Sugar alcohols—their role in the modern world of sweeteners: a review (original) (raw)
Introduction
People always tried to use benefits of the nature; however, just recently in the final years of the twentieth century, a gigantic progress in the food technology could have been observed. It was mainly due to the developments in biological studies, the change of a population lifestyle and the increase in the consumer awareness concerning food products. The health quality of food depends mainly on nutrients, but also on foreign substances such as food additives. The presence of foreign substances in the food can be justified, allowed or tolerated only when they are harmless to our health. Epidemic obesity and diabetes encouraged the growth of the artificial sweetener industry. There are more and more people who are trying to lose weight or keeping the weight off; therefore, sweeteners can be now found in almost all food products. There are two main types of sweeteners, i.e., nutritive and artificial ones. The latter does not provide calories and will not influence blood glucose; however, some of nutritive sweeteners such as sugar alcohols also characterize with lower blood glucose response and can be metabolized without insulin, being at the same time natural compounds.
Sugar alcohols (polyols or polyhydric alcohols) are low digestible carbohydrates, which are obtained by substituting and aldehyde group with a hydroxyl one [1, 2]. As most of sugar alcohols are produced from their corresponding aldose sugars, they are also called alditols [3]. Among sugar alcohols can be listed hydrogenated monosaccharides (sorbitol, mannitol), hydrogenated disaccharides (isomalt, maltitol, lactitol) and mixtures of hydrogenated mono-di- and/or oligosaccharides (hydrogenated starch hydrolysates) [1, 2, 4].
Polyols are naturally present in smaller quantities in fruits as well as in certain kinds of vegetables or mushrooms, and they are also regulated as either generally recognized as safe or food additives [5–7]. Food additives are substances that are added intentionally to foodstuffs in order to perform certain technological functions such as to give color, to sweeten or to help in food preservation. According to the European Union legislation, all food additives are identified by an E number and must be always stated on the packaging in the ingredient lists. All food additives prior their usage must be authorized by particular legislations such as EU and FDA. There are seven sugar alcohols which are defined as nutritive sweeteners according to EU legislation, i.e., sorbitol (E420), mannitol (E421), isomalt (E953), maltitol (E965), lactitol (E966), xylitol (E967) and erythritol (E968) [[8](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR8 "Regulation (EC) no 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:354:0016:0033:en:PDF
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\]. They need to be declared on the products label, and when there is only one sugar alcohol present, the specific name may be substituted for “sugar alcohol,” e.g., xylitol \[[5](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR5 "Reports ADA (2004) Position of the American Dietetic Association: use of nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners. J Am Diet Assoc 104:255–275"), [7](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR7 "Fitch C, Keim KS (2012) Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: use of nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners. J Acad Nutr Diet 112:739–758")\]. Although acceptable daily intake (ADI) dose has not been specified for them, they are known for their potent laxative effect and other gastrointestinal symptoms such as flatulence, bloating, and abdominal discomfort when eaten in excess \[[1](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR1 "Livesey G (2003) Health potential of polyols as sugar replacers, with emphasis on low-glycaemic properties. Nutr Res Rev 16:163–191"), [9](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR9 "Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681"), [10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\]. Therefore, in order to ensure consumers with adequate information, products containing more than 10 % added polyols must include the advisory statement “excessive consumption may produce laxative effects” \[[10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014"), [11](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR11 "European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC of 30 June 1994.
https://www.fsai.ie/uploadedFiles/Dir94.35.pdf
. Accessed 14 June 2014")\].Sugar alcohols’ sweetness is usually lower than the one of monosaccharide, and therefore, they are used volume-for-volume like sugar and are called bulk sweeteners. They are often used in combination with other sweeteners to achieve the desired level of sweetness and flavor. Similarly to carbohydrates, they are not only responsible for sweet taste, but they are also responsible for product texture, its preservation, filling, holding moisture and cooling sensation in the mouth [[12](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR12 "Health Canada (2005) http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/securit/addit/sweeten-edulcor/polyols_polydextose_factsheet-polyols_polydextose_fiche-eng.php
. Accessed 10 May 2014")\] (Table [1](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab1)).Table 1 Characteristics of sugar alcohols
These compounds have a lower nutritional value than sugars (Table 2) [[12](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR12 "Health Canada (2005) http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/securit/addit/sweeten-edulcor/polyols_polydextose_factsheet-polyols_polydextose_fiche-eng.php
. Accessed 10 May 2014")\], due to slower and incomplete absorption from the intestine, which results in indirect metabolism via fermentative degradation by the intestinal flora (Table [3](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab3)). Products of fermentation include short-chain fatty acids and gases \[[9](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR9 "Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681")\]. Sugar alcohols due to lower caloric value might help consumers to reduce their energy intake and lose weight \[[1](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR1 "Livesey G (2003) Health potential of polyols as sugar replacers, with emphasis on low-glycaemic properties. Nutr Res Rev 16:163–191"), [9](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR9 "Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681")\]. What is more, consumption of products containing polyols do not induce (or to very small extent) an increase in blood glucose or insulin secretion, and thus, such products are recommended for people with diabetes \[[6](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR6 "Wheeler ML, Pi-Sunyer X (2008) Carbohydrate issues. Type and amount. J Am Diet Assoc 108:S34–S39"), [9](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR9 "Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681"), [10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014"), [13](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR13 "Nakamura S (2005) Bioavailability of cellobiose and other non-digestible and/or nonabsorbable sugar substitutes and related topics. Nutrition 21:1158–1159"); Table [2](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab2)\]. Polyols also act as prebiotics, anti-cariogenic agents and similar to fiber can help normalize intestine function \[[1](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR1 "Livesey G (2003) Health potential of polyols as sugar replacers, with emphasis on low-glycaemic properties. Nutr Res Rev 16:163–191"), [9](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR9 "Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681"), [10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\]. Sugar alcohols such as maltitol and lactitol were found to increase mineral bioavailability in human and rats \[[13](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR13 "Nakamura S (2005) Bioavailability of cellobiose and other non-digestible and/or nonabsorbable sugar substitutes and related topics. Nutrition 21:1158–1159"), [14](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR14 "Xiao J, Li X, Min X, Sakaguchi E (2013) Mannitol improves absorption and retention of calcium and magnesium in growing rats. Nutrition 29:325–331")\].Table 2 Caloric value, sweetness and glycemic index of sugar alcohols
Table 3 Metabolism of sugar alcohols
Nutritive sweeteners are generally recognized as safe, yet concern exists about increasing sweetener intakes relative to optimal nutrition and health. The present review focuses on the role, metabolism and dietary characteristic of the chosen sugar alcohols such as erythritol, isomalt, lactitol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol and xylitol.
Sugar alcohols characteristics
Erythritol
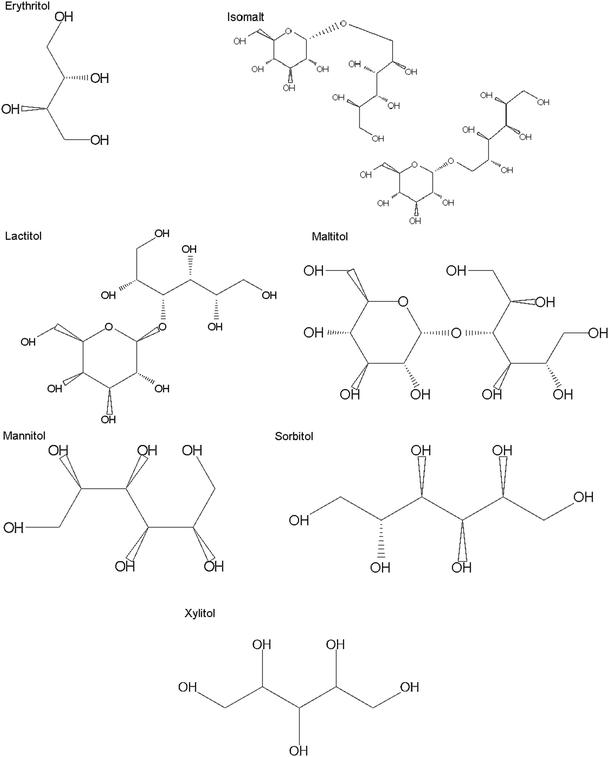
1,2,3,4-Butanetetrol, which is a chemical name of erythritol (Fig. 1), can be naturally found in small quantities in vegetables, fruits (melons, peaches), mushrooms and fermented foods such as wine, beer, sake and soy sauce [15–22]. It can be also found in several human tissues such as semen, lens, cerebrospinal fluid and serum [18, 20, 23]. Erythritol consumption from natural sources is estimated to amount from 25 mg/person/day in the USA to 106 mg/person/day in Japan [23].
Fig. 1
Chemical structures of sugar alcohols
Properties and applications
This sugar alcohol characterizes with a high stability in temperature and acid or alkaline environments as well as does not take part in Maillard-type browning reactions [23]. It is also a non-hygroscopic substance. Erythritol is currently used as a low-calorie, tooth-friendly, bulk sweetener, which provides volume, texture as well as microbiological stability in such products as tooth-friendly chewing gums, candy products, ice creams and also ipocaloric beverages [22, 23].
Besides heaving a high digestive tolerance, it is non-glycemic and does not promote tooth decay [3, 21, 24] (Table 4). Erythritol inhibits the growth of mutans streptococci and combined with xylitol may potentially act caries limiting [3, 25]. Moreover, Runnel et al. [25] in a three-year study found that consumption of erythritol-containing candies by initially 7- to 8-year-old children resulted in reduced plaque growth, lower levels of plaque acetic acid and propionic acid.
Table 4 Biological activities of sugar alcohols
Erythritol, characterizes with a clean sweet taste, is approximately 70 % as sweet as sucrose, with no aftertaste and a mild cooling effect in the mouth [18, 20, 22, 26]. It can be easily blended with artificial sweeteners such as acesulfame potassium and aspartame or other polyols, i.e., sorbitol and xylitol or other sweeteners such as stevia to give a similar flavor to the one of table sugar [22, 27]. Even slight amounts of aspartame or acesulfame K increase erythritol sweetness by about 30 %. It can also improve mouthfeel and mask certain unwanted aftertastes of intense sweeteners [23]. Erythritol was also reported to protect endothelial cells under hyperglycemic conditions (Table 4) [28]. In vitro studies have also shown that erythritol is an excellent radical scavenger with membrane-protecting properties [19, 23]. Moreover, it was also found that simultaneous intake of equimolar amounts of erythritol and fructose results in the impaired absorption of the latter [29].
Metabolism
Based on clinical studies, it was stated that erythritol is well (60–90 %) and rapidly absorbed in the small intestine and then excreted intact in urine within 24 h (Table 3). Only small amounts are subjected to intestinal fermentation, and thus laxative side effects associated with excessive polyol consumption are unlikely to observe [1, 15, 19, 20, 23]. Gastrointestinal effects were recorded when high doses were consumed, up to 1000 mg/kg body [15]. Oku and Okazaki [18] also stated that women are more resistant to diarrhea resulting from a high ingestion of erythritol than men. What is more, the diarrheal effect of sorbitol is greater than that of erythritol [18]. According to American and Japanese legislation, it provides 0.2 kcal/g, whereas EU directives set this value at 2.4 kcal/g [Table 2; 21]. It has been intensively tested for safe use in both animals and humans, and thus no ADI have been specified for this polyol [30].
Production
Contrary to other polyols, it is not produced by direct catalytic hydrogenation due to the high cost of substrate erythrose [31; Table 5]. Its industrial manufacturing is based on fermentation processes led by osmophilic yeasts such as Moniliella pollinis or Trichosporonoides megachiliensis [16, 21, 22, 26, 32] as well as some species of lactic acid bacteria, i.e., Oenococcus oeni, Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Lactobacillus sanfranciscencis [33–35]. Eythritol can also be produced from glycerol by _Yarrowia lipolyt_ica MK1 [[36](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR36 "Mirończuk AM, Dobrowolski A, Rakicka M, Rywińska A, Rymowicz W (2014) Newly isolated mutant of Yarrowia lipolytica MK1 as a proper host for efficient erythritol biosynthesis from glycerol. Process Biochem. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.10.020
")–[38](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR38 "Yang L-B, Zhan X-B, Zheng Z-Y, Wu J-R, Gao M-J, Lin C-C (2014) A novel osmotic pressure control fed-batch fermentation strategy for improvement of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol. Bioresour Technol 151:120–127")\].Table 5 Industrial manufacturing of sugar alcohols
Isomalt
Isomalt, which is a mixture of two isomeric disaccharide alcohols: gluco-mannitol (α-D-gluco-pyranosyl-1-6-mannitol) and gluco-sorbitol (α-d-gluco-pyranosyl-1-6-Sorbitol), was discovered in the 1960s (Fig. 1).
Production
It is produced from sucrose in a two-step process, which makes isomalt chemically and enzymatically more stable than the sucrose. It starts by sugar enzymatic transglucosidation into maltulose that is subsequently hydrogenated into isomalt, which is a combination of two disaccharide alcohols, 6-_O_-α-d-glucopyranosyl-d-sorbitol (1,6-GPS) and 1-_O_-α-d-glucopyranosyl-d-mannitol dihydrate (1,1-GPM) [39, 40].
Properties and applications
Isomalt is resistant to the loss of sweetness during heating; thus, it can be used in products, which are subjected to high temperatures [41]. Its sweetness depends on concentration, temperature as well the form of product in which it is used; on average it has 45–65 % of the sweetness of sucrose [40, 41]. Besides resembling table sugar physically (white, crystalline and odorless), it is also slightly hygroscopic substance and enhances flavor transfer in foods [40, 41]. Moreover, it does not crystallize as quickly as sucrose, so it can be used for sugar sculptures and other decorative edible products [22]. Contrary to other polyols, it does not give cooling effect in the mouth. It is often combined with non-nutritive sweeteners, because it helps masking the bitter aftertaste of some sweet food additives and bulking agents [40]. Aside from being sweetener, it also acts as a bulking agent, anti-caking agent and glazing agent [[42](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR42 "FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Isomalt. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=180
. Accessed 7 May 2014"); Table [1](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab1)\]. It is synergistic with other sweeteners, especially those intense ones, is anti-cariogenic and does not increase blood glucose or insulin levels (Table [4](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab4)). Similarly to other polyols, products sweetened with isomalt may be labeled safe for teeth \[[10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014"), [43](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR43 "Takatsuka T, Exterkate RAM, ten Cate JM (2008) Effects of isomalt on enamel de-and remineralization, a combined in vitro pH-cycling model and in situ study. Clin Oral Invest 12:173–177")\]. What is more, isomalt-containing toothpastes were found to enhance teeth remineralization \[[43](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR43 "Takatsuka T, Exterkate RAM, ten Cate JM (2008) Effects of isomalt on enamel de-and remineralization, a combined in vitro pH-cycling model and in situ study. Clin Oral Invest 12:173–177")\].It has been available in Europe since the early 1980s and is currently used in a wide variety of products such as hard candies, toffees, chewing gum, chocolates, baked goods, nutritional supplements, cough drops and throat lozenges [[42](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR42 "FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Isomalt. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=180
. Accessed 7 May 2014")\].Metabolism
Isomalt absorption is very low amounting to 10 % and 90 % of the absorbed part is being fermented [1, 40]. The bacterial fermentation products are short-chain fatty acids, CO2, CH4 and H2 [40]. Due to its partial digestion in the intestines, it supplies only half of the caloric value of sucrose (Table 2). However, it cannot be fermented by a large number of yeasts and other microorganisms found in nature [39]. In vitro studies have demonstrated that this polyol is a good source of butyrate and increases growth of bifidobacteria, which results in prebiotic effect [39, 44].
ADI for isomalt has been established by the Joint Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) as “not specified.” When consumed in high amounts may result in laxative effect, which is greater when isomalt is consumed in liquid food. However, its intolerance depends on many factors such as individual sensitivity, the moment and frequency of consumption [Table 6; 39].
Table 6 Reported side effects of sugar alcohols
Lactitol
It was discovered in 1920 by a French food chemist but not commercially used until 1980’s. Lactitol is a disaccharide polyol, which is composed of sorbitol and galactose (Fig. 1). It is produced from lactose by a catalytic hydrogenation using Raney nickel as the catalyst [45–47].
Metabolism
Although it is produced from lactose, it is not hydrolyzed by lactase, but is broken down by gut microflora (Table 3). Lactitol is metabolized by bacteria in the large intestine, where it is converted into biomass, carbon dioxide, a small amount of hydrogen and organic acids [45, 47], which are further metabolized to give energy in the amount of 2–2.4 calories per gram (Table 2). It was also found that lactitol is used as an energy source by special intestinal microflora in the colon, i.e., Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus spp [47, 48]. Overconsumption might result in laxative effect, which varies depending on the mode and frequency of ingestion, diet, age and general gut health [46].
Properties and applications
Lactitol characterizes with a clean sweet taste and a sweetening power of 40 % of that of sucrose [47]. However, it is used as a sucrose 1:1 substitute in calorie-controlled foods, mainly due to its good solubility. It can be dissolved at lower temperatures than sucrose, which results in saving of energy and processing costs [45, 46]. It does not take part in non-enzymatic browning (Maillard) reactions and can be stored for long periods [46].
Its characteristic mild sweetness helps in better perception of product flavor, and thus, it is usually combined with low-calorie sweeteners such as acesulfame K, aspartame, cyclamate, neotame, saccharin, stevia sweeteners and sucralose. Lactitol sweetness increases with the concentration level, but it has a very small cooling effect. This sugar alcohol is non-hygroscopic, stable in high temperatures as well as acidic and alkaline conditions. Besides sweetening, it can be used as a thickener and emulsifier [[49](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR49 "FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Lactitol, http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=156
. Accessed 7 May 2014")\]. Lactitol has a negligible effect on blood glucose levels and can be metabolized without insulin \[[45](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR45 "Koivistoinen M (2007) Lactitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 187–198")\]. Similarly to other sugar alcohols, it also does not contribute to dental caries \[[10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076.
http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014"), [45](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR45 "Koivistoinen M (2007) Lactitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 187–198")\]. Lactitol also acts as a prebiotic that is capable of promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon such as _Bifidobacteria_ and _Lactobacilli_, but also reduces the population of putrefactive bacteria selectively and lowers the intestinal pH as well as the production and absorption of ammonia \[[45](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR45 "Koivistoinen M (2007) Lactitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 187–198"), [46](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR46 "Zacharis C (2012) Lactitol. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex"), [48](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR48 "Ballongue J, Schumann C, Quignon P (1997) Effects of lactulose and lactitol on colonic microflora and enzymatic activity. Scand J Gastroenterol 222:41–44"), [50](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR50 "Finney M, Smullen J, Foster HA, Brokx S, Storey DM (2007) Effects of low doses of lactitol on faecal microflora, pH, short chain fatty acids and gastrointestinal symptomology. Eur J Nutr 46:307–314"), [51](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR51 "Ouwenhand AC, Tiihonen K, Saarinen M, Putaala H, Rautonen N (2009) Influence of a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol on healthy elderly: intestinal and immune parameters. Br J Nutr 101:367–375")\]. Lactitol was also applied in treating encephalopathy and constipation \[[52](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR52 "Chen C, Li L, Wu Z, Chen H, Fu S (2007) Effects of lactitol on intestinal microflora and plasma endotoxin in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. J Infect 54:98–102")–[56](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR56 "Morillas RM, Sala M, Planas R (2014) Prevention of hepatic encephalopathy. Med Clin 142:512–514")\].Due to its properties, lactitol is used in certain pharmaceutical applications, in food for diabetics, low-calorie, low-fat and/or sugar-free foods such as ice cream, chocolate, hard and soft candies, baked goods, sugar-reduced preserves, chewing gums and sugar substitutes [[49](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR49 "FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Lactitol, http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=156
. Accessed 7 May 2014"), [52](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR52 "Chen C, Li L, Wu Z, Chen H, Fu S (2007) Effects of lactitol on intestinal microflora and plasma endotoxin in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. J Infect 54:98–102"), [57](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR57 "Kummel KF, Brokx S (2001) Lactitol as a functional prebiotic. Cereal Food World 46:424–429"), [58](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR58 "Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB (1995) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr 125:1401–1412")\]. However, due to its low sweetness, it is usually mixed with intense sweeteners \[[47](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR47 "Zacharis C, Stowell J (2012) Lactitol. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton")\]. Similar to other polyols, it is reckoned as safe and has been allocated an ADI “not specified” by JECFA (Table [6](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab6)) \[[45](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR45 "Koivistoinen M (2007) Lactitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 187–198")\].Maltitol
Maltitol, also called 4-_O_-α-d-glucopyranosyl-_d_-glucitol (Fig. 1), is a disaccharide polyol that consists of glucose and sorbitol in equal parts and is obtained from starch, by hydrogenating maltose or very high maltose glucose syrup [1, 59, 60].
Properties and applications
Among polyols, maltitol characterizes with properties the most resembling the ones of sucrose [60, 61]. Its sweetness is clean and pleasant and amounts up to 90 % of the one attributed to sucrose, but its caloric value amounts to 2.1–2.4 kcal/g (Table 2). Maltitol is also a non-cariogenic agent, which characterizes a pleasant sweet taste that is similar to sucrose; however, due to slow absorption, the insulin response associated with its ingestion is significantly reduced [1, [10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\]. It has been reported that its simultaneous application with short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides in sugar-free food product formulations lowers postprandial glycemic responses \[[62](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR62 "Respondek F, Hilpipre C, Chauveau P, Cazaubiel M, Gendre D, Maudet C, Wagner A (2014) Digestive tolerance and postprandial glycaemic and insulinaemic responses after consumption of dairy desserts containing maltitol and fructo-oligosaccharides in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 68(5):575–580")\].It does not undergo carmelization and browning process, and it cooling effect is negligible when compared with other polyols. Besides replacing sweeteners, it can also be used as a fat substitute, as it gives a creamy texture to food [59–61, [63](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR63 "FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Maltitol. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=159
. Accessed 7 May 2014")\]. Due to its low hygroscopicity and stability in high temperatures, it is used in many baked products as well as a variety of reduced calorie, reduced fat and sugar-free foods \[[21](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR21 "Evrendilek GA (2012) Sugar alcohols (Polyols). In: Varzakas T, Labropoulos A, Anestis S (eds) Sweeteners: nutritional aspects, applications, and production technology. CRC Press, Boca Raton"), [59](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR59 "Lawson P (2007) Maltitol and maltitol syrup. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 199–217"), [60](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR60 "Kearsley MW, Boghani N (2012) Maltitol. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton")\].Metabolism
Maltitol absorption ranges from 5 to 80 %, but is must be preceded by hydrolysis which leads to glucose and sorbitol [1]. It is slowly digested in the small intestine, and the non-absorbed part passes to the colon where is undergoes fermentation by bacteria [64]. Although its ADI was not specified, it reveals laxative effects when consumed in amounts exceeding 25–30 g/kg body weight per day [59].
Currently, its use is approved in most countries including Canada, Europe, Australia, New Zealand and Japan, but awaits approval of Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, US food manufacturers may use maltitol since FDA has accepted the petition concerning this compound [61].
Mannitol
This 6-carbon sugar alcohol is an isomer of sorbitol (Fig. 1). Mannitol is used as a reserve carbohydrate by some bacteria, fungi, brown seaweeds and some higher plants [65, 66].
Production
Its production is based on the catalytic hydrogenation of glucose/fructose (1:1) mixture, obtained from invert sugar or starch, at high temperatures and pressure [67–69]. However, this process characterizes with low efficiency yielding only 25 % of mannitol in the obtained mixture and a need of elaborate purification step. Thus, fermentative processes have been researched, especially with the use of heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria, resulting in a complete conversion of d-fructose into d-mannitol in mild conditions [70–73]. Recently, cyanobacteria were found useful for mannitol production, mainly due to the fact that sugars are the primary products of photosynthesis [66]. As it can be found in high amounts in the exudates of certain trees, especially from Manna ash (Fraxinus ornus), figs, olives, larches, edible fungi, yeasts and seaweed, its production through extraction from natural sources is also considered [17, 65, 68, 69, 74, 75].
Metabolism
Mannitol is poorly absorbed, and thus, the rise in blood glucose and demand for insulin is much less than would be experienced after sucrose ingestion. It is only partially absorbed (~25 %) from the small intestine and not metabolized (Table 3). However, in the lower part of the intestinal tract, colonic bacteria can slowly metabolize some of the non-absorbed portion, and thus, consumption of doses exceeding 20 g/day might have a laxative effect [Table 6; 1, 68, 72]. The fermentation yields organic acids production, which can be utilized by human organism [14].
Properties and applications
It is about 50 % as sweet as sucrose and has a desirable cooling effect, which is efficient in masking bitter tastes [1, 17, 68]. Mannitol can be mixed with other ingredients and sweeteners what can result in a synergistic effect of better sweetness and tasting. This sugar alcohol characterizes with a pleasant taste, stability, even in high temperatures, and a high melting point (165–169° C). Thus, it is commonly used in pharmaceuticals and nutritional tablets as well as in food industry, i.e., in chocolate-flavored coating agents for ice cream and confections or “breath-freshening” and “sugar-free” products. Mannitol can be also used as a feedstock for bioethanol production [76]. As mannitol is non-hygroscopic, it is used as a bulking agent for sugar-free coatings and a dusting powder for chewing gum to prevent the gum from sticking to manufacturing equipment and wrappers [68, 77, 78].
It can be also applied as a potent osmotic diuretic and is a well-known antioxidant [17, 19, 31, 68, 69, 79]. Moreover, it acts as a scavenger of hydroxyl radicals and is claimed to protect against the development of colon cancer [68, 80]. Mannitol is also presumed to be health promoting, and thus, its addition to foods can result in extra nutritional value [72]. When mannitol is inhaled, it helps in mucus and cough clearance in asthmatics and other hypersecretory diseases [81, 82]. Mannitol accompanied with hydration during endovascular aortic aneurysm repair might improve renal function [83].
Besides being non-cariogenic, it is also characterized with a low caloric value (Table 2). As mannitol is not metabolized by humans, it does not induce hyperglycemia and has glycemic and insulinemic indexes of 0 [1, 24, 69, 72].
Similar to other polyols, mannitol is also resistant to oral bacteria which prevents from the increase in the acidity of the mouth after ingestion (Table 4). Thus, according to the US FDA and European Commission, products containing mannitol can have a health claim on the labeling stating “does not promote tooth decay” [[10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\]. FDA as well as JECFA have approved usage of mannitol as a food additive, which is regarded as safe (Table [6](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab6)).Sorbitol
Sorbitol, which has a systematic name d-glucitol (Fig. 1), is a 6-carbon sugar alcohol that was discovered by a French chemist in the berries of the mountain ash in 1872. This polyol can be naturally found in apples, pears, peaches, apricots and nectarines as well as in dried fruits, such as prunes, dates and raisins and in some vegetables [17, 22, 75, 84–88].
Production
Sorbitol is produced from glucose or sucrose, by a catalytic hydrogenation with hydrogen gas and nickel catalyst at high temperatures [17, 21, 22, 89]. However, it can be also produced by electrochemical reduction of dextrose in alkaline conditions [21, 22]. Although there are known several industrial processes which are used for the production of sorbitol, only a few microorganisms, including three yeast strains and bacteria such as Zymomonas mobilis and Candida boidini, have been suggested as potential sorbitol producers [17, 73, 87, 90–92].
Properties and applications
Sorbitol supplies fewer calories than sugars, and its sweetness amounts to about 60 % of the one assigned to sucrose (Table 2). It also characterizes with a 20-fold higher solubility in water than mannitol. [17, 84, 87]. It is manufactured in both liquid and crystalline form [75, 84]. Similarly to xylitol and erythritol, it has a negative heat of solution, and thus it gives a cooling sensation in the mouth. Sorbitol has a sweet, cool and pleasant taste. Besides acting as a sweetener, it is also an excellent humectant, softener, texturizing and anti-crystallizing agent [17, 90] (Table 1). It is easily compressible substance but has a great technological disadvantage, which is high hygroscopicity [77, 78]. This polyol is chemically inert and stable, even in high temperatures, and does not undergo Maillard reactions [75, 93, 94]. Sorbitol can combine well with other food components such as sugars, gelling agents, proteins and fats. It also may reveal synergistic effects with other sweeteners that result in greater sweetness and better taste. This sugar alcohol is important for fruits carbon metabolism and affects the quality of starch accumulation and sugar–acid balance [22].
Sorbitol is resistant to digestion by oral bacteria which break down sugars and starches to release acids that may lead to cavities or erode tooth enamel. According to the US FDA and European Commission, products containing this sugar alcohol can have a health claim on the labeling stating “does not promote tooth decay” [[10](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR10 "EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf
. Accessed 10 June 2014")\].Due to its non-cariogenic properties, it is used in products for special nutritional purposes designated for people with diabetes, but it also finds its application in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Sorbitol can be added to a wide variety of products, including sugar-free candies, chewing gums and sugar-free foods such as frozen desserts and baked goods. As it prevents loss of moisture content, it is used in the production of confectionery, baked goods and chocolate, which have a tendency to become dry or harden during storage. Sorbitol is also used as an important precursor of the vitamin C production, sorbose as well as surfactants [5, 87, 92]. The worldwide production of sorbitol is estimated to be higher than 500,000 tons/year, and the market is continuously increasing, and about 25 % of that production is used for the synthesis of vitamin C [73, 85, 87]. What is more, 25 % of total sorbitol production is used in manufacturing of syrups [21].
Its safety has been supported by many scientific studies, and JECFA has defined an acceptable daily intake (ADI) for sorbitol as “not specified,” and thus, no limits are placed on its use. Similar to other polyols, it might reveal laxative effect when eaten in excess [22; Table 6].
Xylitol
It is a 5-carbon polyol which is produced from d-xylose (Fig. 1). It was discovered in 1891 and since the 1960s has been used as a sweetener. It can be found in nature in many fruits and vegetables, berries, oats and mushrooms and is produced in small quantities in human organism [21, 22, 95–99].
Production
Main substrate for its production is xylan, which is usually obtained from birch trees and other hardwood [95, 97, 100]. Similarly to other sugar alcohols, xylitol is produced by metal catalyzed hydrogenation of a corresponding sugar, i.e., D-xylose [26, 98, 101]. This process starts with xylan isolation from wood material followed by its hydrolysis to xylose. Then xylose is chromatographically purified, and the resulting solution is subjected to hydrogenation in the presence of nickel catalyst. Commercial xylitol production might be also started by xylose solution hydrogenation, its purification and final crystallization in orthorhombic form [21, 99].
However, due to high production cost, biotechnological production systems from corn cobs, the waste of sugarcane and other fibers were developed, but still they are not introduced on commercial scale [99, 102–106]. It can be also efficiently produced by yeasts that naturally obtain xylitol as an intermediate during D-xylose metabolism [17, 73]. The genus Candida is their best source, but it cannot be used in food industry as it is a pathogenic one [17, 73]. Recombinant microalgae were also reported to produce xylitol [107].
Metabolism
Xylitol is approximately absorbed in 50 % in small intestine and its fermentation, which takes place in large bowel, ranges from 50 to 75 % [1]. It can be metabolized directly in the liver or indirectly by fermentative degradation by intestinal flora (Table 3) [108]. Human tolerance of xylitol amounts to 100 g per day [96].
Properties and applications
Xylitol is the sweetest among all sugar alcohols (Table 2). It characterizes with the same sweetness and bulk as sucrose with one-third fewer calories and no unpleasant aftertaste [21]. Insulin is not required for its metabolism [26, 97]. It quickly dissolves and produces a cooling sensation in the mouth [3, 98, 99].
Xylitol is widely used in biomedical and other applications [3]. Its regular consumption in adequate doses results in the reduction of tooth decay [26, 97, 109]. Besides reducing the development of dental caries, it also plays a role in a decrease in plaque formation as it inhibits the growth and metabolism of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus, which are responsible for caries and dental plaque acid production, respectively [96, 110–113]. There are results of several clinical studies which confirm that the daily usage of small amounts of xylitol significantly decreases the risk of dental caries [3, 95, 114]. It has been also reported that maternal xylitol consumption results in reduced occurrence of dental caries in children [115]. Xylitol increases pH values in the oral cavity that contributes to teeth remineralization as well as forms complexes with Ca(II) which is supposed to play a huge role in tooth mineralization [3, 116, 117]. Moreover, xylitol acts as a statherin, which is a polypeptide that provides a protective and stabilized environment for teeth [3]. There is also data implying that xylitol reduces the incidence of ear infections and has an anti-bacterial effect on pneumococcal nasal colonization [96, 118–120]. This sugar alcohol is used as an energy source in infusion therapy [121]. It also acts as an antioxidant agent of fish oil [122], as a sanitizer [123] and as a preventive factor of adrenocortical suppression during steroid therapy [121] and phenylenediamine-induced hepatotoxicity [124].
Due to its properties and only few reported side effects, mainly gastrointestinal (Table 6), it is widely used in food, pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, especially in such products as chewing gums and candies [98, 99]. FDA approved its use in 1960 s and in Europe, it is known as E967 food additive, which is safe for use with children [95].
Sugar alcohols versus artificial sweeteners
The health and safety agencies from different countries regulate which sweeteners are allowed as well as the maximum amount that can be added to a specific food group. Sweeteners may be used separately or in combination with other sweeteners, and the latter is becoming increasingly popular in recent years owing to technical, health and commercial advantages. The consumption of low-calorie foods by the worldwide population has dramatically increased, as well as health concerns associated with the consequent high intake of sweeteners both nutritive and non-nutritive.
Nutritive sweeteners include refined sugar, honey, high fructose, corn syrup, dextrose and sugar alcohols. There are eight non-nutritive sweeteners included in EU legislation that are allowed for use in food, i.e., acesulfame K (E950), aspartame (E951), cyclamic acid and its Na, Ca salts (E952), saccharin and its Na, K, Ca salts (E954), sucralose (E955), thaumatin (E957), neohesperidine DC (E959) and salt of aspartame–acesulfame K (E962) [[11](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR11 "European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC of 30 June 1994. https://www.fsai.ie/uploadedFiles/Dir94.35.pdf
. Accessed 14 June 2014")\].One of the most important differences between artificial sugar substitutes and polyols is that the first ones contain zero calories, with the exception of aspartame that provides 4 kcal per gram but is consumed in very small amounts, contributing negligible energy. Sugar alcohols contain from 0.2 to 2.7 calories per gram (Table 2), while common sugars supply 4 kcal/g.
Unlike artificial sweeteners, polyols can raise blood glucose but less than sugars, which is due to their incomplete absorption in human organism. However, particular sugar alcohols are metabolized differently and thus can exhibit various impacts on glucose levels in organism (Table 2). Polyols are in general partially digested in the intestines, and the non-absorbed part is slowly metabolized by colonic bacteria yielding volatile short-chain fatty acids (Table 3). Most of artificial intense sweeteners are not metabolized (acesulfame potassium), but aspartame is digested to phenylalanine, aspartic acid and methanol; thus, people with phenylketonuria, a rare genetic disorder, cannot consume products sweetened with this substance [2, 26].
The sweetness of sugar alcohols varies from 25 to 100 % as compared with table sugar (Table 2), whereas artificial sweeteners are 30 to even 13,000 times sweeter than sucrose [2, 26]. Thus, they can be used in small amounts to achieve desired sweetness in such products as beverages, ice cream chewing gum, chocolate, jams/jellies, yogurt and salad dressings [2]. However, artificial intense sweeteners are used only for sweetening, whereas polyols can be used as anti-caking and glazing agents as well as stabilizers and thickeners (Table 1). Similar to common sugars, they can be also used as bulking agents besides being excellent natural sweeteners. They also help food keep moisture, prevent browning when heated and add a cooling sensation to products. Some artificial sweeteners may leave an aftertaste, but mixing with particular polyols such as erythritol, isomalt or lactitol can result in a similar flavor to the one of table sugar [22, 27, 40].
The use of sugar alcohols in food products is defined in the Regulation (EC) 1333/2008 on food additives, and they are authorized to be added on where quantum satis level for all purposes, i.e., sweetening and others [[8](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR8 "Regulation (EC) no 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:354:0016:0033:en:PDF
. Accessed 10 June 2014"); Table [6](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab6)\]. However, each artificial sweetener has been established an acceptable daily intake (ADI) and are used in foods within specified limits \[[11](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR11 "European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC of 30 June 1994.
https://www.fsai.ie/uploadedFiles/Dir94.35.pdf
. Accessed 14 June 2014")\]. Although there are some controversies over the safety of artificial sweeteners, especially aspartame, they have been approved both by the FDA as well as JECFA (The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives) \[[2](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR2 "Shankar P, Ahuja S, Sriram K (2013) Non-nutritive sweeteners: review and update. Nutrition 29:1293–1299"), [26](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#ref-CR26 "Chattopadhyay S, Raychaudhuri U, Chakraborty R (2014) Artificial sweeteners—a review. J Food Sci Technol 51:611–621")\]. Sugar alcohols have been also associated with few side effects when eaten in excess, which include bloating, abdominal pain and diarrhea (Table [6](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab6)). However, in reasonable amounts, artificial sweeteners and polyols might be helpful in diabetes and weight control, but tooth decay prevention can be only associated to the latter consumption. Besides that, sugar alcohols exhibit many health protection roles (Table [4](/article/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7#Tab4)).All in all, both groups of sweeteners can be useful in diabetes management and are good option for people on low-carbohydrate diet. The highest polyol intake can be associated with consumption of confectionery products, fish/meat product and miscellaneous foods. However, such estimates might differ in dependence on scenario adopted for exposure modeling [125]. Overconsumption of polyols can be only of concern in view of digestive comfort, while artificial sweeteners must be always estimated with respect to the maximum amounts allowed, which are considered safe for human consumption. Therefore, it might be worth using sugar alcohols in food products marketed to patients with diabetes and individuals considering energy restricted diets more frequently but bearing in mind their gastrointestinal effects. However, optimal diet should be based on fresh unprocessed foods with the minimal amounts of food additives, and then the sugar replacers such as sugar alcohols or even artificial sweeteners will not have a significant role in the daily diet.
Conclusion
Due to increasing epidemic of obesity and diabetes, it is important to educate consumers to make reasonable and healthy food choices. Consumption of added sugars has risen dramatically over the past few decades and has negatively contributed to human health. Foods rich in added sugar contribute mainly extra calories to diet usually without nutritional value. Unfortunately, people crave sweetness, and thus, sugar substitutes have drawn attention of consumers as well as producers and dieticians. However, human body response is not identical when we compare artificial sweeteners with those of natural origin, especially sugar alcohols that characterize with many attractive properties not only to producers but also to consumers. As these compounds are new, there is a need for education as products containing polyols are a rapidly growing category of nutraceuticals and functional food. Therefore, there is a constant need for studies regarding sugar alcohols metabolism and physiological effects on human bodies.
References
- Livesey G (2003) Health potential of polyols as sugar replacers, with emphasis on low-glycaemic properties. Nutr Res Rev 16:163–191
CAS Google Scholar - Shankar P, Ahuja S, Sriram K (2013) Non-nutritive sweeteners: review and update. Nutrition 29:1293–1299
CAS Google Scholar - Mäkinen KK (2011) Sugar alcohol sweeteners as alternatives to sugar with special consideration of xylitol. Med Princ Pract 20:303–320
Google Scholar - Ellwood KC (1995) Methods available to estimate the energy values of sugar alcohols. Am J Clin Nutr 62:S1169–S1174
Google Scholar - Reports ADA (2004) Position of the American Dietetic Association: use of nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners. J Am Diet Assoc 104:255–275
Google Scholar - Wheeler ML, Pi-Sunyer X (2008) Carbohydrate issues. Type and amount. J Am Diet Assoc 108:S34–S39
CAS Google Scholar - Fitch C, Keim KS (2012) Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: use of nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners. J Acad Nutr Diet 112:739–758
Google Scholar - Regulation (EC) no 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:354:0016:0033:en:PDF. Accessed 10 June 2014
- Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2008) Perspectives in practice low-digestible carbohydrates in practice. J Am Diet Assoc 108:1677–1681
Google Scholar - EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers xylitol, D-tagatose, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, D-tagatose, isomaltulose, sucralose and polydextrose and maintenance of tooth mineralisation by decreasing tooth demineralisation. EFSA Journal 9(4): 2076. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/2076.pdf. Accessed 10 June 2014
- European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35/EC of 30 June 1994. https://www.fsai.ie/uploadedFiles/Dir94.35.pdf. Accessed 14 June 2014
- Health Canada (2005) http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/securit/addit/sweeten-edulcor/polyols_polydextose_factsheet-polyols_polydextose_fiche-eng.php. Accessed 10 May 2014
- Nakamura S (2005) Bioavailability of cellobiose and other non-digestible and/or nonabsorbable sugar substitutes and related topics. Nutrition 21:1158–1159
Google Scholar - Xiao J, Li X, Min X, Sakaguchi E (2013) Mannitol improves absorption and retention of calcium and magnesium in growing rats. Nutrition 29:325–331
CAS Google Scholar - Bernt WO, Borzelleca JF, Flamm G, Munro IC (1996) Erythritol: a review of biological and toxicological studies. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 24:S191–S197
CAS Google Scholar - Embuscado ME, Patil SK (2001) Erythritol. In: Dekker M (ed) Food science and technology, vol 17 Alternative sweeteners, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 235–254
Google Scholar - Ortiz ME, Bleckwedel J, Raya RR, Mozzi F (2013) Biotechnological and in situ food production of polyols by lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4713–4726
CAS Google Scholar - Oku T, Okazaki M (1996) Laxative threshold of sugar alcohol erythritol in human subjects. Nutr Res 16:577–589
CAS Google Scholar - den Hartog GJ, Boots AW, Adam-Perrot A, Brouns F, Verkooijen IW, Weseler AR, Haenen GR, Bast A (2010) Erythritol is a sweet antioxidant. Nutrition 26:449–458
Google Scholar - Munro IC, Bernt WO, Borzelleca JF, Flamm G, Lynch BS, Kennepohl E, Bär EA, Modderman J (1998) Erythritol: an interpretive summary of biochemical, metabolic, toxicological and clinical data. Food Chem Toxicol 36:1139–1174
CAS Google Scholar - Evrendilek GA (2012) Sugar alcohols (Polyols). In: Varzakas T, Labropoulos A, Anestis S (eds) Sweeteners: nutritional aspects, applications, and production technology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Google Scholar - Barbieri G, Barone C, Bhagat A, Caruso G, Conley Z R, Parisi S (2014) Sweet compounds in foods: sugar alcohols. In: Springer (ed) The influence of chemistry on new foods and traditional products. Springer International Publishing, Berlin
- Cock P (2012) Erythritol. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Livesey G (2012) Glycaemic responses and toleration. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Runnel R, Mäkinen KK, Honkala S, Olak J, Mäkinen P-L, Nõmmela R, Vahlberg T, Honkala E, Saag M (2013) Effect of three-year consumption of erythritol, xylitol and sorbitol candies on various plaque and salivary caries-related variables. J Dent 41:1236–1244
CAS Google Scholar - Chattopadhyay S, Raychaudhuri U, Chakraborty R (2014) Artificial sweeteners—a review. J Food Sci Technol 51:611–621
CAS Google Scholar - Boileau A, Fry JC, Murray R (2012) A new calorie-free sugar substitute from the leaf of the stevia plant arrives in the UK. Nutr Bull 37(1):47–50
Google Scholar - Boesten DM, Berger A, de Cock P, Dong H, Hammock BD, den Hartog GJ, Bast A (2013) Multi-targeted mechanisms underlying the endothelial protective effects of the diabetic-safe sweetener erythritol. PLoS ONE 8(6):e65741
CAS Google Scholar - Kim Y, Park SC, Wolf BW, Hertzler SR (2011) Combination of erythritol and fructose increases gastrointestinal symptoms in healthy adults. Nutr Res 31:836–841
CAS Google Scholar - Lawson P (2007) Erythritol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 153–166
Google Scholar - Monedero V, Pérez-Martínez G, Yebra MJ (2010) Perspectives of engineering lactic acid bacteria for biotechnological polyol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1003–1015
CAS Google Scholar - Lin S-J, Wen C-Y, Wang P-M, Huang J-C, Wei C-L, Chang J-W, Chu W-S (2010) High-level production of erythritol by mutants of osmophilic Moniliella sp. Process Biochem 45:973–979
CAS Google Scholar - Veiga-da-Cunha M, Santos H, van Schaftingen E (1993) Pathway and regulation of erythritol formation in Leuconostoc oenos. J Bacteriol 175:3941–3948
CAS Google Scholar - Stolz P, Biicker G, Hammes WP, Vogel RF (1995) Utilization of electron acceptors by lactobacilli isolated from sourdough. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 201:91–96
CAS Google Scholar - Richter H, Vlad D, Unden G (2001) Significance of pantothenate for glucose fermentation by Oenococcus oeni and for suppression of the erythritol and acetate production. Arch Microbiol 175:26–31
CAS Google Scholar - Mirończuk AM, Dobrowolski A, Rakicka M, Rywińska A, Rymowicz W (2014) Newly isolated mutant of Yarrowia lipolytica MK1 as a proper host for efficient erythritol biosynthesis from glycerol. Process Biochem. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.10.020
- Tomaszewska L, Rywińska A, Rymowicz W (2014) High selectivity of erythritol production from glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biomass Bioenerg 64:309–320
CAS Google Scholar - Yang L-B, Zhan X-B, Zheng Z-Y, Wu J-R, Gao M-J, Lin C-C (2014) A novel osmotic pressure control fed-batch fermentation strategy for improvement of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol. Bioresour Technol 151:120–127
CAS Google Scholar - Sentko A, Bernard J (2012) Isomalt. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
- Sentko A, Willibald-Ettle I (2012) Isomalt. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Ferguson T, Sentko A, Willibald-Ettle I (2007) Isomalt. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 167–177
Google Scholar - FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Isomalt. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=180. Accessed 7 May 2014
- Takatsuka T, Exterkate RAM, ten Cate JM (2008) Effects of isomalt on enamel de-and remineralization, a combined in vitro pH-cycling model and in situ study. Clin Oral Invest 12:173–177
Google Scholar - Gostner A, Blaut M, Schäffer V, Kozianowski G, Theis S, Klingeberg M, Dombrowski Y, Martin D, Ehrhardt S, Taras D, Schwiertz A, Kleessen B, Lührs H, Schauber J, Dorbath D, Menzel T, Scheppach W (2006) Effect of isomalt consumption on faecal microflora and colonic metabolism in healthy volunteers. Br J Nutr 95(1):40–50
CAS Google Scholar - Koivistoinen M (2007) Lactitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 187–198
Google Scholar - Zacharis C (2012) Lactitol. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Zacharis C, Stowell J (2012) Lactitol. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
- Ballongue J, Schumann C, Quignon P (1997) Effects of lactulose and lactitol on colonic microflora and enzymatic activity. Scand J Gastroenterol 222:41–44
CAS Google Scholar - FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Lactitol, http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=156. Accessed 7 May 2014
- Finney M, Smullen J, Foster HA, Brokx S, Storey DM (2007) Effects of low doses of lactitol on faecal microflora, pH, short chain fatty acids and gastrointestinal symptomology. Eur J Nutr 46:307–314
CAS Google Scholar - Ouwenhand AC, Tiihonen K, Saarinen M, Putaala H, Rautonen N (2009) Influence of a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol on healthy elderly: intestinal and immune parameters. Br J Nutr 101:367–375
Google Scholar - Chen C, Li L, Wu Z, Chen H, Fu S (2007) Effects of lactitol on intestinal microflora and plasma endotoxin in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. J Infect 54:98–102
Google Scholar - Mas A, Rodes J, Sunyer L, Rodrigo L, Planas R, Vargas V, Castells L, Rodríguez-Martínez D, Fernández-Rodríguez C, Coll I, Pardo A (2003) Comparison of rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol 38:51–58
CAS Google Scholar - Salerno F, Moser P, Maggi A, Vitaliani G, Benetti G (1994) Effects of long-term administration of low-dose lactitol in patients with cirrhosis but without overt encephalopathy. J Hepatol 21:1092–1096
CAS Google Scholar - Cammà C, Fiorello F, Tinè F, Marchesini G, Fabbri A, Pagliaro L (1993) Lactitol in treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 38:916–922
Google Scholar - Morillas RM, Sala M, Planas R (2014) Prevention of hepatic encephalopathy. Med Clin 142:512–514
Google Scholar - Kummel KF, Brokx S (2001) Lactitol as a functional prebiotic. Cereal Food World 46:424–429
CAS Google Scholar - Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB (1995) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr 125:1401–1412
CAS Google Scholar - Lawson P (2007) Maltitol and maltitol syrup. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 199–217
Google Scholar - Kearsley MW, Boghani N (2012) Maltitol. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Google Scholar - Kearsley MW, Deis RC (2012) Maltitol powder. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Respondek F, Hilpipre C, Chauveau P, Cazaubiel M, Gendre D, Maudet C, Wagner A (2014) Digestive tolerance and postprandial glycaemic and insulinaemic responses after consumption of dairy desserts containing maltitol and fructo-oligosaccharides in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 68(5):575–580
CAS Google Scholar - FAO-WHO Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius (2014) GSFA Online. Maltitol. http://www.codexalimentarius.net/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=159. Accessed 7 May 2014
- Grabitske HA, Slavin JL (2009) Gastrointestinal effects of low-digestible carbohydrates. Crit Rev Food Sci 49:327–360
CAS Google Scholar - Ruperez P, Toledano G (2003) Celery by-products as a source of mannitol. Eur Food Res Technol 216:224–226
CAS Google Scholar - Jacobsen JH, Frigaard N-U (2014) Engineering of photosynthetic mannitol biosynthesis from CO2 in a cyanobacterium. Metab Eng 21:60–70
CAS Google Scholar - Makkee M, Kieboom APG, Van Bekkum H (1985) Production methods of D-mannitol. Starch Starke 37:136–141
CAS Google Scholar - Ghoreishi SM, Shahrestani RG (2009) Innovative strategies for engineering mannitol production. Trends Food Sci Techol 20:263–270
CAS Google Scholar - Song SH, Vieille C (2009) Recent advances in the biological production of mannitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:55–62
CAS Google Scholar - Soetaert W, Buchholz K, Vandamme EJ (1995) Production of D-mannitol and D-lactic acid by fermentation with Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Agro Food Ind Hi Tech 6:41–44
CAS Google Scholar - von Weymarn N, Hujanen M, Leisola M (2002) Production of D-mannitol by heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria. Process Biochem 37:1207–1213
Google Scholar - Wisselink HW, Weusthuis RA, Eggink G, Hugenholtz J, Grobben GJ (2002) Mannitol production by lactic acid bacteria: a review. Int Dairy J 12:151–161
CAS Google Scholar - Akinterinwa O, Khankal R, Cirino PC (2008) Metabolic engineering for bioproduction of sugar alcohols. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:461–467
CAS Google Scholar - Wilson P (2007) Mannitol. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 219–225
Google Scholar - Deis RC, Kearsley MW (2012) Sorbitol and mannitol. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Wang J, Kim YM, Rhee HS, Lee MW, Park JM (2013) Bioethanol production from mannitol by a newly isolated bacterium, Enterobacter sp. JMP3. Bioresour Technol 135:199–206
CAS Google Scholar - Gombás Á, Szabó-Révész P, Regdon G, Erӧs I (2003) Study of thermal behaviour of sugar alcohols. J Therm Anal Calorim 73:615–621
Google Scholar - Jamieson PR (2012) Sorbitol and mannitol. In: O’Brien Nabors L (ed) Alternative sweeteners. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Racton
Google Scholar - Saha BC, Racine FM (2010) Effects of pH and corn steep liquor variability on mannitol production by Lactobacillus intermedius NRRL B-3693. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:553–560
CAS Google Scholar - Gaspar P, Neves AR, Ramos A, Gasson MJ, Shearman CA, Santos H (2004) Engineering Lactococcus lactis for production of mannitol: high yields from food-grade strains deficient in lactate dehydrogenase and the mannitol transport system. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1466–1474
CAS Google Scholar - Daviskas E, Anderson SD, Eberl S, Young IH (2010) Beneficial effect of inhaled mannitol and cough in asthmatics with mucociliary dysfunction. Respir Med 104:1645–1653
Google Scholar - Daviskas E, Anderson SD, Young IH (2010) Effect of mannitol and repetitive coughing on the sputum properties in bronchiectasis. Respir Med 104:371–377
Google Scholar - Kalimeris K, Nikolakopoulos N, Riga M, Christodoulaki K, Moulakakis KG, Dima C, Papasideris C, Sidiropoulou T, Kostopanagiotou G, Pandazi A (2014) Mannitol and renal dysfunction after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair procedures: a randomized trial. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 28(4):966–971
CAS Google Scholar - Lawson P (2007) Sorbitol and sorbitol syrup. In: Wilson R (ed) Sweeteners. Blackwell Publishing and Leatherhead Publishing, UK, pp 227–238
Google Scholar - Budavari S, O´Neil M, Smith A, Heckelman PE, Kinneary JF (1996) The Merck index. An encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals. Merck, Whitehouse Station, pp 1490–1491
- Gutierrez AJE, Gaudillere JP (1996) Distribution, metabolism and role of sorbitol in higher plants. A review. Agronomie 5:281–298
Google Scholar - Silveira MM, Jonas R (2002) The biotechnological production of sorbitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:400–408
CAS Google Scholar - Milala J, Kosmala M, Sójka M, Kołodziejczyk K, Zbrzeźniak M, Markowski J (2013) Plum pomaces as a potential source of dietary fibre: composition and antioxidant properties. J Food Sci Technol 50(5):1012–1017
CAS Google Scholar - Kusserow B, Schimpf S, Claus P (2003) Hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol over nickel and ruthenium catalysts. Adv Synth Catal 345:289–299
CAS Google Scholar - Jonas R, Silveira MM (2004) Sorbitol can be produced not only chemically but also biotechnologically. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 118:321–336
CAS Google Scholar - Silveira MM, Wisbeck E, Lemmel C, Erzinger G, da Costa JP, Bertasso M, Jonas R (1999) Bioconversion of glucose and fructose to sorbitol and gluconic acid by untreated cells of Zymomonas mobilis. J Biotechnol 75:99–103
CAS Google Scholar - Ladero V, Ramos A, Wiersma A, Goffin P, Schanck A, Kleerebezem M, Hugenholtz J, Smid EJ, Hols P (2007) High-level production of the low-calorie sugar sorbitol by Lactobacillus plantarum through metabolic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1864–1872
CAS Google Scholar - Le AS, Mulderrig KB (2001) Sorbitol and mannitol. In: Nabors LO (ed) Alternative sweeteners, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Google Scholar - Basu S, Shivhare US (2013) Rheological, textural, microstructural, and sensory properties of sorbitol-substituted mango jam. Food Bioprocess Technol 6:1401–1413
CAS Google Scholar - Ly KA, Milgrom P, Rothen M (2006) Xylitol, sweeteners, and dental caries. Pediatr Dent 28:154–163
Google Scholar - Lee BD, Park MK (2014) Effects and safety of xylitol on middle ear epithelial cells. Int Adv Otol 10:19–24
Google Scholar - Nigam P, Singh D (1995) Processes for fermentative production of xylitol—a sugar substitute. Process Biochem 30:117–124
CAS Google Scholar - Granstrӧm TB, Izumori K, Leisola M (2007) A rare sugar xylitol. Part I: The biochemistry and biosynthesis of xylitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:277–281
Google Scholar - Zacharis C (2012) Xylitol. In: O’Donnell K, Kearsley MW (eds) Sweeteners and sugar alternatives in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex
Google Scholar - Zhang J, Geng A, Yao C, Lu Y, Li Q (2012) Xylitol production from D-xylose and horticultural waste hemicellulosic hydrolysate by a new isolate of Candida athensensis SB18. Bioresour Technol 105:134–141
CAS Google Scholar - Zakaria A (2001) Production of natural and rare pentoses using microorganisms and their enzymes. Electron J Biotechnol 4:103–111
Google Scholar - Tada K, Horiuchi J, Kanno T, Kobayashi M (2004) Microbial xylitol production from corn cobs using Candida magnoliae. J Biosci Bioeng 98:228–230
CAS Google Scholar - Latif F, Rajoka MI (2001) Production of ethanol and xylitol from corn cobs by yeasts. Bioresour Technol 77:57–63
CAS Google Scholar - Buhner J, Agblevor FA (2004) Effect of detoxification of dilute- acid corn fiber hydrolysate on xylitol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 119:13–30
CAS Google Scholar - Dominguez JM, Gong CS, Tsao GT (1996) Pretreatment of sugar cane bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate for xylitol production by yeast. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 57–58:49–56
Google Scholar - Santos JC, Pinto IR, Carvalho W, Mancilha IM, Felipe MG, Silva SS (2005) Sugarcane bagasse as raw material and immobilization support for xylitol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 121–124:673–683
Google Scholar - Pourmir A, Noor-Mohammadi S, Johannes TW (2013) Production of xylitol by recombinant microalgae. J Biotechnol 165(3–4):178–183
CAS Google Scholar - Sheet BS, Artık N, Ayed MA, Abdulaziz OF (2014) Some alternative sweeteners (xylitol, sorbitol, sucralose and stevia): review. Karaelmas Sci Eng J 4(1):63–70
Google Scholar - Söderling E, Hirvonen A, Karjalainen S, Fontana M, Catt D, Seppä L (2011) The effect of xylitol on the composition of the oral flora: a pilot study. Eur J Dent 5:24–31
Google Scholar - Söderling EM, Ekman TC, Taipale TJ (2008) Growth inhibition of Streptococcus mutans with low xylitol concentrations. Curr Microbiol 56:382–385
Google Scholar - Lee SH, Choi BK, Kim YJ (2012) The cariogenic characters of xylitol-resistant and xylitol-sensitive Streptococcus mutans in biofilm formation with salivary bacteria. Arch Oral Biol 57:697–703
CAS Google Scholar - Misra S, Raghuwanshi S, GuptacP Saxena RK (2012) Examine growth inhibition pattern and lactic acid production in Streptococcus mutans using different concentrations of xylitol produced from Candida tropicalis by fermentation. Anaerobe 18:273–279
CAS Google Scholar - ElSalhy M, Sayed Zahid I, Honkala E (2012) Effects of xylitol mouthrinse on Streptococcus mutans. J Dent 40:1151–1154
CAS Google Scholar - Milgrom P, Zero DT, Tanzer JM (2009) An examination of the advances in science technology of prevention of tooth decay in young children since the surgeon general’s report on oral health. Acad Pediatr 9:404–409
Google Scholar - Söderling E, Isokangas P, Pienihakkinen K, Tenovuo J, Alanen P (2001) Influence of maternal xylitol consumption on mother-child transmission of mutans streptococci: 6-year-follow-up. Caries Res 35:173–177
Google Scholar - Tanzer JM (1995) Xylitol chewing gum and dental caries. Int Dent J 45:65–76
CAS Google Scholar - Bahador A, Lesan S, Kashi N (2012) Effect of xylitol on cariogenic and beneficial oral streptococci: a randomized, double-blind crossover trial. Iran J Microbiol 4:75–81
CAS Google Scholar - Nyyssölä A, Pihlajaniemi A, Palva A, von Weymarn N, Leisola M (2005) Production of xylitol from d-xylose by recombinant Lactococcus lactis. J Biotechnol 118:55–66
Google Scholar - Uhari M, Tapiainen T, Kontiokari T (2000) Xylitol is preventing acute otitis media. Vaccine 19:144–147
Google Scholar - Vernacchio L, Vezina RM, Mitchell AA (2007) Tolerability of oral xylitol solution in young children: implications for otitis media prophylaxis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:89–94
Google Scholar - Georgieff M, Moldawer LL, Bistrian BR, Blackburn GL (1985) Xylitol, an energy source for intra-venous nutrition after trauma. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 9:199–209
CAS Google Scholar - Faraji H, Lindsay RC (2004) Characterization of antioxidant activity of sugars and polyhydric alcohols in fish oil emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 52:7164–7171
CAS Google Scholar - Kwon NH, Kim SH, Kim JY, Lim JY, Kim JM, Jung WK, Park KT, Bae WK, Noh KM, Choi JW, Hur J, Park YH (2003) Antimicrobial performance of alkaline ionic fluid (GC-100X) and its ability to remove Escherichia coli O157:H7 from the surface of tomatoes. J Food Prot 66:1604–1610
CAS Google Scholar - Sood C, Khan S, O’Brien PJ (1997) Phenylenediamine induced hepatocytes cytotoxicity redox. Cycling mediated oxidative stress without oxygen activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1335:343–352
CAS Google Scholar - Tennant DR (2014) Potential intakes of total polyols based on UK usage survey data. Food Addit Contam Part A 31(4):574–586
CAS Google Scholar - Arrigoni E, Brouns F, Amadò R (2005) Human gut microbiota does not ferment erythritol. Br J Nutr 94:643–646
CAS Google Scholar - Vasilescu R, Ionescu AM, Mihai A, Carniciu S, Ionescu-Tîrgovişte C (2011) Sweeteners and metabolic diseases: xylitol as a new player. Proc Rom Acad Series B 2:125–128
Google Scholar - Sreenivas RR, Prakasham RS, Krishna PK, Rajesham S, Sharma PN, Venkateswar RL (2004) Xylitol production by Candida sp.: parameter optimization using taguchi approach. Process Biochem 39:951–956
Google Scholar - Culbert SJ, Wang YM, Fritsche HA, Carr D, Lantin E, van Eys J (1986) Oral xylitol in American adults. Nutr Res 6:913–922
CAS Google Scholar - Storey D, Lee A, Bornet F, Brouns F (2007) Gastrointestinal tolerance of erythritol and xylitol ingested in a liquid. Eur J Clin Nutr 61:349–354
CAS Google Scholar