Cache settings for REST APIs in API Gateway (original) (raw)
You can enable API caching in API Gateway to cache your endpoint's responses. With caching, you can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API.
When you enable caching for a stage, API Gateway caches responses from your endpoint for a specified time-to-live (TTL) period, in seconds. API Gateway then responds to the request by looking up the endpoint response from the cache instead of making a request to your endpoint. The default TTL value for API caching is 300 seconds. The maximum TTL value is 3600 seconds. TTL=0 means caching is disabled.
Note
Caching is best-effort. You can use the CacheHitCount and CacheMissCount metrics in Amazon CloudWatch to monitor requests that API Gateway serves from the API cache.
The maximum size of a response that can be cached is 1048576 bytes. Cache data encryption may increase the size of the response when it is being cached.
This is a HIPAA Eligible Service. For more information about AWS, U.S. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), and using AWS services to process, store, and transmit protected health information (PHI), see HIPAA Overview.
Important
When you enable caching for a stage, only GET methods have caching enabled by default. This helps to ensure the safety and availability of your API. You can enable caching for other methods by overriding method settings.
Important
Caching is charged by the hour based on the cache size that you select. Caching is not eligible for the AWS Free Tier. For more information, see API Gateway Pricing.
Enable Amazon API Gateway caching
In API Gateway, you can enable caching for a specific stage.
When you enable caching, you must choose a cache capacity. In general, a larger capacity gives a better performance, but also costs more. For supported cache sizes, see cacheClusterSize in the API Gateway API Reference.
API Gateway enables caching by creating a dedicated cache instance. This process can take up to 4 minutes.
API Gateway changes caching capacity by removing the existing cache instance and creating a new one with a modified capacity. All existing cached data is deleted.
Note
The cache capacity affects the CPU, memory, and network bandwidth of the cache instance. As a result, the cache capacity can affect the performance of your cache.
API Gateway recommends that you run a 10-minute load test to verify that your cache capacity is appropriate for your workload. Ensure that traffic during the load test mirrors production traffic. For example, include ramp up, constant traffic, and traffic spikes. The load test should include responses that can be served from the cache, as well as unique responses that add items to the cache. Monitor the latency, 4xx, 5xx, cache hit, and cache miss metrics during the load test. Adjust your cache capacity as needed based on these metrics. For more information about load testing, see How do I select the best API Gateway cache capacity to avoid hitting a rate limit?.
AWS Management Console
In the API Gateway console, you configure caching on the Stages page. You provision the stage cache and specify a default method-level cache setting. If you turn on the default method-level cache, method-level caching is turned on for all GET methods on your stage, unless that method has a method override. Any additional GET methods that you deploy to your stage will have a method-level cache. To configure method-level caching setting for specific methods of your stage, you can use method overrides. For more information about method overrides, see Override API Gateway stage-level caching for method-level caching.
To configure API caching for a given stage:
- Sign in to the API Gateway console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway.
- Choose Stages.
- In the Stages list for the API, choose the stage.
- In the Stage details section, choose Edit.
- Under Additional settings, for Cache settings, turn onProvision API cache.
This provisions a cache cluster for your stage. - To activate caching for your stage, turn on Default method-level caching.
This turns on method-level caching for allGETmethods on your stage. Any additionalGETmethods that you deploy to this stage will have a method-level cache.
Note
If you have an existing setting for a method-level cache, changing the default method-level caching setting doesn't affect that existing setting.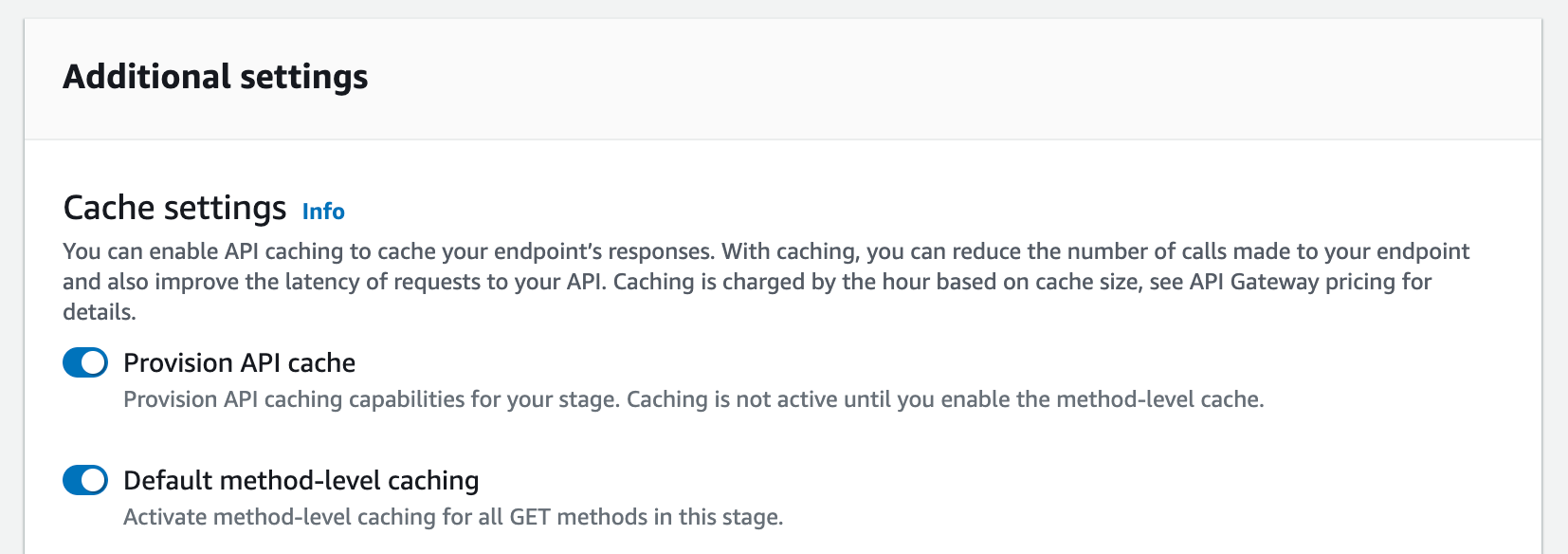 7. Choose Save changes.
7. Choose Save changes.
AWS CLI
The following update-stage command updates a stage to provision a cache and turns on method-level caching for all GET methods on your stage:
aws apigateway update-stage \
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 \
--stage-name 'prod' \
--patch-operations file://patch.jsonThe contents of patch.json are the following:
[
{
"op": "replace",
"path": "/cacheClusterEnabled",
"value": "true"
},
{
"op": "replace",
"path": "/cacheClusterSize",
"value": "0.5"
},
{
"op": "replace",
"path": "/*/*/caching/enabled",
"value": "true"
}
]Note
If you have an existing setting for a method-level cache, changing the default method-level caching setting doesn't affect that existing setting.
Note
Creating or deleting a cache takes about 4 minutes for API Gateway to complete.
When a cache is created, the Cache cluster value changes from Create in progress toActive. When cache deletion is completed, the Cache cluster value changes fromDelete in progress to Inactive.
When you turn on method-level caching for all methods on your stage, the Default method-level caching value changes toActive. If you turn off method-level caching for all methods on your stage, the Default method-level caching value changes to Inactive. If you have an existing setting for a method-level cache, changing the status of the cache doesn't affect that setting.
When you enable caching within a stage's Cache settings, only GET methods are cached. To ensure the safety and availability of your API, we recommend that you don't change this setting. However, you can enable caching for other methods by overriding method settings.
If you would like to verify if caching is functioning as expected, you have two general options:
- Inspect the CloudWatch metrics of CacheHitCount and CacheMissCount for your API and stage.
- Put a timestamp in the response.
Note
Don't use the X-Cache header from the CloudFront response to determine if your API is being served from your API Gateway cache instance.
Override API Gateway stage-level caching for method-level caching
You can override stage-level cache settings by turning on or turning off caching for a specific method. You can also modify the TTL period or turn encryption on or off for cached responses.
If you anticipate that a method that you are caching will receive sensitive data in its responses, encrypt your cache data. You might need to do this to comply with various compliance frameworks. For more information, see Amazon API Gateway controls in the AWS Security Hub User Guide.
AWS Management Console
If you change the default method-level caching setting in the Stage details, it doesn't affect the method-level cache settings that have overrides.
If you anticipate that a method that you are caching will receive sensitive data in its responses, in Cache Settings, choose Encrypt cache data.
To configure API caching for individual methods using the console:
- Sign in to the API Gateway console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway.
- Choose the API.
- Choose Stages.
- In the Stages list for the API, expand the stage and choose a method in the API.
- In the Method overrides section, chooseEdit.
- In the Method settings section, turn on or offEnable method cache or customize any other desired options.
Note
Caching is not active until you provision a cache cluster for your stage. 7. Choose Save.
AWS CLI
The following update-stage command turns off the cache only for the GET /pets method:
aws apigateway update-stage /
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 /
--stage-name 'prod' /
--patch-operations file://patch.jsonThe contents of patch.json are the following:
[{
"op": "replace",
"path": "/~1pets/GET/caching/enabled",
"value": "false"
}]Use method or integration parameters as cache keys to index cached responses
You can use a method or integration parameter as cache keys to index cached responses. This includes custom headers, URL paths, or query strings. You can specify some or all of these parameters as the cache key, but you must specify at least one value. When you have a cache key, API Gateway caches the responses from each key value separately, including when the cache key isn't present.
Note
Cache keys are required when setting up caching on a resource.
For example, suppose you have a request in the following format:
GET /users?type=... HTTP/1.1
host: example.com
...
In this request, type can take a value of admin orregular. If you include the type parameter as part of the cache key, the responses from GET /users?type=admin are cached separately from those from GET /users?type=regular.
When a method or integration request takes more than one parameter, you can choose to include some or all of the parameters to create the cache key. For example, you can include only the type parameter in the cache key for the following request, made in the listed order within a TTL period:
GET /users?type=admin&department=A HTTP/1.1
host: example.com
...
The response from this request is cached and is used to serve the following request:
GET /users?type=admin&department=B HTTP/1.1
host: example.com
...
AWS Management Console
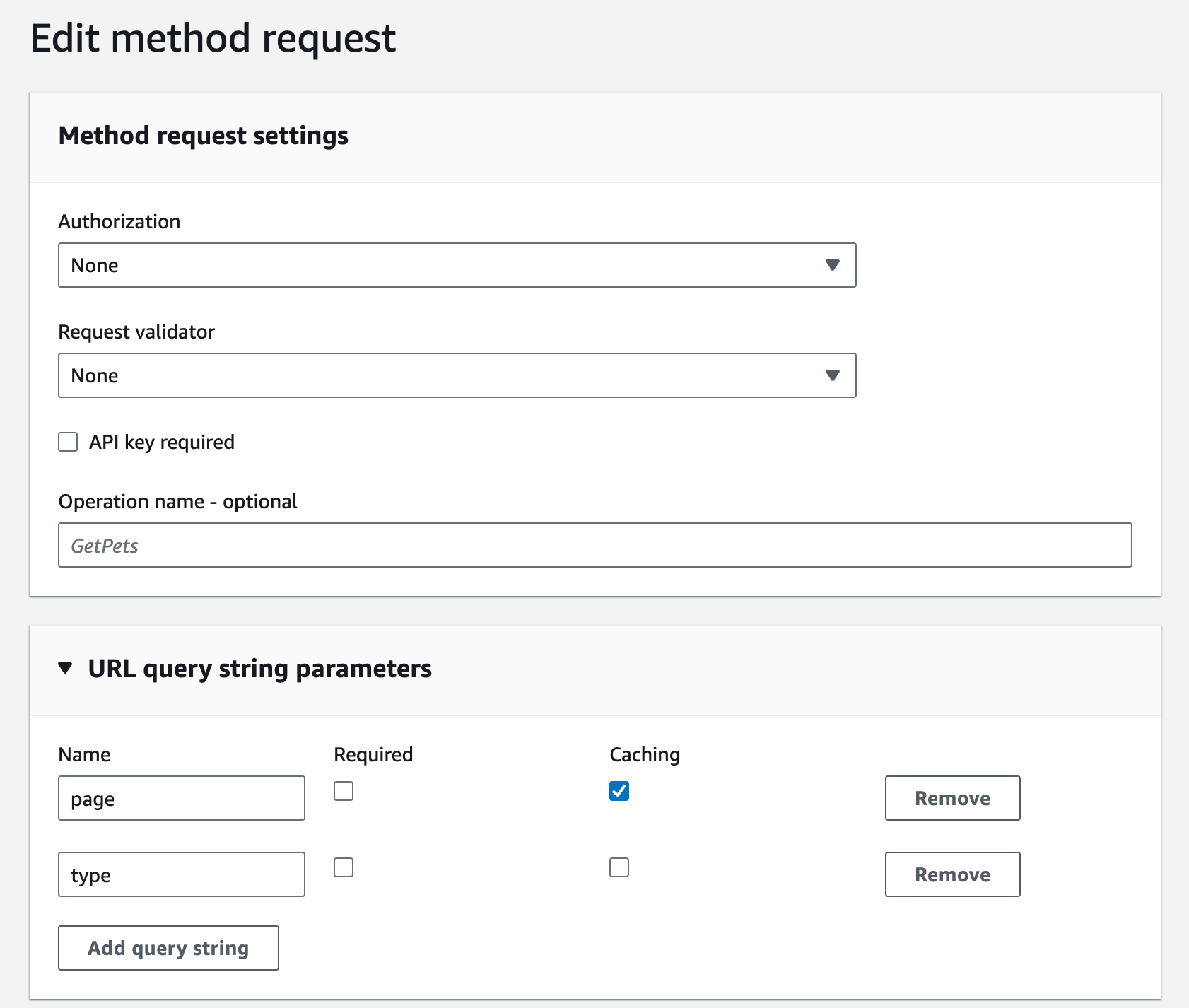
To include a method or integration request parameter as part of a cache key in the API Gateway console, select Caching after you add the parameter.
AWS CLI
The following put-method command creates aGET method and requires the type query string parameter:
aws apigateway put-method /
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 /
--resource-id aaa111 /
--http-method GET /
--authorization-type "NONE" /
--request-parameters "method.request.querystring.type=true"The following put-integration command creates an integration for the GET method with an HTTP endpoint and specifies that API Gateway caches the type method request parameter:
aws apigateway put-integration /
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 /
--resource-id aaa111 /
--http-method GET /
--type HTTP /
--integration-http-method GET /
--uri 'https://example.com' /
--cache-key-parameters "method.request.querystring.type"To specify API Gateway cache an integration request parameter, useintegration.request.location.name as the cache key parameter.
Flush the API stage cache in API Gateway
When API caching is enabled, you can flush your API stage's cache to ensure that your API's clients get the most recent responses from your integration endpoints.
AWS Management Console
To flush the API stage cache
- Sign in to the API Gateway console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway.
- Choose an API that has a stage with a cache.
- In the main navigation pane, choose Stages, and then choose your stage with a cache.
- Choose the Stage actions menu, and then selectFlush stage cache.
AWS CLI
The following flush-stage-cache command flushes the stage cache:
aws apigateway flush-stage-cache \
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 \
--stage-name prodNote
After the cache is flushed, responses are serviced from the integration endpoint until the cache is built up again. During this period, the number of requests sent to the integration endpoint may increase. This may temporarily increase the overall latency of your API.
Invalidate an API Gateway cache entry
A client of your API can invalidate an existing cache entry and reload it from the integration endpoint for individual requests. The client must send a request that contains the Cache-Control: max-age=0 header. The client receives the response directly from the integration endpoint instead of the cache, provided that the client is authorized to do so. This replaces the existing cache entry with the new response, which is fetched from the integration endpoint.
To grant permission for a client, attach a policy of the following format to an IAM execution role for the user.
Note
Cross-account cache invalidation is not supported.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"execute-api:InvalidateCache"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:execute-api:region:account-id:api-id/stage-name/GET/resource-path-specifier"
]
}
]
}
This policy allows the API Gateway execution service to invalidate the cache for requests on the specified resource (or resources). To specify a group of targeted resources, use a wildcard (*) character for account-id, api-id, and other entries in the ARN value of Resource. For more information on how to set permissions for the API Gateway execution service, see Control access to a REST API with IAM permissions.
If you don't impose an InvalidateCache policy (or choose theRequire authorization check box in the console), any client can invalidate the API cache. If most or all of the clients invalidate the API cache, this could significantly increase the latency of your API.
When the policy is in place, caching is enabled and authorization is required.
You can specify how API Gateway handles unauthorized requests by choosing from the following options:
Fail the request with 403 status code
API Gateway returns a 403 Unauthorized response.
To set this option using the API, use FAIL_WITH_403.
Ignore cache control header; Add a warning in response header
API Gateway processes the request and adds a warning header in the response.
To set this option using the API, useSUCCEED_WITH_RESPONSE_HEADER.
Ignore cache control header
API Gateway processes the request and doesn't add a warning header in the response.
To set this option using the API, useSUCCEED_WITHOUT_RESPONSE_HEADER.
You can set the unauthorized request handling behavior using the API Gateway console or AWS CLI.
AWS Management Console
To specify how unauthorized requests are handled
- Sign in to the API Gateway console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway.
- Choose an API that has a stage with a cache.
- In the main navigation pane, choose Stages, and then choose your stage with a cache.
- For Stage details, choose Edit.
- For Unauthorized request handling, select an option.
- Choose Continue.
- Review your changes and choose Save changes.
AWS CLI
The following update-stage command updates a stage to handle unauthorized requests by failing the request with 403 status code:
aws apigateway update-stage /
--rest-api-id a1b2c3 /
--stage-name 'prod' /
--patch-operations 'op=replace,path=/*/*/caching/unauthorizedCacheControlHeaderStrategy,value="FAIL_WITH_403"'AWS CloudFormation example of a stage with a cache
The following AWS CloudFormation template creates an example API, provisions a 0.5 GB cache for the Prod stage, and turns on method-level caching for all GET methods.
Important
Caching is charged by the hour based on the cache size that you select. Caching is not eligible for the AWS Free Tier. For more information, see API Gateway Pricing.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Resources:
Api:
Type: 'AWS::ApiGateway::RestApi'
Properties:
Name: cache-example
PetsResource:
Type: 'AWS::ApiGateway::Resource'
Properties:
RestApiId: !Ref Api
ParentId: !GetAtt Api.RootResourceId
PathPart: 'pets'
PetsMethodGet:
Type: 'AWS::ApiGateway::Method'
Properties:
RestApiId: !Ref Api
ResourceId: !Ref PetsResource
HttpMethod: GET
ApiKeyRequired: true
AuthorizationType: NONE
Integration:
Type: HTTP_PROXY
IntegrationHttpMethod: GET
Uri: http://petstore-demo-endpoint.execute-api.com/petstore/pets/
ApiDeployment:
Type: 'AWS::ApiGateway::Deployment'
DependsOn:
- PetsMethodGet
Properties:
RestApiId: !Ref Api
ApiStage:
Type: 'AWS::ApiGateway::Stage'
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Description: Prod Stage with a cache
RestApiId: !Ref Api
DeploymentId: !Ref ApiDeployment
CacheClusterEnabled: True
CacheClusterSize: 0.5
MethodSettings:
- ResourcePath: /*
HttpMethod: '*'
CachingEnabled: True