(Part 3) Serving on vLLM, SGLang, ExecuTorch (original) (raw)
Created On: Dec 17, 2025 | Last Updated On: Dec 17, 2025
TorchAO provides an end-to-end pre-training, fine-tuning, and serving model optimization flow by leveraging our quantization and sparsity techniques integrated into our partner frameworks. This is part 3 of 3 such tutorials showcasing this end-to-end flow, focusing on the serving step.
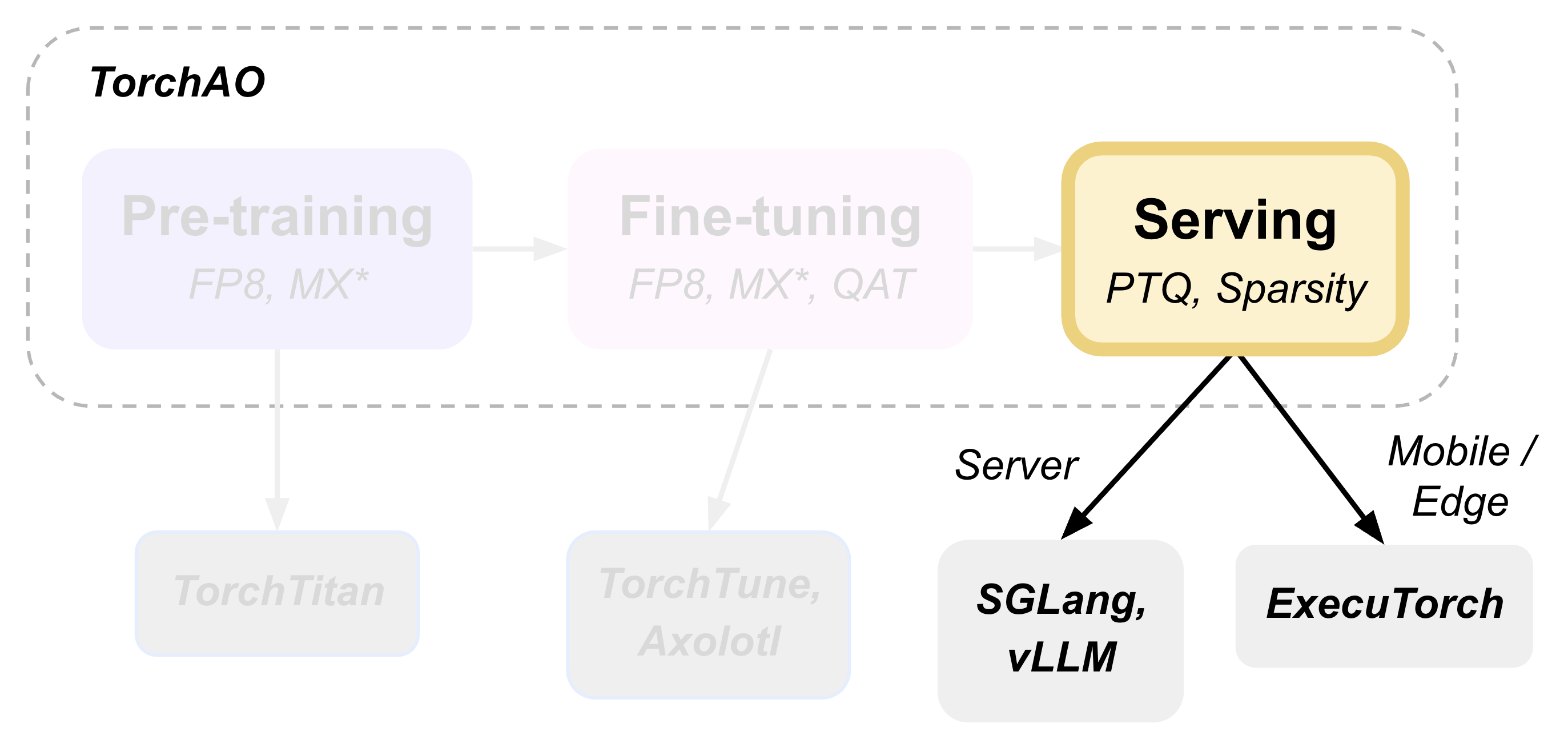
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform post-training quantization and deploy models for inference using torchao as the underlying optimization engine, seamlessly integrated through HuggingFace Transformers, vLLM, and ExecuTorch.
- Post-training Quantization with HuggingFace
- Serving and Inference
- Mobile Deployment with ExecuTorch
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
Post-training Quantization with HuggingFace#
HuggingFace Transformers provides seamless integration with torchao quantization. The TorchAoConfig automatically applies torchao’s optimized quantization algorithms during model loading. Please check out our HF Integration Docs for examples on how to use quantization and sparsity in Transformers and Diffusers and TorchAOConfig Reference for all available torchao configs to use.
Serving and Inference#
Serving and Inference with vLLM#
vLLM automatically leverages torchao’s optimized kernels when serving quantized models, providing significant throughput improvements.
First, install vLLM with torchao support:
pip install vllm --pre --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/vllm/ pip install --pre torchao --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu128
To serve in vLLM, we’re using the model we quantized and pushed to Hugging Face hub in the previous step Post-training Quantization with HuggingFace.
Server
vllm serve pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8 --tokenizer microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct -O3
Client
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{ "model": "pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8", "messages": [ {"role": "user", "content": "Give me a short introduction to large language models."} ], "temperature": 0.6, "top_p": 0.95, "top_k": 20, "max_tokens": 32768 }'
Serving a float8 dynamic quantized model with vLLM shows 36% VRAM reduction, 1.15x-1.2x inference speedup and little to no accuracy impact on H100. Memory Benchmarking and Performance Benchmarking for more details.
Serving and Inference with SGLang#
(Coming soon!)
Inference with Transformers#
Install the required packages:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers@main pip install torchao pip install torch pip install accelerate
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
model_path = "pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-float8dq"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained( model_path, device_map="auto", dtype="auto", trust_remote_code=True, ) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful AI assistant."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Can you provide ways to eat combinations of bananas and dragonfruits?"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "Sure! Here are some ways to eat bananas and dragonfruits together: 1. Banana and dragonfruit smoothie: Blend bananas and dragonfruits together with some milk and honey. 2. Banana and dragonfruit salad: Mix sliced bananas and dragonfruits together with some lemon juice and honey."}, {"role": "user", "content": "What about solving an 2x + 3 = 7 equation?"}, ]
pipe = pipeline( "text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, )
generation_args = { "max_new_tokens": 500, "return_full_text": False, "temperature": 0.0, "do_sample": False, }
output = pipe(messages, **generation_args) print(output[0]['generated_text'])
Mobile Deployment with ExecuTorch#
ExecuTorch enables on-device inference using torchao’s mobile-optimized quantization schemes. The 8da4w (8-bit dynamic activation, 4-bit weight) configuration is specifically designed for mobile deployment. Optionally, before lowering to ExecuTorch, we can finetune a model using QAT (Part 2) Fine-tuning with QAT, QLoRA, and float8, which has demonstrated some improvements in the quality of quantized models.
[Optional] Untie Embedding Weights#
Optionally, we can quantize the embedding and lm_head differently, since those layers are tied, we first need to untie the model:
from transformers import ( AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoProcessor, AutoTokenizer, ) import torch from transformers.modeling_utils import find_tied_parameters
model_id = "microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct" untied_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, dtype="auto", device_map="auto") tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
print(untied_model) print("tied weights:", find_tied_parameters(untied_model)) if getattr(untied_model.config.get_text_config(decoder=True), "tie_word_embeddings"): setattr(untied_model.config.get_text_config(decoder=True), "tie_word_embeddings", False)
untied_model._tied_weights_keys = [] untied_model.lm_head.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(untied_model.lm_head.weight.clone())
print("tied weights:", find_tied_parameters(untied_model))
USER_ID = "YOUR_USER_ID" MODEL_NAME = model_id.split("/")[-1] save_to = f"{USER_ID}/{MODEL_NAME}-untied-weights"
untied_model.push_to_hub(save_to) tokenizer.push_to_hub(save_to)
or save locally
save_to_local_path = f"{MODEL_NAME}-untied-weights" untied_model.save_pretrained(save_to_local_path) tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_to)
Step 1: Create Mobile-Optimized Quantization#
Quantizing the model for mobile deployment using TorchAO’s Int8DynamicActivationIntxWeightConfig configuration. If we’ve untied the embedding and lm_head following the previous step, we can quantize embedding using IntxWeightOnlyConfig configuration, and lm_head using Int8DynamicActivationIntxWeightConfig configuration.
from transformers import ( AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoProcessor, AutoTokenizer, TorchAoConfig, ) from torchao.quantization.quant_api import ( IntxWeightOnlyConfig, Int8DynamicActivationIntxWeightConfig, FqnToConfig, quantize_, ) from torchao.quantization.granularity import PerGroup, PerAxis import torch
we start from the model with untied weights
model_id = "microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct" USER_ID = "YOUR_USER_ID" MODEL_NAME = model_id.split("/")[-1] untied_model_id = f"{USER_ID}/{MODEL_NAME}-untied-weights" untied_model_local_path = f"{MODEL_NAME}-untied-weights"
embedding_config is required only if we untied the embedding and lm_head in the previous step, else we can use only linear config for quantization
embedding_config = IntxWeightOnlyConfig( weight_dtype=torch.int8, granularity=PerAxis(0), ) linear_config = Int8DynamicActivationIntxWeightConfig( weight_dtype=torch.int4, weight_granularity=PerGroup(32), weight_scale_dtype=torch.bfloat16, ) quant_config = FqnToConfig({"_default": linear_config, "model.embed_tokens": embedding_config}) quantization_config = TorchAoConfig(quant_type=quant_config, include_embedding=True, untie_embedding_weights=True, modules_to_not_convert=[])
either use untied_model_id or untied_model_local_path
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(untied_model_id, dtype=torch.float32, device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
Push to hub
MODEL_NAME = model_id.split("/")[-1] save_to = f"{USER_ID}/{MODEL_NAME}-8da4w" quantized_model.push_to_hub(save_to, safe_serialization=False) tokenizer.push_to_hub(save_to)
Step 2: Export to ExecuTorch#
Convert the quantized model to .pte file, which can be run on mobile device.
Install ExecuTorch
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/executorch.git cd executorch ./install_requirements.sh
Convert checkpoint format for ExecuTorch
python -m executorch.examples.models.phi_4_mini.convert_weights pytorch_model.bin pytorch_model_converted.bin
Export to PTE format with torchao optimizations preserved
PARAMS="executorch/examples/models/phi_4_mini/config.json"
python -m executorch.examples.models.llama.export_llama
--model "phi_4_mini"
--checkpoint "pytorch_model_converted.bin"
--params "$PARAMS"
-kv
--use_sdpa_with_kv_cache
-X
--metadata '{"get_bos_id":199999, "get_eos_ids":[200020,199999]}'
--max_seq_length 128
--max_context_length 128
--output_name="phi4-mini-8da4w.pte"
The .pte file can be run with ExecuTorch on a mobile phone. Follow the instructions for doing this on an iOS device.
Mobile Performance Characteristics#
The torchao-optimized 8da4w model provides:
- Memory: ~3.2GB on iPhone 15 Pro
- Speed: ~17 tokens/sec on iPhone 15 Pro
- Accuracy: Maintained within 5-10% of original model on most benchmarks
Evaluation#
Model Quality Assessment#
Evaluate quantized models using lm-evaluation-harness:
Install evaluation framework
Need to install lm-eval from source: https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness#install
Evaluate baseline model
lm_eval --model hf --model_args pretrained=microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --tasks hellaswag --device cuda:0 --batch_size 8
Evaluate torchao-quantized model (FP8)
lm_eval --model hf --model_args pretrained=pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8 --tasks hellaswag --device cuda:0 --batch_size 8
Memory Benchmarking#
For Phi-4-mini-instruct, when quantized with float8 dynamic quant, we can reduce the peak memory usage by 36% compared to the baseline model.
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
use "microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct" or "pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8"
model_id = "pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8" quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="auto", dtype=torch.bfloat16) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
prompt = "Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me?" messages = [ { "role": "system", "content": "", }, {"role": "user", "content": prompt}, ] templated_prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True, ) print("Prompt:", prompt) print("Templated prompt:", templated_prompt) inputs = tokenizer( templated_prompt, return_tensors="pt", ).to("cuda") generated_ids = quantized_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128) output_text = tokenizer.batch_decode( generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False ) print("Response:", output_text[0][len(prompt):])
mem = torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved() / 1e9 print(f"Peak Memory Usage: {mem:.02f} GB")
Output:
Prompt: Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me? Templated prompt: <|system|><|end|><|user|>Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me?<|end|><|assistant|> Response: Hello! Yes, I am a digital assistant, and I am fully operational and ready to assist you. How can I help you today? Peak Memory Usage: 5.70 GB
Performance Benchmarking#
Latency Benchmarking#
baseline
vllm bench latency --input-len 256 --output-len 256 --model microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --batch-size 1
FP8
VLLM_DISABLE_COMPILE_CACHE=1 vllm bench latency --input-len 256 --output-len 256 --model pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8 --batch-size 1
Serving Benchmarking#
We benchmarked the throughput in a serving environment.
Setup: Get vllm source code
git clone git@github.com:vllm-project/vllm.git
Install vllm
VLLM_USE_PRECOMPILED=1 pip install --editable .
Run the benchmarks under vllm root folder:
Download sharegpt dataset:
Other datasets can be found in: https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/tree/main/benchmarks
Note: you can change the number of prompts to be benchmarked with --num-prompts argument for benchmark_serving script.
For baseline
Server:
vllm serve microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --tokenizer microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct -O3
Client:
vllm bench serve --backend vllm --dataset-name sharegpt --tokenizer microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --dataset-path ./ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json --model microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --num-prompts 1
For FP8
Server:
VLLM_DISABLE_COMPILE_CACHE=1 vllm serve pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8 --tokenizer microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct -O3
Client:
vllm bench serve --backend vllm --dataset-name sharegpt --tokenizer microsoft/Phi-4-mini-instruct --dataset-path ./ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json --model pytorch/Phi-4-mini-instruct-FP8 --num-prompts 1
Results (H100 machine)#
Conclusion#
This tutorial demonstrated how torchao’s quantization and sparsity techniques integrate seamlessly across the entire ML deployment stack:
- HuggingFace Transformers provides easy model loading with torchao quantization
- vLLM leverages torchao’s optimized kernels for high-throughput serving
- ExecuTorch enables mobile deployment with torchao’s mobile-optimized schemes
- lm-evaluation-harness provides model quality assessment
All these frameworks use torchao as the underlying optimization engine, ensuring consistent performance gains and ease of integration. The quantization techniques shown provide significant memory reduction (3-4x) and performance improvements (1.5-2x) while maintaining model quality within acceptable bounds for most applications.
For production deployments, always benchmark on your specific use case and hardware to validate the performance and accuracy trade-offs.