Ibuprofen, inflammation and Alzheimer disease (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: September 2000
Nature Medicine volume 6, pages 973–974 (2000)Cite this article
- 659 Accesses
- 53 Citations
- 3 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Mounting evidence suggests that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be useful in reducing the risk of Alzheimer disease. After much study, the mechanism by which these drugs reduce the amyloid deposition associated with the disease is still open to speculation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
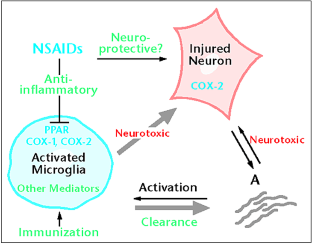
Figure 1: Potential effects of ibuprofen on AD-type pathology.
References
- Akiyama, H. et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroinflammation working group. Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lim, G.P. et al. Ibuprofen suppresses plaque pathology and inflammation in a mouse model for Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 20, 5709–5714 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kisilevsky, R. & Fraser, P. E. Aβ amyloidogenesis: unique, or variation on a systemic theme? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32, 361–404 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Younkin, S.G. Evidence that Aβ42 is the real culprit in Alzheimer's disease. Ann. Neurol. 37, 287–288 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Yankner, B.A. Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 16, 921–932 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Selkoe, D.J. Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 399 (Suppl), A23–31 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kaufmann, W.E., Andreasson, K.I., Isakson, P.C. & Worley, P.F. Cyclooxygenases and the central nervous system. Prostaglandins 54, 601–624 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lehmann, J.M., Lenhard, J.M., Oliver, B.B., Ringold, G.M. & Kliewer, S.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 3406–3410 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Mucke, L. et al. High-level neuronal expression of Aβ1-42 in wild-type human amyloid protein precursor transgenic mice: synaptotoxicity without plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 20, 4050–4058 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bales, K.R. et al. Lack of apolipoprotein E dramatically reduces amyloid β-peptide deposition. Nature Genet. 17, 263–264 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Yan, S.D., Roher, A., Schmidt, A.M. & Stern, D.M. Cellular cofactors for amyloid β-peptide-induced cell stress. Moving from cell culture to in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 155, 1403–1411 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Schenk, D. et al. Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400, 173–177 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Flaris, N.A., Densmore, T.L., Molleston, M.C. & Hickey, W.F. Characterization of microglia and macrophages in the central nervous system of rats: definition of the differential expression of molecules using standard and novel monoclonal antibodies in the normal CNS and in four models of parenchymal reaction. Glia 7, 34–40 (1993).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hsia, A. et al. Plaque-independent disruption of neural circuits in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 3228–3233 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lue, L.-F. et al. Soluble amyloid β peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 155, 853–862 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease and Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, 94141, California
Tony Wyss-Coray & Lennart Mucke
Authors
- Tony Wyss-Coray
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Lennart Mucke
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wyss-Coray, T., Mucke, L. Ibuprofen, inflammation and Alzheimer disease.Nat Med 6, 973–974 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/79661
- Issue Date: September 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/79661