypt the secret, or use the KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager.
RDS manages the settings for the secret and rotates the secret every seven days by default. You can modify some of the settings, such as the rotation schedule. If you delete a DB instance that manages a secret in Secrets Manager, the secret and its associated metadata are also deleted.
To connect to a DB instance or Multi-AZ DB cluster with the credentials in a secret, you can retrieve the secret from Secrets Manager. For more information, see Retrieve secrets from AWS Secrets Manager and Connect to a SQL database with credentials in an AWS Secrets Manager secret in the_AWS Secrets Manager User Guide_.
Benefits of managing master user passwords with Secrets Manager
Managing RDS master user passwords with Secrets Manager provides the following benefits:
- RDS automatically generates database credentials.
- RDS automatically stores and manages database credentials in AWS Secrets Manager.
- RDS rotates database credentials regularly, without requiring application changes.
- Secrets Manager secures database credentials from human access and plain text view.
- Secrets Manager allows retrieval of database credentials in secrets for database connections.
- Secrets Manager allows fine-grained control of access to database credentials in secrets using IAM.
- You can optionally separate database encryption from credentials encryption with different KMS keys.
- You can eliminate manual management and rotation of database credentials.
- You can monitor database credentials easily with AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch.
For more information about the benefits of Secrets Manager, see the AWS Secrets Manager User Guide.
Permissions required for Secrets Manager integration
Users must have the required permissions to perform operations related to Secrets Manager integration. You can create IAM policies that grant permissions to perform specific API operations on the specified resources they need. You can then attach those policies to the IAM permission sets or roles that require those permissions. For more information, see Identity and access management for Amazon RDS.
For create, modify, or restore operations, the user who specifies that Amazon RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager must have permissions to perform the following operations:
kms:DescribeKeysecretsmanager:CreateSecretsecretsmanager:TagResource
The kms:DescribeKey permission is required to access your customer-managed key for the MasterUserSecretKmsKeyId and to describe aws/secretsmanager.
For create, modify, or restore operations, the user who specifies the customer managed key to encrypt the secret in Secrets Manager must have permissions to perform the following operations:
kms:Decryptkms:GenerateDataKeykms:CreateGrant
For modify operations, the user who rotates the master user password in Secrets Manager must have permissions to perform the following operation:
secretsmanager:RotateSecret
Enforcing RDS management of the master user password in AWS Secrets Manager
You can use IAM condition keys to enforce RDS management of the master user password in AWS Secrets Manager. The following policy doesn't allow users to create or restore DB instances or DB clusters or create or modify tenant databasesunless the master user password is managed by RDS in Secrets Manager.
JSON
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Deny",
"Action": ["rds:CreateDBInstance", "rds:CreateDBCluster", "rds:RestoreDBInstanceFromS3", "rds:RestoreDBClusterFromS3",
"rds:RestoreDBInstanceFromDBSnapshot", "rds:RestoreDBInstanceToPointInTime", "rds:CreateTenantDatabase",
"rds:ModifyTenantDatabase"],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"Bool": {
"rds:ManageMasterUserPassword": false
}
}
}
]
}
Note
This policy enforces password management in AWS Secrets Manager at creation. However, you can still disable Secrets Manager integration and manually set a master password by modifying theinstance.
To prevent this, include rds:ModifyDBInstance,rds:ModifyDBCluster in the action block of the policy. Be aware, this prevents the user from applying any further modifications to existing instances that don't have Secrets Manager integration enabled.
For more information about using condition keys in IAM policies, see Policy condition keys for Amazon RDS and Example policies: Using condition keys.
Managing the master user password for a DB instance with Secrets Manager
You can configure RDS management of the master user password in Secrets Manager when you perform the following actions:
- Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance
- Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance
- Restoring a backup into an Amazon RDS for MySQL DB instance
- Restoring to a DB instance (RDS for Oracle only)
- Restoring a DB instance to a specified time for Amazon RDS (RDS for Oracle only)
You can perform the preceding operations using the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
Follow the instructions for creating or modifying a DB instance with the RDS console:
- Creating a DB instance
- Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance
- Importing data from Amazon S3 to a new MySQL DB instance
When you use the RDS console to perform one of these operations, you can specify that the master user password is managed by RDS in Secrets Manager. When you're creating or restoring a DB instance, select Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager in Credential settings. When you're modifying a DB instance, select Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager in Settings.
The following image is an example of the Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager setting when you are creating or restoring a DB instance.
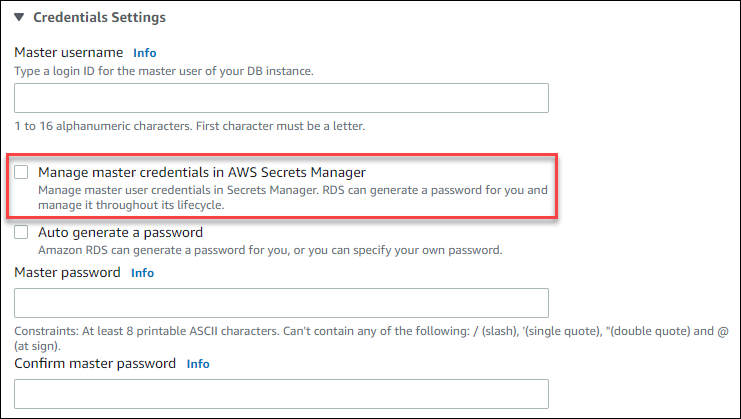
When you select this option, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
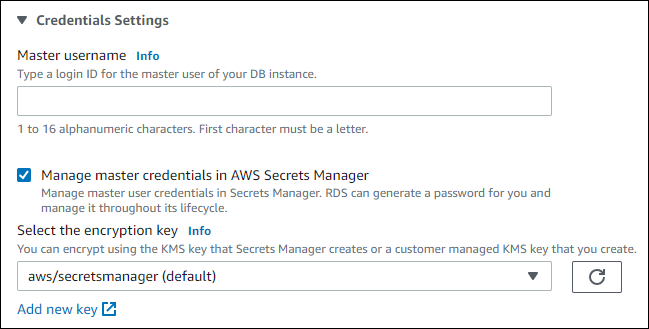
You can choose to encrypt the secret with a KMS key that Secrets Manager provides or with a customer managed key that you create. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB instance, you can't change the KMS key used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements. For more information about the available settings when you're creating a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances. For more information about the available settings when you're modifying a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances.
To manage the master user password with RDS in Secrets Manager, specify the --manage-master-user-password option in one of the following AWS CLI commands:
- create-db-instance
- modify-db-instance
- restore-db-instance-from-s3
- restore-db-instance-from-db-snapshot (RDS for Oracle only)
- restore-db-instance-to-point-in-time (RDS for Oracle only)
When you specify the --manage-master-user-password option in these commands, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use the --master-user-secret-kms-key-id option to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB instance, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements. For more information about the available settings when you are creating a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances. For more information about the available settings when you are modifying a DB instance, see Settings for DB instances.
The following example creates a DB instance and specifies that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager. The secret is encrypted using the KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-instance \
--db-instance-identifier mydbinstance \
--engine mysql \
--engine-version 8.0.39 \
--db-instance-class db.r5b.large \
--allocated-storage 200 \
--master-username testUser \
--manage-master-user-passwordFor Windows:
aws rds create-db-instance ^
--db-instance-identifier mydbinstance ^
--engine mysql ^
--engine-version 8.0.39 ^
--db-instance-class db.r5b.large ^
--allocated-storage 200 ^
--master-username testUser ^
--manage-master-user-passwordTo specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager, set the ManageMasterUserPassword parameter to true in one of the following RDS API operations:
- CreateDBInstance
- ModifyDBInstance
- RestoreDBInstanceFromS3
- RestoreDBInstanceFromSnapshot (RDS for Oracle only)
- RestoreDBInstanceToPointInTime (RDS for Oracle only)
When you set the ManageMasterUserPassword parameter to true in one of these operations, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use the MasterUserSecretKmsKeyId parameter to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB instance, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
Managing the master user password for an RDS for Oracle tenant database with Secrets Manager
You can configure RDS management of the master user password in Secrets Manager when you perform the following actions:
- Adding an RDS for Oracle tenant database to your CDB instance
- Modifying an RDS for Oracle tenant database
You can use the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API to perform the preceding actions.
Follow the instructions for creating or modifying an RDS for Oracle tenant database with the RDS console:
- Adding an RDS for Oracle tenant database to your CDB instance
- Modifying an RDS for Oracle tenant database
When you use the RDS console to perform one of the preceding operations, you can specify that RDS manage the master password in Secrets Manager. When you create a tenant database, selectManage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager inCredential settings. When you modify a tenant database, selectManage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager inSettings.
The following image is an example of the Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager setting when you are creating a tenant database.

When you select this option, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.

You can choose to encrypt the secret with a KMS key that Secrets Manager provides or with a customer managed key that you create. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a tenant database, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements. For more information about the available settings when you are creating a tenant database, see Settings for DB instances. For more information about the available settings when you are modifying a tenant database, see Settings for DB instances.
To manage the master user password with RDS in Secrets Manager, specify the--manage-master-user-password option in one of the following AWS CLI commands:
When you specify the --manage-master-user-password option in the preceding commands, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use the--master-user-secret-kms-key-id option to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a tenant database, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements. For more information about the available settings when you are creating a tenant database, see create-tenant-database. For more information about the available settings when you are modifying a tenant database, see modify-tenant-database.
The following example creates an RDS for Oracle tenant database and specifies that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager. The secret is encrypted using the KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-tenant-database --region us-east-1 \
--db-instance-identifier my-cdb-inst \
--tenant-db-name mypdb2 \
--master-username mypdb2-admin \
--character-set-name UTF-16 \
--manage-master-user-passwordFor Windows:
aws rds create-tenant-database --region us-east-1 ^
--db-instance-identifier my-cdb-inst ^
--tenant-db-name mypdb2 ^
--master-username mypdb2-admin ^
--character-set-name UTF-16 ^
--manage-master-user-passwordTo specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager, set theManageMasterUserPassword parameter to true in one of the following RDS API operations:
When you set the ManageMasterUserPassword parameter totrue in one of these operations, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use theMasterUserSecretKmsKeyId parameter to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a tenant database, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
Managing the master user password for a Multi-AZ DB cluster with Secrets Manager
You can configure RDS management of the master user password in Secrets Manager when you perform the following actions:
You can use the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API to perform these actions.
Follow the instructions for creating or modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster with the RDS console:
When you use the RDS console to perform one of these operations, you can specify that the master user password is managed by RDS in Secrets Manager. To do so when you are creating a DB cluster, select Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager inCredential settings. When you are modifying a DB cluster, select Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager inSettings.
The following image is an example of the Manage master credentials in AWS Secrets Manager setting when you are creating a DB cluster.
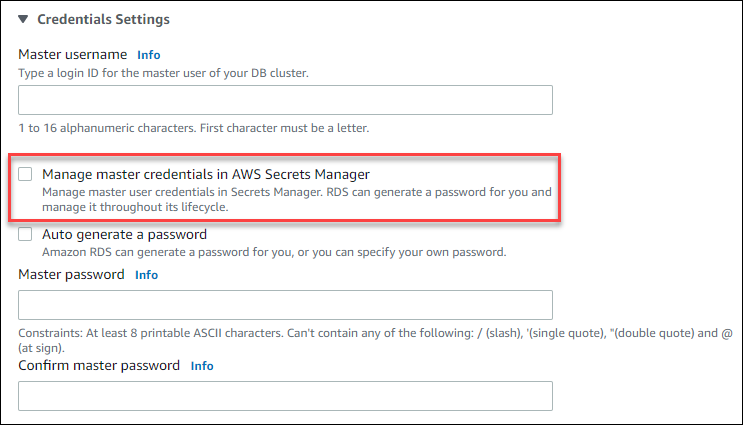
When you select this option, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
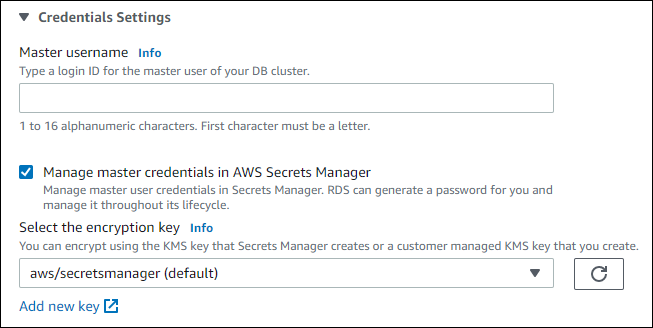
You can choose to encrypt the secret with a KMS key that Secrets Manager provides or with a customer managed key that you create. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB cluster, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements.
For more information about the available settings when you are creating a Multi-AZ DB cluster, see Settings for creating Multi-AZ DB clusters. For more information about the available settings when you are modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster, see Settings for modifying Multi-AZ DB clusters.
To specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager, specify the --manage-master-user-password option in one of the following commands:
When you specify the --manage-master-user-password option in these commands,RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use the --master-user-secret-kms-key-id option to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB cluster, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
You can choose other settings to meet your requirements.
For more information about the available settings when you are creating a Multi-AZ DB cluster, see Settings for creating Multi-AZ DB clusters. For more information about the available settings when you are modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster, see Settings for modifying Multi-AZ DB clusters.
This example creates a Multi-AZ DB cluster and specifies that RDS manages the password in Secrets Manager. The secret is encrypted using the KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-cluster \
--db-cluster-identifier mysql-multi-az-db-cluster \
--engine mysql \
--engine-version 8.0.39 \
--backup-retention-period 1 \
--allocated-storage 4000 \
--storage-type io1 \
--iops 10000 \
--db-cluster-instance-class db.r6gd.xlarge \
--master-username testUser \
--manage-master-user-passwordFor Windows:
aws rds create-db-cluster ^
--db-cluster-identifier mysql-multi-az-db-cluster ^
--engine mysql ^
--engine-version 8.0.39 ^
--backup-retention-period 1 ^
--allocated-storage 4000 ^
--storage-type io1 ^
--iops 10000 ^
--db-cluster-instance-class db.r6gd.xlarge ^
--master-username testUser ^
--manage-master-user-passwordTo specify that RDS manages the master user password in Secrets Manager, set the ManageMasterUserPassword parameter to true in one of the following operations:
When you set the ManageMasterUserPassword parameter to true in one of these operations, RDS generates the master user password and manages it throughout its lifecycle in Secrets Manager.
To encrypt the secret, you can specify a customer managed key or use the default KMS key that is provided by Secrets Manager. Use the MasterUserSecretKmsKeyId parameter to specify a customer managed key. The AWS KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different AWS account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. After RDS is managing the database credentials for a DB cluster, you can't change the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret.
Rotating the master user password secret for a DB instance
When RDS rotates a master user password secret, Secrets Manager generates a new secret version for the existing secret. The new version of the secret contains the new master user password. Amazon RDS changes the master user password for the DB instance to match the password for the new secret version.
You can rotate a secret immediately instead of waiting for a scheduled rotation. To rotate a master user password secret in Secrets Manager, modify the DB instance. For information about modifying a DB instance, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
You can rotate a master user password secret immediately with the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API. The new password is always 28 characters long and contains at least one upper and lowercase character, one number, and one punctuation.
To rotate a master user password secret using the RDS console, modify the DB instance and select Rotate secret immediately in Settings.
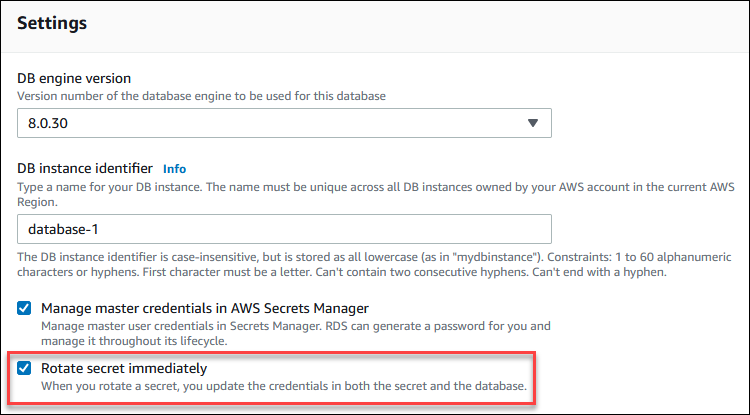
Follow the instructions for modifying a DB instance with the RDS console in Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance. You must choose Apply immediately on the confirmation page.
To rotate a master user password secret using the AWS CLI, use the modify-db-instance command and specify the --rotate-master-user-password option. You must specify the --apply-immediately option when you rotate the master password.
This example rotates a master user password secret.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-instance \
--db-instance-identifier mydbinstance \
--rotate-master-user-password \
--apply-immediatelyFor Windows:
aws rds modify-db-instance ^
--db-instance-identifier mydbinstance ^
--rotate-master-user-password ^
--apply-immediatelyYou can rotate a master user password secret using the ModifyDBInstance operation and setting the RotateMasterUserPassword parameter to true. You must set the ApplyImmediately parameter to true when you rotate the master password.
Rotating the master user password secret for a Multi-AZ DB cluster
When RDS rotates a master user password secret, Secrets Manager generates a new secret version for the existing secret. The new version of the secret contains the new master user password.Amazon RDS changes the master user password for the Multi-AZ DB cluster to match the password for the new secret version.
You can rotate a secret immediately instead of waiting for a scheduled rotation. To rotate a master user password secret in Secrets Manager, modify the Multi-AZ DB cluster. For information about modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster, see Modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster for Amazon RDS.
You can rotate a master user password secret immediately with the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API. The new password is always 28 characters long and contains atleast one upper and lowercase character, one number, and one punctuation.
To rotate a master user password secret using the RDS console, modify the Multi-AZ DB cluster and selectRotate secret immediately inSettings.
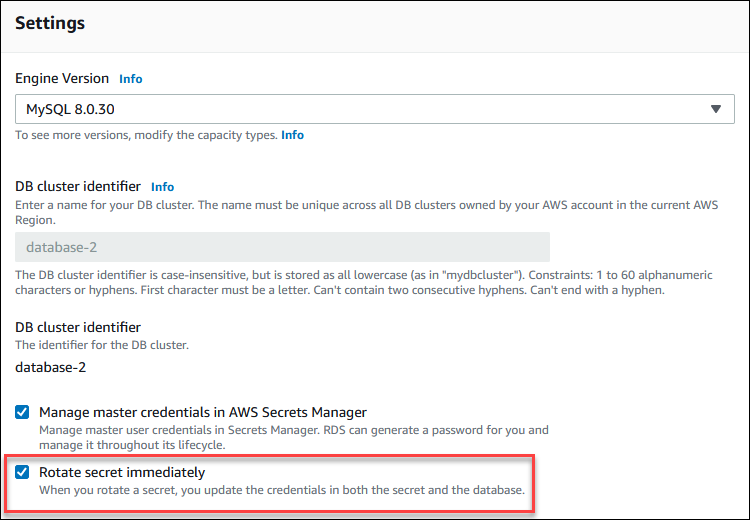
Follow the instructions for modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster with the RDS console in Modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster for Amazon RDS. You must chooseApply immediately on the confirmation page.
To rotate a master user password secret using the AWS CLI, use the modify-db-cluster command and specify the --rotate-master-user-password option. You must specify the --apply-immediately option when you rotate the master password.
This example rotates a master user password secret.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-cluster \
--db-cluster-identifier mydbcluster \
--rotate-master-user-password \
--apply-immediatelyFor Windows:
aws rds modify-db-cluster ^
--db-cluster-identifier mydbcluster ^
--rotate-master-user-password ^
--apply-immediatelyYou can rotate a master user password secret using the ModifyDBCluster operation and setting the RotateMasterUserPassword parameter to true. You must set the ApplyImmediately parameter to true when you rotate the master password.
Viewing the details about a secret for a DB instance
You can retrieve your secrets using the console (https://console.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/) or the AWS CLI (get-secret-value Secrets Manager command).
You can find the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager with the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
To view the details about a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/.
- In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
- Choose the name of the DB instance to show its details.
- Choose the Configuration tab.
In Master Credentials ARN, you can view the secret ARN.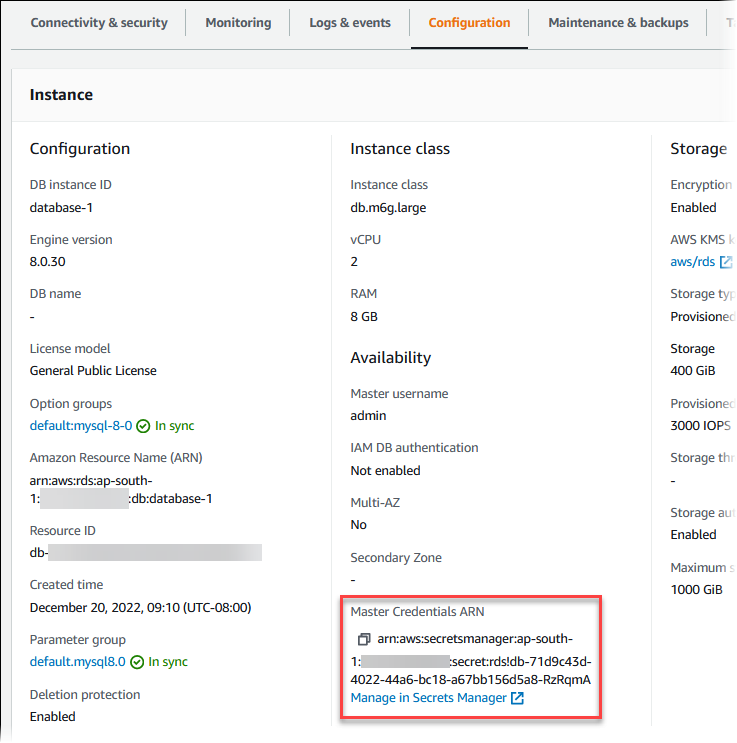
You can follow the Manage in Secrets Manager link to view and manage the secret in the Secrets Manager console.
You can use the describe-db-instances RDS CLI command to find the following information about a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager:
SecretArn– The ARN of the secretSecretStatus– The status of the secret
The possible status values include the following:creating– The secret is being created.active– The secret is available for normal use and rotation.rotating– The secret is being rotated.impaired– The secret can be used to access database credentials, but it can't be rotated. A secret might have this status if, for example, permissions are changed so that RDS can no longer access the secret or the KMS key for the secret.
When a secret has this status, you can correct the condition that caused the status. If you correct the condition that caused status, the status remainsimpaireduntil the next rotation. Alternatively, you can modify the DB instance to turn off automatic management of database credentials, and then modify the DB instance again to turn on automatic management of database credentials. To modify the DB instance, use the--manage-master-user-passwordoption in the modify-db-instance command.
KmsKeyId– The ARN of the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret
Specify the --db-instance-identifier option to show output for a specific DB instance. This example shows the output for a secret that is used by a DB instance.
aws rds describe-db-instances --db-instance-identifier mydbinstanceFollowing is sample output for a secret:
"MasterUserSecret": {
"SecretArn": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!db-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx",
"SecretStatus": "active",
"KmsKeyId": "arn:aws:kms:eu-west-1:123456789012:key/0987dcba-09fe-87dc-65ba-ab0987654321"
}When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the get-secret-value Secrets Manager CLI command.
This example shows the details for the secret in the previous sample output.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value \
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!db-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx'For Windows:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value ^
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!db-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx'You can view the ARN, status, and KMS key for a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager by using the DescribeDBInstances operation and setting the DBInstanceIdentifier parameter to a DB instance identifier. Details about the secret are included in the output.
When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the GetSecretValue Secrets Manager operation.
Viewing the details about a secret for a Multi-AZ DB cluster
You can retrieve your secrets using the console (https://console.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/) or the AWS CLI (get-secret-value Secrets Manager command).
You can find the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager with the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
To view the details about a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/.
- In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
- Choose the name of the Multi-AZ DB cluster to show its details.
- Choose the Configuration tab.
In Master Credentials ARN, you can view the secret ARN.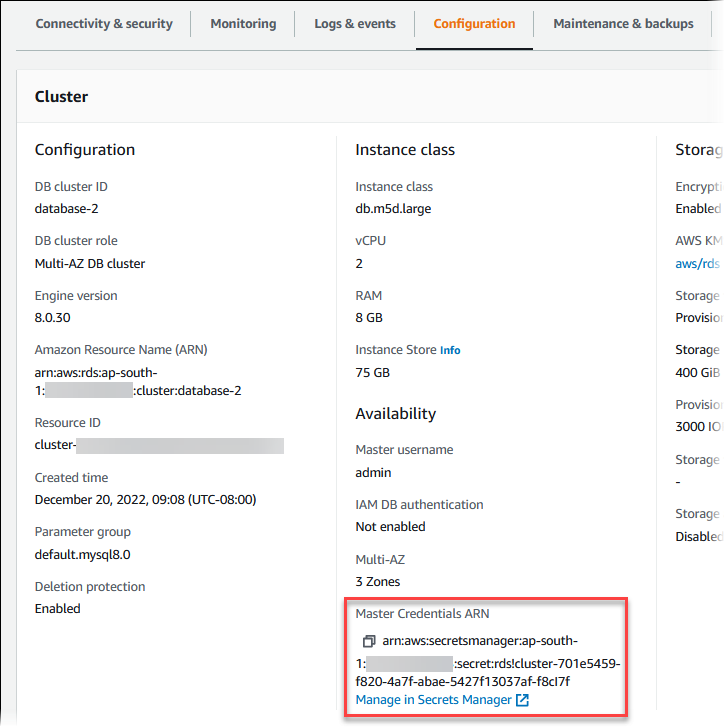
You can follow the Manage in Secrets Manager link to view and manage the secret in the Secrets Manager console.
You can use the RDS AWS CLI describe-db-clusters command to find the following information about a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager:
SecretArn– The ARN of the secretSecretStatus– The status of the secret
The possible status values include the following:creating– The secret is being created.active– The secret is available for normal use and rotation.rotating– The secret is being rotated.impaired– The secret can be used to access database credentials, but it can't be rotated. A secret might have this status if, for example, permissions are changed so that RDS can no longer access the secret or the KMS key for the secret.
When a secret has this status, you can correct the condition that caused the status. If you correct the condition that caused status, the status remainsimpaireduntil the next rotation. Alternatively, you can modify the DB cluster to turn off automatic management of database credentials, and then modify the DB cluster again to turn on automatic management of database credentials. To modify the DB cluster, use the--manage-master-user-passwordoption in the modify-db-cluster command.
KmsKeyId– The ARN of the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret
Specify the --db-cluster-identifier option to show output for a specific DB cluster. This example shows the output for a secret that is used by a DB cluster.
aws rds describe-db-clusters --db-cluster-identifier mydbclusterThe following sample shows the output for a secret:
"MasterUserSecret": {
"SecretArn": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!cluster-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx",
"SecretStatus": "active",
"KmsKeyId": "arn:aws:kms:eu-west-1:123456789012:key/0987dcba-09fe-87dc-65ba-ab0987654321"
}When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the get-secret-value Secrets Manager CLI command.
This example shows the details for the secret in the previous sample output.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value \
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!cluster-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx'For Windows:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value ^
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:eu-west-1:123456789012:secret:rds!cluster-033d7456-2c96-450d-9d48-f5de3025e51c-xmJRDx'You can view the ARN, status, and KMS key for a secret managed by RDS in Secrets Manager using the DescribeDBClusters RDS operation and setting the DBClusterIdentifier parameter to a DB cluster identifier. Details about the secret are included in the output.
When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the GetSecretValue Secrets Manager operation.
Viewing the details about a secret for a tenant database
You can retrieve your secrets using the console (https://console.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/) or the AWS CLI (get-secret-value Secrets Manager command).
You can find the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of a secret managed by Amazon RDS in AWS Secrets Manager with the Amazon RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the Amazon RDS API.
To view the details about a secret managed by Amazon RDS in AWS Secrets Manager for a tenant database
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/.
- In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
- Choose the name of the DB instance that contains the tenant database to show its details.
- Choose the Configuration tab.
In the Tenant databases section, find the tenant database and view its Master Credentials ARN.
You can follow the Manage in Secrets Manager link to view and manage the secret in the Secrets Manager console.
You can use the describe-tenant-databases Amazon RDS AWS CLI command to find the following information about a secret managed by Amazon RDS in AWS Secrets Manager for a tenant database:
SecretArn– The ARN of the secretSecretStatus– The status of the secret
The possible status values include the following:creating– The secret is being created.active– The secret is available for normal use and rotation.rotating– The secret is being rotated.impaired– The secret can be used to access database credentials, but it can't be rotated. A secret might have this status if, for example, permissions are changed so that Amazon RDS can no longer access the secret or the KMS key for the secret.
When a secret has this status, you can correct the condition that caused the status. If you correct the condition that caused status, the status remainsimpaireduntil the next rotation. Alternatively, you can modify the tenant database to turn off automatic management of database credentials, and then modify the tenant database again to turn on automatic management of database credentials. To modify the tenant database, use the--manage-master-user-passwordoption in the modify-tenant-database command.
KmsKeyId– The ARN of the KMS key that is used to encrypt the secret
Specify the --db-instance-identifier option to show output for tenant databases in a specific DB instance. You can also specify the --tenant-db-name option to show output for a specific tenant database. This example shows the output for a secret that is used by a tenant database.
aws rds describe-tenant-databases \
--db-instance-identifier database-3 \
--query "TenantDatabases[0].MasterUserSecret"Following is sample output for a secret:
{
"SecretArn": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-2:123456789012:secret:rds!db-ABC123",
"SecretStatus": "active",
"KmsKeyId": "arn:aws:kms:us-east-2:123456789012:key/aa11bb22-####-####-####-fedcba123456"
}When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the get-secret-value Secrets Manager AWS CLI command.
This example shows the details for the secret in the previous sample output.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value \
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-2:123456789012:secret:rds!db-ABC123'For Windows:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value ^
--secret-id 'arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-2:123456789012:secret:rds!db-ABC123'You can view the ARN, status, and KMS key for a secret managed by Amazon RDS in AWS Secrets Manager by using the DescribeTenantDatabases operation and setting the DBInstanceIdentifier parameter to a DB instance identifier. You can also set the TenantDBName parameter to a specific tenant database name. Details about the secret are included in the output.
When you have the secret ARN, you can view details about the secret using the GetSecretValue Secrets Manager operation.
Region and version availability
Feature availability and support varies across specific versions of each database engine and across AWS Regions. For more information about version and Region availability with Secrets Manager integration with Amazon RDS, see Supported Regions and DB engines for the Secrets Manager integration with Amazon RDS.