Genetic characterisation of Fasciola samples from different host species and geographical localities revealed the existence of F. hepatica and F. gigantica in Niger (original) (raw)
Abstract
In the present study, 16 samples representing Fasciola (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Digenea) from sheep and cattle from seven geographical locations in Niger were characterized genetically by sequences of the first (ITS-1) and second (ITS-2) internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA (rDNA). The ITS rDNA was amplified from individual liver flukes by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and the amplicons were sequenced directly. The lengths of the ITS-1 and ITS-2 sequences were 422 and 361/362 bp, respectively, for all liver fluke samples sequenced. Comparison of the ITS sequences of the Niger Fasciola samples examined in the present study with that of Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica, and the “intermediate _Fasciola_” from elsewhere revealed that the Niger Fasciola samples examined represent two species, namely F. hepatica and F. gigantica. This is the first demonstration of the existence of both F. hepatica and F. gigantica in Niger by a genetic approach, which provides foundation for further studies on F. hepatica and F. gigantica in Niger and has implications for studying the population genetic structure of the Niger Fasciola and for the diagnosis and control of the disease they cause.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Starting from 10 chapters or articles per month
- Access and download chapters and articles from more than 300k books and 2,500 journals
- Cancel anytime View plans
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
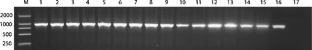
Fig. 1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Agatsuma T, Arakawa Y, Iwagami M, Honzako Y, Cahyaningsih U, Kang SY, Hong SJ (2000) Molecular evidence of natural hybridization between Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. Parasitol Int 49:231–238
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Alasaad S, Huang CQ, Li QY, Granados JE, García C, Pérez JM, Zhu XQ (2007) Characterisation of Fasciola samples from different host species and geographical localities in Spain by sequences of internal transcribed spacers of rDNA. Parasitol Res 101:1245–1250
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Chilton NB, Gasser RB, Beveridge I (1995) Differences in a ribosomal DNA sequence of morphologically indistinguishable species within the Hypodontus macropi complex (Nematoda: Strongyloidea). Int J Parasitol 25:647–651
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Haseeb AN, el-Shazly AM, Arafa MA, Morsy AT (2002) A review on fascioliasis in Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 32:317–354
PubMed Google Scholar - Huang WY, He B, Wang CR, Zhu XQ (2004) Characterisation of Fasciola species from Mainland China by ITS-2 ribosomal DNA sequence. Vet Parasitol 120:75–83
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Ishii Y, Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Nawa Y (2002) A praziquantel-ineffective fascioliasis case successfully treated with triclabendazole. Parasitol Int 51:205–209
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Itagaki T, Tsutsumi K (1998) Triploid form of Fasciola in Japan: genetic relationships between Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica determined by ITS-2 sequence of nuclear rDNA. Int J Parasitol 28:777–781
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Itagaki T, Kikawa M, Sakaguchi K, Shimo J, Terasaki K, Shibahara T, Fukuda K (2005a) Genetic characterization of parthenogenic Fasciola sp. in Japan on the basis of the sequences of ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA. Parasitology 131:679–685
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Itagaki T, Kikawa M, Terasaki K, Shibahara T, Fukuda K (2005b) Molecular characterization of parthenogenic Fasciola sp. in Korea on the basis of DNA sequences of ribosomal ITS1 and mitochondrial NDI gene. J Vet Med Sci 67:1115–1118
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Keyyu JD, Kassuku AA, Msalilwa LP, Monrad J, Kyvsgaard NC (2006) Cross-sectional prevalence of helminth infections in cattle on traditional, small-scale and large-scale dairy farms in Iringa district, Tanzania. Vet Res Commun 30:45–55
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Lin RQ, Dong SJ, Nie K, Wang CR, Li AX, Song HQ, Huang WY, Zhu XQ (2007) Sequence analysis of the first internal transcribed spacer of rDNA supports the existence of an intermediate Fasciola between F. hepatica and F. gigantica in Mainland China. Parasitol Res 101:813–817
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Luton K, Walker D, Blair D (1992) Comparisons of ribosomal internal transcribed spacers from two congeneric species of flukes (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Digenea). Mol Biochem Parasitol 56:323–327
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Mas-Coma MS, Esteban JG, Bargues MD (1999) Epidemiology of human fascioliasis: a review and proposed new classification. Bull World Health Organ 77:340–346
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD, Valero MA (2005) Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int J Parasitol 35:1255–1278
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Mekroud A, Titi A, Benakhla A, Rondelaud D (2006) The proportion of liver excised in Algerian abattoirs is not a good indicator of Fasciola hepatica infections in local cattle breeds. J Helminthol 80:319–321
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Mungube EO, Bauni SM, Tenhagen BA, Wamae LW, Nginyi JM, Mugambi JM (2006) The prevalence and economic significance of Fasciola gigantica and Stilesia hepatica in slaughtered animals in the semi-arid coastal Kenya. Trop Anim Health Prod 38:475–483
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Pfukenyi DM, Mukaratirwa S, Willingham AL, Monrad J (2006) Epidemiological studies of Fasciola gigantica infections in cattle in the highveld and lowveld communal grazing areas of Zimbabwe. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 73:37–51
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Phiri AM, Phiri IK, Chota A, Monrad J (2007) Trematode infections in freshwater snails and cattle from the Kafue wetlands of Zambia during a period of highest cattle–water contact. J Helminthol 81:85–92
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Spithill TW, Dalton JP (1998) Progress in development of liver fluke vaccines. Parasitol Today 14:224–228
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Vara-Del Río MP, Villa H, Martinez-Valladares M, Rojo-Vázquez FA (2007) Genetic heterogeneity of Fasciola hepatica isolates in the northwest of Spain. Parasitol Res 101:1003–1006
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Yamaguti S (1958) Systema helminthum, vol I. The digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. Interscience Publishers, New York
Google Scholar - Zhu XQ, D’Amelio S, Palm HW, Paggi L, George-Nascimento M, Gasser RB (2002) SSCP-based identification of members within the Pseudoterranova decipiens complex (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea: Anisakidae) using genetic markers in the internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA. Parasitology 124:615–623
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgments
Project support was provided in part by grants from the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in Chinese Universities (grant no. IRT0723) to XQZ and from the International Foundation for Science (IFS; grant no. B/4184-1) to HA. The authors would like to thank the kind collaboration of many people for assistance in collection of Fasciola samples. The experiments comply with the current laws of the countries in which the experiments were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- College of Veterinary Medicine, South China Agricultural University, 483 Wushan Street, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, 510642, People’s Republic of China
H. Ali, L. Ai, H. Q. Song, R. Q. Lin & X. Q. Zhu - Institute of Research and Development (IRD), 276 Maradi Avenue, Box 11416, Niamey, People’s Republic of Niger
S. Ali - Veterinary Laboartory, Ministry of Animal Resources, Niamey, People’s Republic of Niger
B. Seyni & G. Issa
Authors
- H. Ali
- L. Ai
- H. Q. Song
- S. Ali
- R. Q. Lin
- B. Seyni
- G. Issa
- X. Q. Zhu
Corresponding author
Correspondence toX. Q. Zhu.
Additional information
H. Ali and L. Ai contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, H., Ai, L., Song, H.Q. et al. Genetic characterisation of Fasciola samples from different host species and geographical localities revealed the existence of F. hepatica and F. gigantica in Niger.Parasitol Res 102, 1021–1024 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0870-7
- Received: 11 December 2007
- Accepted: 21 December 2007
- Published: 09 January 2008
- Issue date: April 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0870-7