Bacterial photosynthesis genes in a virus (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 14 August 2003
Marine ecosystems
Nature volume 424, page 741 (2003)Cite this article
- 7362 Accesses
- 405 Citations
- 24 Altmetric
- Metrics details
A bacteriophage may protect itself and its host against a deadly effect of bright sunlight.
Abstract
Cyanobacteria contribute to the overall photosynthetic production of oxygen in the oceans, but they are susceptible to infection by viruses and also to photo-inhibition when sunlight is too intense. Here we show that the genomic sequence of one such virus, a bacteriophage known as S-PM2, encodes the D1 and D2 proteins that are key components of one of the photosynthetic reaction centres (photosystem II, PSII), which are crucial sites of damage in photo-inhibition. The presence of this virus, and others like it, in the ocean may ensure that photo-inhibition is prevented in infected cells, allowing photosynthesis to continue and therefore provide the energy needed by the virus for its replication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: The bacteriophage S-PM2 (here artificially coloured blue), which infects marine cyanobacteria.
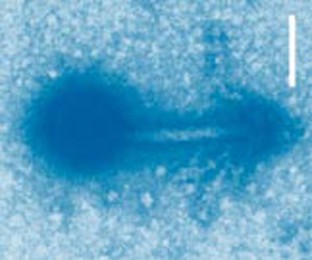
REF. 6
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Partensky, F., Blanchot, J. & Vaulot, D. in Marine Cyanobacteria (eds Charpy, L. & Larkum, A. W. D.) Vol. 19, 457–475 (Institut Océanographique, Monaco, 1999).
Google Scholar - Piazena, H., Perez-Rodrigues, E., Häder, D.-P. & Lopez-Figueroa, F. Deep Sea Res. II 49, 3513–3528 (2002).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Aro, E. M., Virgin, I. & Andersson, B. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1143, 113–134 (1993).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Fuhrman, J. A. Nature 399, 541–548 (1999).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Wilson, W. H., Joint, I. R., Carr, N. G. & Mann, N. H. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 3736–3743 (1993).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Hambly, E. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11411–11416 (2001).
Article CAS ADS Google Scholar - Deshpande, N. N., Bao, Y. & Herrin, D. L. RNA 3, 37–48 (1997).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Seaton, G. G. R., Hurry, V. M. & Rohozinsky, J. FEBS Lett. 389, 319–323 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Biological Sciences, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL, UK
Nicholas H. Mann, Annabel Cook, Andrew Millard, Shaun Bailey & Martha Clokie
Authors
- Nicholas H. Mann
- Annabel Cook
- Andrew Millard
- Shaun Bailey
- Martha Clokie
Corresponding author
Correspondence toNicholas H. Mann.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mann, N., Cook, A., Millard, A. et al. Bacterial photosynthesis genes in a virus.Nature 424, 741 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/424741a
- Issue Date: 14 August 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/424741a