Deploy on Kubernetes (original) (raw)
Docker Desktop includes a standalone Kubernetes server and client, as well as Docker CLI integration, enabling local Kubernetes development and testing directly on your machine.
The Kubernetes server runs as a single or multi-node cluster, within Docker container(s). This lightweight setup helps you explore Kubernetes features, test workloads, and work with container orchestration in parallel with other Docker functionalities.
Kubernetes on Docker Desktop runs alongside other workloads, including Swarm services and standalone containers.

The following actions are triggered in the Docker Desktop backend and VM:
- Generation of certificates and cluster configuration
- Download and installation of Kubernetes internal components
- Cluster bootup
- Installation of additional controllers for networking and storage
Turning the Kubernetes server on or off in Docker Desktop does not affect your other workloads.
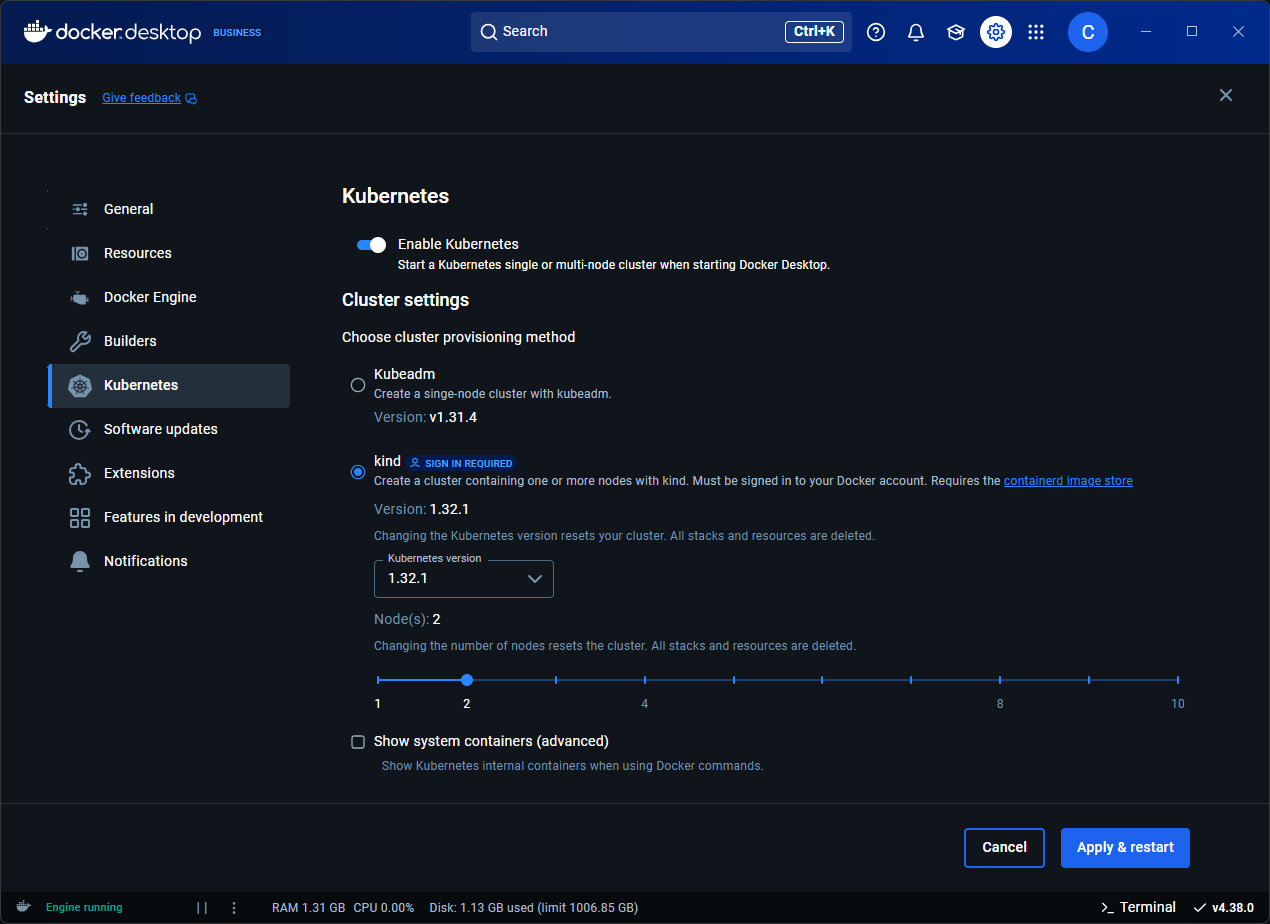
- Open the Docker Desktop Dashboard and navigate to Settings.
- Select the Kubernetes tab.
- Toggle on Enable Kubernetes.
- Choose yourcluster provisioning method.
- Select Apply & Restart to save the settings.
This sets up the images required to run the Kubernetes server as containers, and installs the kubectl command-line tool on your system at /usr/local/bin/kubectl (Mac) or C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin\kubectl.exe (Windows).
Note
Docker Desktop for Linux does not include
kubectlby default. You can install it separately by following theKubernetes installation guide. Ensure thekubectlbinary is installed at/usr/local/bin/kubectl.
When Kubernetes is enabled, its status is displayed in the Docker Desktop Dashboard footer and the Docker menu.
You can check which version of Kubernetes you're on with:
Cluster provisioning method
Docker Desktop Kubernetes can be provisioned with either the kubeadm or kindprovisioners.
kubeadm is the older provisioner. It supports a single-node cluster, you can't select the kubernetes version, it's slower to provision than kind, and it's not supported byEnhanced Container Isolation (ECI), meaning that if ECI is enabled the cluster works but it's not protected by ECI.
kind is the newer provisioner, and it's available if you are signed in and are using Docker Desktop version 4.38 or later. It supports multi-node clusters (for a more realistic Kubernetes setup), you can choose the Kubernetes version, it's faster to provision than kubeadm, and it's supported by ECI (i.e., when ECI is enabled, the Kubernetes cluster runs in unprivileged Docker containers, thus making it more secure). Note however that kind requires that Docker Desktop be configured to use thecontainerd image store (the default image store in Docker Desktop 4.34 and later).
The following table summarizes this comparison.
| Feature | kubeadm | kind |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Docker Desktop 4.0+ | Docker Desktop 4.38+ (requires sign in) |
| Multi-node cluster support | No | Yes |
| Kubernetes version selector | No | Yes |
| Speed to provision | ~1 min | ~30 seconds |
| Supported by ECI | No | Yes |
| Works with containerd image store | Yes | Yes |
| Works with Docker image store | Yes | No |
Additional settings
Viewing system containers
By default, Kubernetes system containers are hidden. To inspect these containers, enable Show system containers (advanced).
You can now view the running Kubernetes containers with docker ps or in the Docker Desktop Dashboard.
Kubernetes integration automatically installs the Kubernetes CLI command at /usr/local/bin/kubectl on Mac and at C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Resources\bin\kubectl.exe on Windows. This location may not be in your shell's PATHvariable, so you may need to type the full path of the command or add it to the PATH.
If you have already installed kubectl and it is pointing to some other environment, such as minikube or a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster, ensure you change the context so that kubectl is pointing to docker-desktop:
Tip
If the
kubectlconfig get-contexts command returns an empty result, try:
- Running the command in the Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Setting the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variable to point to your.kube/configfile.
Verify installation
To confirm that Kubernetes is running, list the available nodes:
If you installed kubectl using Homebrew, or by some other method, and experience conflicts, remove /usr/local/bin/kubectl.
For more information about kubectl, see thekubectl documentation.
Kubernetes clusters are not automatically upgraded with Docker Desktop updates. To upgrade the cluster, you must manually select Reset Kubernetes Cluster in settings.
- If Kubernetes fails to start, make sure Docker Desktop is running with enough allocated resources. Check Settings > Resources.
- If the
kubectlcommands return errors, confirm the context is set todocker-desktopYou can then try checking the logs of theKubernetes system containers if you have enabled that setting. - If you're experiencing cluster issues after updating, reset your Kubernetes cluster. Resetting a Kubernetes cluster can help resolve issues by essentially reverting the cluster to a clean state, and clearing out misconfigurations, corrupted data, or stuck resources that may be causing problems. If the issue still persists, you may need to clean and purge data, and then restart Docker Desktop.
To turn off Kubernetes in Docker Desktop:
- From the Docker Desktop Dashboard, select the Settings icon.
- Select the Kubernetes tab.
- Deselect the Enable Kubernetes checkbox.
- Select Apply & Restart to save the settings. This stops and removes Kubernetes containers, and also removes the
/usr/local/bin/kubectlcommand.