Mutations in CAV3 cause mechanical hyperirritability of skeletal muscle in rippling muscle disease (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: July 2001
- Benedikt G. H. Schoser2,3 na1,
- Dagmar Kasper2,
- Kenneth Ricker4,
- Alfredo Ramírez1,
- Valentin Stein2,
- Torberg Torbergsen5,
- Young-Ae Lee6,
- Markus M. Nöthen1 nAff10,
- Thomas F. Wienker7,
- Jean-Pierre Malin8,
- Peter Propping1,
- André Reis6,
- Wilhelm Mortier9,
- Thomas J. Jentsch2,
- Matthias Vorgerd8 &
- …
- Christian Kubisch1
Nature Genetics volume 28, pages 218–219 (2001)Cite this article
- 891 Accesses
- 150 Citations
- 4 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
Hereditary rippling muscle disease (RMD) is an autosomal dominant human disorder characterized by mechanically triggered contractions of skeletal muscle1,2,3,4. Genome-wide linkage analysis has identified an RMD locus on chromosome 3p25. We found missense mutations in positional candidate CAV3 (encoding caveolin 3; ref. 5) in all five families analyzed. Mutations in CAV3 have also been described in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1C (LGMD1C; refs. 6,7), demonstrating the allelism of dystrophic and non-dystrophic muscle diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
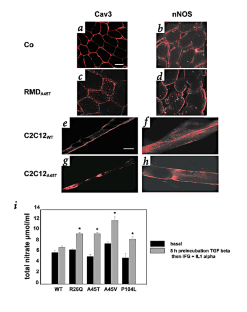
Figure 1: Expression of caveodin 3 and nNOS, and NO stimulation assay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Torbergsen, T. Acta Neurol. Scand. 51, 225–232 (1975).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ricker, K., Moxley, R.T. & Rohkamm, R. Arch. Neurol. 46, 405–408 (1989).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Stephan, D.A. et al. Neurology 44, 1915–1920.
- Vorgerd, M. et al. Neurology 52, 1453–1459 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Tang, Z. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2255–2261 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Minetti, C. et al. Nature Genet. 18, 365–368 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Herrmann, R. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 2335–2340 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Carbone, I. et al. Neurology 54, 1373–1376 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Galbiati, F., Volont, D., Minetti, C., Chu, J.B. & Lisanti, M.P. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25632–25641 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Michel, T. & Feron, O. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2146–2152 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Stamler, J.S. & Meissner, G. Physiol. Rev. 81, 209–237 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hagiwara, Y. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 3047–3054 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Sunada, Y. et al. T Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 173–178 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Williams, G., Becker, L., Bryant, D., Willis, S. & Giroir, B.P. Am. J. Physiol. 270, R145–R152 (1996).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Tidball, J.G. et al. Am. J. Physiol. 275, C260–C266 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Author notes
- Markus M. Nöthen
Present address: Department of Medical Genetics, University of Antwerp, Belgium - Regina C. Betz and Benedikt G. H. Schoser: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
- Institut für Humangenetik, Universität Bonn, Wilhelmstrasse 31, Bonn, D-53111, Germany
Regina C. Betz, Alfredo Ramírez, Markus M. Nöthen, Peter Propping & Christian Kubisch - Zentrum für Molekulare Neurobiologie, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Benedikt G. H. Schoser, Dagmar Kasper, Valentin Stein & Thomas J. Jentsch - Neurologische Klinik, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Benedikt G. H. Schoser - Neurologische Klinik, Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
Kenneth Ricker - Department of Neurology, University Hospital Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway
Torberg Torbergsen - Gene Mapping Center, Max-Delbrück-Centrum, Berlin, Germany
Young-Ae Lee & André Reis - Institut für Medizinische Biometrie, Informatik und Epidemiologie, Universität Bonn, Bonn, Germany
Thomas F. Wienker - Neurologische, Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany
Jean-Pierre Malin & Matthias Vorgerd - Pädiatrische Klinik, Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany
Wilhelm Mortier
Authors
- Regina C. Betz
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Benedikt G. H. Schoser
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Dagmar Kasper
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Kenneth Ricker
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Alfredo Ramírez
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Valentin Stein
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Torberg Torbergsen
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Young-Ae Lee
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Markus M. Nöthen
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Thomas F. Wienker
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Jean-Pierre Malin
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Peter Propping
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - André Reis
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Wilhelm Mortier
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Thomas J. Jentsch
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Matthias Vorgerd
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Christian Kubisch
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toChristian Kubisch.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Betz, R., Schoser, B., Kasper, D. et al. Mutations in CAV3 cause mechanical hyperirritability of skeletal muscle in rippling muscle disease.Nat Genet 28, 218–219 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/90050
- Received: 02 March 2001
- Accepted: 29 May 2001
- Issue Date: July 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/90050