Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells (original) (raw)
- Scientific Correspondence
- Published: 27 November 1997
- Martin Herrmann1,
- Edith A. Roth1,
- Christian Stach1,
- Joachim R. Kalden1 &
- …
- Irute Girkontaite2
Nature volume 390, pages 350–351 (1997)Cite this article
- 6983 Accesses
- 1496 Citations
- 12 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
Apoptotic cell death is important in the development and homeostasis of multicellular organisms1 and is a highly controlled means of eliminating dangerous, damaged or unnecessary cells without causing an inflammatory response or tissue damage1,2. We now show that the presence of apoptotic cells during monocyte activation increases their secretion of the anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL-10) and decreases secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1 and IL-12. This may inhibit inflammation and contribute to impaired cell-mediated immunity in conditions associated with increased apoptosis, such as viral infections, pregnancy, cancer and exposure to radiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
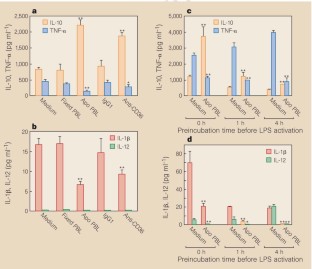
Figure 1: Modulation of cytokine secretion in LPS-activated PBMC and monocytes by apoptotic cells and anti-CD36 antibodies.
References
- Vaux, D. L. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 786–789 (1993).
Google Scholar - Savill, J., Facok, V., Henson, P. & Haslett, C. Immunol. Today 14, 131–136 (1993).
Google Scholar - Abel, E. A. Dermatol. Clinics 13, 841–849 (1995).
Google Scholar - Trott, K. . Strahlenther. Onkol. 170, 1–12 (1994).
Google Scholar - Savill, J., Hogg, N., Ren, Y. & Haslett, C. J. Clin. Invest. 90, 1513–1522 (1992).
Google Scholar - Paul, W. E. & Seder, R. A. Cell 76, 241–251 (1994).
Google Scholar - Mosmann, T. R. Adv. Immunol. 56, 1–26 (1994).
Google Scholar - Kang, K., Hammerberger, C., Meunier, L. & Cooper, K. D. J. Immunol. 153, 5256–5264 (1994).
Google Scholar - Meunier, L., Bata-Csorgo, Z. & Cooper, K. D. J. Invest. Dermatol. 105, 782–788 (1995).
Google Scholar - Parr, E. L., Tung, H. N. & Parr, M. B. Biol. Reprod. 36, 211–225 (1987).
Google Scholar - Nielsen, H. J. Brit. J. Surg. 82, 582–587 (1995).
Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Internal Medicine III, Institute of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, University of Erlangen-Nrnberg, Krankenhausstrasse 12, D-91054, Erlangen, Germany
Reinhard E. Voll, Martin Herrmann, Edith A. Roth, Christian Stach & Joachim R. Kalden - Institute of Experimental Medicine and Connective Tissue Research, University of Erlangen-Nrnberg, Schwabachanlage 10, D-91054, Erlangen, Germany
Irute Girkontaite
Authors
- Reinhard E. Voll
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Martin Herrmann
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Edith A. Roth
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Christian Stach
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Joachim R. Kalden
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Irute Girkontaite
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voll, R., Herrmann, M., Roth, E. et al. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells.Nature 390, 350–351 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/37022
- Issue Date: 27 November 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/37022