A simple, sensitive and selective quantum-dot-based western blot method for the simultaneous detection of multiple targets from cell lysates (original) (raw)
Abstract
Quantum dots (Qdots) are fluorescent nanoparticles that have great potential as detection agents in biological applications. Their optical properties, including photostability and narrow, symmetrical emission bands with large Stokes shifts, and the potential for multiplexing of many different colours, give them significant advantages over traditionally used fluorescent dyes. Here, we report the straightforward generation of stable, covalent quantum dot–protein A/G bioconjugates that will be able to bind to almost any IgG antibody, and therefore can be used in many applications. An additional advantage is that the requirement for a secondary antibody is removed, simplifying experimental design. To demonstrate their use, we show their application in multiplexed western blotting. The sensitivity of Qdot conjugates is found to be superior to fluorescent dyes, and comparable to, or potentially better than, enhanced chemiluminescence. We show a true biological validation using a four-colour multiplexed western blot against a complex cell lysate background, and have significantly improved previously reported non-specific binding of the Qdots to cellular proteins.
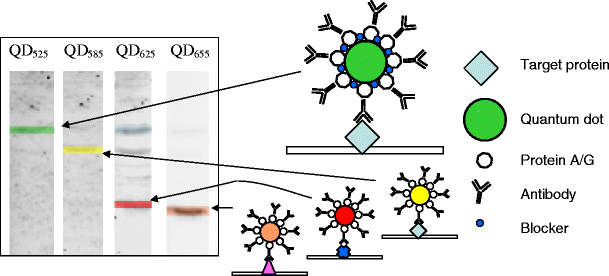
Stable covalent conjugates of Qdots with a range of emission frequencies and protein A/G have been generated. These can be bound to appropriate primary antibodies from many species and used for the selective detection of target proteins within a sample. We have demonstrated this using four-colour detection in a western blot format from a cell lysate.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Starting from 10 chapters or articles per month
- Access and download chapters and articles from more than 300k books and 2,500 journals
- Cancel anytime View plans
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
HRP:
Horse radish peroxidase
ECL:
Enhanced chemiluminescence
QDot:
Quantum dot
QD x :
Quantum dot emitting at wavelength x
MEK:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
RKIP:
Raf kinase inhibitor protein
GST:
Glutathione-_S_-transferase
V5:
Simian virus 5 epitope tag—GKPIPNPLLGLDST
EDC:
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
NHS:
_N_-hydroxysuccinamide
PMT:
Photomultiplier tube
HA:
Hemagglutinin epitope tag—YPYDVPDYA
FRAP:
FKBP–rapamycin-associated protein
FKBP:
FK506 binding protein
FRB:
FKBP12–rapamycin-binding domain of FRAP
References
- Mazumder S, Dey R, Mitra MK, Mukherjee S, Das GC (2009) Review: biofunctionalized quantum dots in biology and medicine. J Nanomater 2009:1–17
Article Google Scholar - Biju V, Itoh T, Anas A, Sujith A, Ishikawa M (2008) Semiconductor quantum dots and metal nanoparticles: syntheses, optical properties, and biological applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2469–2495
Article CAS Google Scholar - Monton H, Nogues C, Rossinyol E, Castell O, Roldan M (2009) QDs versus Alexa: reality of promising tools for immunocytochemistry. J Nanobiotechnol 7:4
Article Google Scholar - Gill R, Zayats M, Willner I (2008) Semiconductor quantum dots for bioanalysis. Angew Chem Int Edit 47:7602–7625
Article CAS Google Scholar - Chan WCW, Nie SM (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Article CAS Google Scholar - Waggoner A (2006) Fluorescent labels for proteomics and genomics. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:62–66
Article CAS Google Scholar - Medintz IL, Mattoussi H, Clapp AR (2008) Potential clinical applications of quantum dots. Int J Nanomed 3:151–167
CAS Google Scholar - Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Article CAS Google Scholar - Goldman ER, Balighian ED, Mattoussi H, Kuno MK, Mauro JM, Tran PT, Anderson GP (2002) Avidin: a natural bridge for quantum dot-antibody conjugates. J Am Chem Soc 124:6378–6382
Article CAS Google Scholar - Goldman ER, Clapp AR, Anderson GP, Uyeda HT, Mauro JM, Medintz IL, Mattoussi H (2004) Multiplexed toxin analysis using four colours of quantum dot fluororeagents. Anal Chem 76:684–688
Article CAS Google Scholar - Peng C, Li Z, Zhu Y, Chen W, Yuan Y, Liu L, Li Q, Xu D, Qiao R, Wang L, Zhu S, Jin S, Xu C (2009) Simultaneous and sensitive determination of multiplex chemical residues based on multicolour quantum dot probes. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3657–3662
Article CAS Google Scholar - Pathak S, Davidson MC, Silva GA (2007) Characterization of the functional binding properties of antibody conjugated quantum dots. Nano Lett 7:1839–1845
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kim MJ, Park HY, Kim J, Ryu J, Hong S, Han SJ, Song R (2008) Western blot analysis using metal-nitrilotriacetate conjugated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Anal Biochem 379:124–126
Article CAS Google Scholar - Scholl B, Liu HY, Long BR, McCarty OJT, O'Hare T, Druker BJ, Vu TQ (2009) Single particle quantum dot imaging achieves ultrasensitive detection capabilities for western immunoblot analysis. ACS Nano 3:1318–1328
Article CAS Google Scholar - Makrides SC, Gasbarro C, Bello JM (2005) Bioconjugation of quantum dot luminescent probes for Western blot analysis. Biotechniques 39:501–506
Article CAS Google Scholar - Goldman ER, Anderson GP, Tran PT, Mattoussi H, Charles PT, Mauro JM (2002) Conjugation of luminescent quantum dots with antibodies using an engineered adaptor protein to provide new reagents for fluoroimmunoassays. Anal Chem 74:841–847
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lim YT, Cho MY, Lee JM, Chung SJ, Chung BH (2009) Simultaneous intracellular delivery of targeting antibodies and functional nanoparticles with engineered protein G system. Biomaterials 30:1197–1204
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kerman K, Endo T, Tsukamoto M, Chikae M, Takamura Y, Tamiya E (2007) Quantum dot-based immunosensor for the detection of prostate-specific antigen using fluorescence microscopy. Talanta 71:1494–1499
Article CAS Google Scholar - Zeng Q, Zhang Y, Song K, Kong X, Aalders MCG, Zhang H (2009) Enhancement of sensitivity and specificity of the fluoroimmunoassay of Hepatitis B virus surface antigen through “flexible” coupling between quantum dots and antibody. Talanta 80:307–312
Article CAS Google Scholar - Eliasson M, Olsson A, Palmcrantz E, Wiberg K, Inganas M, Guss B, Lindberg M, Uhlen M (1988) Chimeric IgG-binding receptors engineered from staphylococcal protein-A and staphylococcal protein-G. J Biol Chem 263:4323–4327
CAS Google Scholar - Gokarna A, Jin LH, Hwang JS, Cho YH, Lim YT, Chung BH, Youn SH, Choi DS, Lim JH (2008) Quantum dot-based protein micro- and nanoarrays for detection of prostate cancer biomarkers. Proteomics 8:1809–1818
Article CAS Google Scholar - Geho D, Lahar N, Gurnani P, Huebschman M, Herrmann P, Espina V, Shi A, Wulfkuhle J, Garner H, Petricoin E, Liotta LA, Rosenblatt KP (2005) Pegylated, streptavidin-conjugated quantum dots are effective detection elements for reverse-phase protein microarrays. Bioconjug Chem 16:559–566
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Susan Gannon for help in the preparation of protein samples used in these experiments and Professor Walter Kolch for gifts of plasmids. This work was supported by the RASOR Interdisciplinary Research Collaboration, funded by BBSRC and EPSRC (BBC5115721), and the Scottish Funding Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Integrative and Systems Biology, Faculty of Biomedical and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, University Avenue, Glasgow, G12 8QQ, UK
Kathryn L. Gilroy, Sarah A. Cumming & Andrew R. Pitt
Authors
- Kathryn L. Gilroy
- Sarah A. Cumming
- Andrew R. Pitt
Corresponding author
Correspondence toAndrew R. Pitt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilroy, K.L., Cumming, S.A. & Pitt, A.R. A simple, sensitive and selective quantum-dot-based western blot method for the simultaneous detection of multiple targets from cell lysates.Anal Bioanal Chem 398, 547–554 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3908-0
- Received: 24 April 2010
- Revised: 04 June 2010
- Accepted: 07 June 2010
- Published: 27 June 2010
- Issue date: September 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3908-0