Kinase regulation in inflammatory response (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 27 July 2000
Signalling pathways
Nature volume 406, pages 367–368 (2000)Cite this article
- 701 Accesses
- 129 Citations
- 3 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
The transcription factor NF-κB is a pivotal regulator of innate immune responses, whose activity is rapidly induced by proinflammatory stimuli, most notably the tumour-necrosis factor TNFα and interleukin-1, viruses, and components of bacterial cell walls[1](/articles/35019154#ref-CR1 "Rothwarf, D. M. & Karin, M. The NF-κ B Activation Pathway: A Paradigm in Information Transfer from Membrane to Nucleus http://www.stke.org/cgi/content/fullOC_sigtrans;1999/5/re1
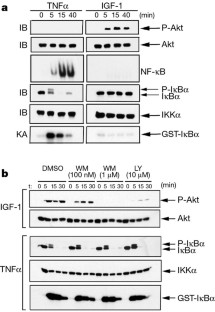
(1999)."). In addition, NF-κB protects cells from the induction of programmed cell death by pro-apoptotic stimuli such as TNFα (refs [2](/articles/35019154#ref-CR2 "Beg, A. A. & Baltimore, D. Science 274, 782–784 (1996)."),[ 3](/articles/35019154#ref-CR3 "Liu, Z.-G, Hu, H., Goeddel, D. V. & Karin, M. Cell 87, 565–576 (1996).")). Another important anti-apoptotic signal-transducing protein is the protein kinase Akt (also known as protein kinase B), whose activity is strongly stimulated by growth factors[4](/articles/35019154#ref-CR4 "Hemmings, B. A. Science 275, 628–630 ( 1997)."). Ozes _et al_.[5](/articles/35019154#ref-CR5 "Ozes, O. N. et al. Nature 401, 82–85 (1999).") have suggested that Akt is involved in the TNFα-mediated activation of NF-κB[5](/articles/35019154#ref-CR5 "Ozes, O. N. et al. Nature 401, 82–85 (1999)."), implying that some of the anti-apoptotic activity of Akt may be mediated through NF-κB. However, we have failed to detect any involvement of Akt in the signalling pathway through which TNFα leads to NF-κB activation.This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Akt is not involved in IKK activation.
Similar content being viewed by others

NF-κB in inflammation and cancer
Article Open access 25 June 2025
References
- Rothwarf, D. M. & Karin, M. The NF-κ B Activation Pathway: A Paradigm in Information Transfer from Membrane to Nucleus http://www.stke.org/cgi/content/fullOC_sigtrans;1999/5/re1 (1999).
- Beg, A. A. & Baltimore, D. Science 274, 782–784 (1996).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Liu, Z.-G, Hu, H., Goeddel, D. V. & Karin, M. Cell 87, 565–576 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hemmings, B. A. Science 275, 628–630 ( 1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ozes, O. N. et al. Nature 401, 82–85 (1999).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Li, Q., Van Antwerp, D., Mercurio, F., Lee, K.-F & Verma, I. M. Science 284, 321–325 (1999).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Hu, Y. et al. Science 284, 316–320 (1999).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Takeda, K. et al. Science 284, 313–316 (1999).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Delhase, M., Hayakawa, M., Chen, Y. & Karin, M. Science 284, 309–313 (1999).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Tojima, Y. et al. Nature 404, 778–782 (2000).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Sizemore, N., Leung, S. & Stark, G. R. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 4798– 4805 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Madrid, L. V. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 1626– 1638 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Laboratory of Gene Regulation and Signal Transduction, University of California at San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, 92093-0636, California, USA
Mireille Delhase, Nanxin Li & Michael Karin
Authors
- Mireille Delhase
- Nanxin Li
- Michael Karin
Corresponding author
Correspondence toMichael Karin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delhase, M., Li, N. & Karin, M. Kinase regulation in inflammatory response .Nature 406, 367–368 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35019154
- Issue Date: 27 July 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35019154