The complete mitochondrial genomes of three cestode species of Taenia infecting animals and humans (original) (raw)
Abstract
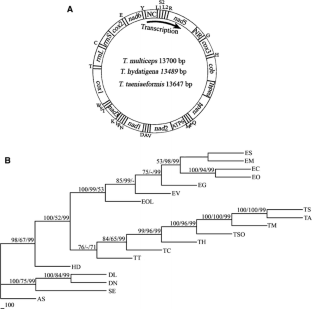
Mitochondrial (mt) genome sequences provide useful markers for investigating population genetic structures, systematics and phylogenetics of organisms. Although Taenia multiceps, T. hydatigena, and T. taeniaeformis are common taeniid tapeworms of ruminants, pigs, dogs, or cats, causing significant economic losses, no published study on their mt genomes is available. The complete mt genomes of T. multiceps, T. hydatigena, and T. taeniaeformis were amplified in two overlapping fragments and then sequenced. The sizes of the entire mt genome were 13700 bp for T. multiceps, 13489 bp for T. hydatigena, and 13647 bp for T. taeniaeformis. Each of the three genomes contains 36 genes, consisting of 12 genes for proteins, 2 genes for rRNA, and 22 genes for tRNA, which are the same as the mt genomes of all other cestode species studied to date. All genes are transcribed in the same direction and have a nucleotide composition high in A and T. The contents of A+T of the complete genomes are 71.3% for T. multiceps, 70.8% for T. hydatigena, and 73.0% for T. taeniaeformis. The AT bias had a significant effect on both the codon usage pattern and amino acid composition of proteins. T. multiceps and T. hydatigena had two noncoding regions, but T. taeniaeformis had only one. Phylogenetic analyses based on concatenated amino acid sequences of 12 protein-coding genes revealed that T. multiceps, T. hydatigena, and T. taeniaeformis were more closely related to the other members of the Taenia genus, consistent with results of previous morphological and molecular studies. The present study determined the complete mt genome sequences for three Taenia species of animal and human health significance, providing useful markers for studying the systematics, population genetics, and molecular epidemiology of these cestode parasites of animals and humans.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Starting from 10 chapters or articles per month
- Access and download chapters and articles from more than 300k books and 2,500 journals
- Cancel anytime View plans
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Fig. 1
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
_atp_6 and _atp_8:
ATPase subunits 6 and 8
bp:
Base pair (s)
_cox_1-3:
Cytochrome c oxidase subunits I–III
_cyt_b:
Cytochrome b
mtDNA:
Mitochondrial DNA
_nad_1–6 and _nad_4L:
NADH dehydrogenase subunits 1–6 and 4L
_rrn_S and _rrn_L:
Small and large subunits ribosomal RNA
tRNA:
Transfer RNA
References
- Boore JL (1999) Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 27:1767–1780
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Yu Z, Wei Z, Kong X et al (2008) Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of oyster _Crassostrea hongkongensis_-a case of “Tandem duplication-random loss” for genome rearrangement in Crassostrea? BMC Genomics 9:e477
Article Google Scholar - Wolstenholme DR (1992) Animal mitochondrial DNA, structure and evolution. Int Rev Cytol 141:173–216
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Hua J, Li M, Dong P et al (2009) The mitochondrial genome of Protohermes concolorus Yang et Yang 1988 (Insecta: Megaloptera: Corydalidae). Mol Biol Rep 36:1757–1765
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Zhang X, Yue B, Jiang W et al (2009) The complete mitochondrial genome of rock carp Procypris rabaudi (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) and phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Rep 36:981–991
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Ki JS, Hwang DS, Park TJ et al (2010) A comparative analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of the Eurasian otter Lutra lutra (Carnivora; Mustelidae). Mol Biol Rep 37:1943–1955
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Shen X, Wang H, Ren J et al (2010) The mitochondrial genome of Euphausia superba (Prydz Bay) (Crustacea: Malacostraca: Euphausiacea) reveals a novel gene arrangement and potential molecular markers. Mol Biol Rep 37:771–784
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Wei SJ, Tang P, Zheng LH et al (2010) The complete mitochondrial genome of Evania appendigaster (Hymenoptera: Evaniidae) has low A + T content and a long intergenic spacer between atp8 and atp6. Mol Biol Rep 37:1931–1942
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Gauci C, Vural G, Oncel T et al (2008) Vaccination with recombinant oncosphere antigens reduces the susceptibility of sheep to infection with Taenia multiceps. Int J Parasitol 38:1041–1050
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Sissay MM, Uggla A, Waller PJ (2008) Prevalence and seasonal incidence of larval and adult cestode infections of sheep and goats in eastern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 40:387–394
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Ngowi HA, Kassuku AA, Maeda GE et al (2004) A slaughter slab survey for extra-intestinal porcine helminth infections in Northern Tanzania. Trop Anim Health Prod 36:335–340
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Dalimi A, Sattari A, Motamedi G (2006) A study on intestinal helminthes of dogs, foxes and jackals in the western part of Iran. Vet Parasitol 142:129–133
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Wang CR, Qiu JH, Zhao JP et al (2006) Prevalence of helminthes in adult dogs in Heilongjiang Province, the People’s Republic of China. Parasitol Res 99:627–630
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - El-Shehabi FS, Abdel-Hafez SK, Kamhawi SA (1999) Prevalence of intestinal helminths of dogs and foxes from Jordan. Parasitol Res 85:928–934
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Dai RS, Li ZY, Li F et al (2009) Severe infection of adult dogs with helminths in Hunan Province, China poses significant public health concerns. Vet Parasitol 160:348–350
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Benifla M, Barrelly R, Shelef I et al (2007) Huge hemispheric intraparenchymal cyst caused by Taenia multiceps in a child. Case report. J Neurosurg 107:S511–S514
Google Scholar - Ekanayake S, Warnasuriya ND, Samarakoon PS et al (1999) An unusual ‘infection’ of a child in Sri Lanka, with Taenia taeniaeformis of the cat. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 93:869–873
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Nakao M, Abmed D, Yamasaki H et al (2007) Mitochondrial genomes of the human broad tapeworms Diphyllobothrium latum and Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae). Parasitol Res 101:233–236
Article PubMed Google Scholar - von Nickisch-Rosenegk M, Brown WM, Boore JL (2001) Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta: gene arrangements indicate that Platyhelminths are Eutrochozoans. Mol Biol Evol 18:721–730
Google Scholar - Nakao M, McManus DP, Schantz PM et al (2007) A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes. Parasitology 134:713–722
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Jeon HK, Eom KS (2006) Taenia asiatica and Taenia saginata: Genetic divergence estimated from their mitochondrial genomes. Exp Parasitol 113:58–61
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Nakao M, Sako Y, Ito A (2003) The mitochondrial genome of the tapeworm Taenia solium: a finding of the abbreviated stop codon U. J Parasitol 89:633–635
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Yang YR, Rosenzvit MC, Zhang LH et al (2005) Molecular study of Echinococcus in west-central China. Parasitology 131:547–555
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Nakao M, Yokoyama N, Sako Y et al (2002) The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the cestode Echinococcus multilocularis (Cyclophyllidea: Taeniidae). Mitochondrion 1:497–509
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Jeon H-K, Kim K-H, Eom KS (2007) Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Taenia saginata: comparison with T. solium and T. asiatica. Parasitol Int 56:243–246
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Schmidt GD (1986) Handbook of tapeworm identification. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Google Scholar - Gasser RB, Zhu X, Woods W (1999) Genotyping Taenia tapeworms by single-strand conformation polymorphism of mitochondrial DNA. Electrophoresis 20:2834–2837
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Gasser RB, Zhu X, McManus DP (1999) NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I sequences compared for members of the genus Taenia (Cestoda). Int J Parasitol 29:1965–1970
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP (1992) Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:165–173
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F et al (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Article Google Scholar - Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Felsenstein J (1995) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), version 3. 57c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Google Scholar - Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M et al (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Strimmer K, Haeseler AV (1996) Quartet puzzling: A quartet maximum likelihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol Biol Evol 13:964–969
CAS Google Scholar - Asakawa S, Himeno H, Miura K et al (1995) Nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the starfish Asterina pectinifera mitochondrial genome. Genetics 140:1047–1060
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Mayta H, Talley A, Gilman RH et al (2000) Differentiating Taenia solium and Taenia saginata infections by simple Hematoxylin-Eosin staining and PCR-restriction enzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol 38:133–137
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Chapman A, Vallejo V, Mossie KG et al (1995) Isolation and characterization of species-specific DNA probes from Taenia solium and Taenia saginata and their use in an egg detection assay. J Clin Microbiol 33:1283–1288
PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Xiao N, Qiu J, Nakao M et al (2005) Echinococcus shiquicus n. sp., a taeniid cestode from Tibetan fox and plateau pika in China. Int J Parasitol 35:693–701
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar - Okamoto M, Nakao M, Blair D et al (2010) Evidence of hybridization between Taenia saginata and Taenia asiatica. Parasitol Int 59:70–74
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Key Laboratory of Veterinary Parasitology of Gansu Province, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, CAAS, Lanzhou, Gansu Province, 730046, People’s Republic of China
Guo-Hua Liu, Hui-Qun Song & Xing-Quan Zhu - Laboratory of Parasitology, College of Veterinary Medicine, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510642, People’s Republic of China
Rui-Qing Lin & Zi-Guo Yuan - Department of Infectious Diseases, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510630, People’s Republic of China
Kou-Xing Zhang - Department of Veterinary Medicine, Agricultural College, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, 524088, People’s Republic of China
Ming-Wei Li - Laboratory of Parasitology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, Hunan, 410128, People’s Republic of China
Guo-Hua Liu, Wei Liu & Yi Liu - College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A & F University, Yangling, Shaanxi, 712100, People’s Republic of China
Guang-Hui Zhao
Authors
- Guo-Hua Liu
- Rui-Qing Lin
- Ming-Wei Li
- Wei Liu
- Yi Liu
- Zi-Guo Yuan
- Hui-Qun Song
- Guang-Hui Zhao
- Kou-Xing Zhang
- Xing-Quan Zhu
Corresponding authors
Correspondence toKou-Xing Zhang or Xing-Quan Zhu.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, GH., Lin, RQ., Li, MW. et al. The complete mitochondrial genomes of three cestode species of Taenia infecting animals and humans.Mol Biol Rep 38, 2249–2256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0355-0
- Received: 31 January 2010
- Accepted: 16 September 2010
- Published: 05 October 2010
- Issue date: April 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0355-0