Flagellar motility is required for the viability of the bloodstream trypanosome (original) (raw)
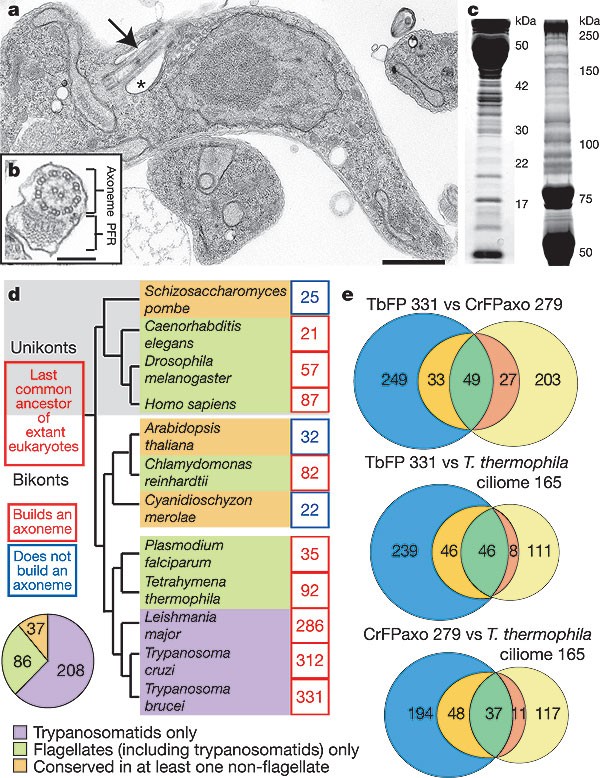
Flagellum-mediated migration between the gut and salivary glands of its tsetse fly vector is essential for progression of the trypanosome life cycle. However, the necessity for motility in an extracellular bloodstream-form trypanosome is unclear. In both forms, a single attached flagellum emerges from a posterior flagellar pocket (Fig. 1a) and comprises a membrane-bound axoneme and associated paraflagellar rod (PFR; Fig 1b). We isolated the structural axoneme and associated PFR and basal body from procyclic trypanosomes by a well-characterized procedure of detergent and high-salt treatment4. Bands and spots were cut from one- (Fig. 1c) and two-dimensional gels and digested with trypsin, and the resulting peptides analysed by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Bands and spots excised from ten representative gels were analysed, resulting in the identification of 522 nonredundant proteins.
Figure 1: The T. brucei flagellar proteome.
a, Transmission electron micrograph showing the flagellum (arrow) and flagellar pocket (asterisk). b, The 9 + 2 axoneme and the PFR. c, One-dimensional electrophoretic separation of isolated flagella. d, Distribution of TbFP protein homologues. e, Comparison of the T. brucei, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (CrFPaxo) and T. thermophila flagellar proteomes. For each comparison, green indicates present in both; orange/red indicates present in opposing genome but not opposing proteome; blue/yellow indicates no homologue in opposing genome. Homology determined by alignment to each genome with reciprocal alignment by BLASTP. Scale bars, 1 µm (a); 200 nm (b).
Further manual mass spectrometric validation confirmed 380 proteins (see Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Fig. 1 for peptide numbers and coverage). Highly basic proteins are known to contaminate microtubule preparations owing to charge interactions4, and we noted some highly basic ribosomal proteins as recognizable contaminants. To limit contamination, we filtered the data by using an isolectric point (pI) value of 10.2 as a cut-off (the pI of the most acidic ribosomal protein), and placed 49 proteins (30 of which were ribosomal proteins) in a separate pool undoubtedly containing some genuine flagella components (for example, TbDIP13). The remaining 331 proteins constitute a T. brucei flagellum proteome (TbFP) characterized by both the inclusion of many known flagellar proteins and a lack of proteins from other subcellular compartments.
We subjected the TbFP to an in silico screen, testing which of these 331 proteins (and the pI-filtered set) were encoded in genomes of flagellated and non-flagellated eukaryotes (Supplementary Fig. 1). The TbFP is characterized by the absence of homologues in the genomes of non-flagellated eukaryotes (land plants, fungi and red algae; Fig. 1d). Shared components, such as α- or β-tubulin, are expected. We found that many TbFP proteins have homologues in the related trypanosomatid parasites Trypanosoma cruzi (312) and Leishmania major (286). Conservation of homologues between trypanosomatids and other flagellates reflects known structural differences among flagella of evolutionarily divergent organisms, being highest in Tetrahymena, human and Chlamydomonas (Fig. 1d). We found a much reduced proportion of homologues shared with Plasmodium, Caenorhabditis and Drosophila, which build motile or sensory cilia that are divergent in aspects of axoneme or basal body structure or formation5. We found that 208 TbFP proteins (Fig. 1d) are trypanosomatid-specific and probably represent organism-specific flagellar structures and functions. Although these most obviously include the PFR, some are likely to be axonemal.
Several studies have sought to identify components of the eukaryotic flagellum by proteomic6,7,8,9 or bioinformatic10,11 strategies. Although highly informative, bioinformatic and comparative genomic approaches exclude genuine conserved flagella components that have homologues and orthologues in non-flagellates. Similarly, occurrence of a protein in proteomes reflects the biochemical nature of the purified material. The TbFP, the Tetrahymena thermophila ciliome9 and the axonemal fraction of the Chlamydomonas flagellar proteome8 are data sets derived from comparable preparations of insoluble flagellar architectures, with shared and organism-specific structures. To carry out a meta-analysis of these three data sets (Fig. 1e), we devised a stringent reciprocal BLASTP protocol that necessitated reanalysis of each data set to acquire the most current gene models available. After unification by applying the pI filter to all data sets, we undertook three reciprocal pairwise comparisons. We found that the TbFP contains the largest number of proteins in any of the three data sets. The presence of the PFR, an extra-axonemal, trypanosome-specific structure might explain the large number of proteins not encoded in the genomes of the other two organisms (indeed, the TbFP contains all of the known PFR proteins). However, the Chlamydomonas and Tetrahymena pairwise axoneme-only comparisons revealed correspondingly large cohorts not represented in the genome of the opposing organism. Thus, the structural homogeneity of the 9 + 2 axoneme seems to be dependent on a relatively few evolutionarily conserved proteins and masks considerable organism-specific elaborations that go beyond the presence of obvious extra-axonemal structures.
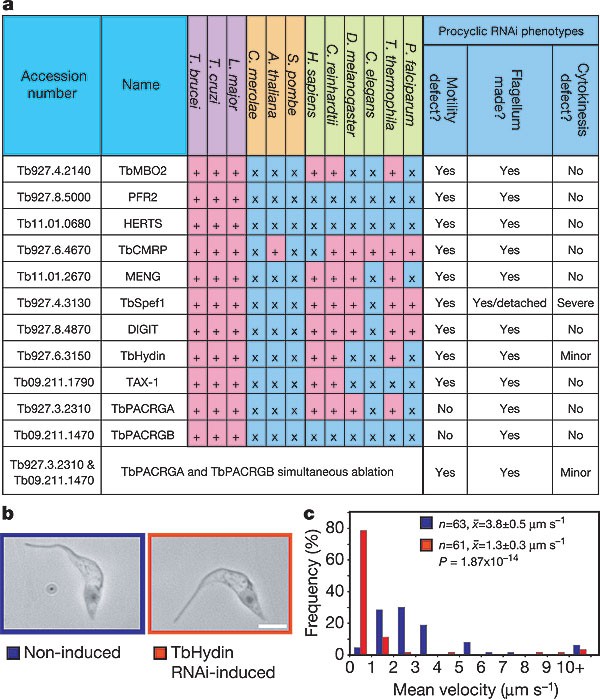
Present in the conserved subset are proteins with implications for human inherited diseases. Ciliary diseases are characterized by clinical presentations such as retinal degeneration, primary ciliary dyskinesia, hydrocephalus, polycystic kidney disease and polydactyly1. In addition to all three axonemal dyneins known to cause primary ciliary dyskinesia12, interrogation of the TbFP identified homologues of a further seven proteins directly implicated in diseases of human, mouse or zebrafish (Supplementary Fig. 2a). This list includes Hydin13, PACRG14 and Scorpion15; two of these, TbHydin and TbPACRG, are validated functionally here for the first time to our knowledge. We determined the human chromosomal locus for every homologue represented in the TbFP, which identified 34 genes mapping to 25 loci where diseases with a clinical spectrum suggestive of ciliary dysfunction have been mapped genetically, but where the causal gene has not been identified. We suggest that these 34 genes (Supplementary Fig. 2b) represent candidates underlying syndromes including primary ciliary dyskinesia, polycystic kidney disease, macular and cone-rod dystrophies, retinitis pigmentosa, Rieger and BRESEK (see http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=OMIM for syndrome details).
We subjected the orthologue of the cryptic hydrocephalus-inducing protein Hydin to functional analysis by using inducible RNAi in procyclic trypanosomes. This resulted in a severe motility defect, revealing an impairment of ciliary function as a likely explanation for the aetiology of this disease model (Fig. 2). A further ten TbFP proteins were interrogated by this RNAi approach (Fig. 2a), eight of which (including the trypanosome-specific proteins PFR2 and HERTS) showed a flagellar phenotype on ablation (Fig. 2a). All mutants were viable except one in which flagellar detachment caused pleiotropic effects16. Two genes (TbPACRGA and TbPACRGB) comprise a gene family in T. brucei and gave no phenotype on individual ablation. Simultaneous knockdown, however, produced paralysed flagella, suggesting functional redundancy.
Figure 2: Biological verification of the T. brucei flagellar proteome.
a, Biological validation of the TbFP by RNAi of procyclic trypanosomes, showing phylogenetic distribution and RNAi phenotype. ‘ + ’ indicates presence of homologues; ‘x’ indicates absence of homologues. b, c, Phenotype of T. brucei Hydin (TbHydin). On RNAi induction the flagellum is built (b), but motility is severely compromised in individual cells and the cell population (c). Scale bar, 5 µm (b). Blue indicates non-induced control; red indicates TbHydin RNAi-induced. P value determined by Mann–Whitney _U_-test. Population statistic given as the mean ± s.e.m.
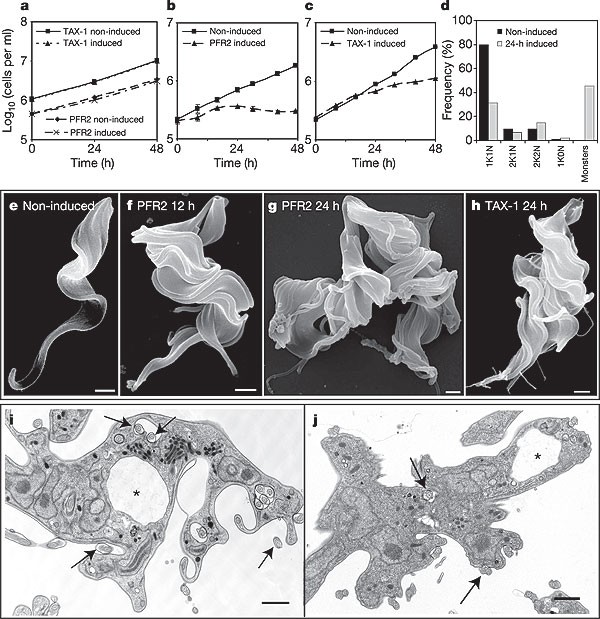
The high success rate of the RNAi interrogation provides experimental evidence for the integrity of the TbFP. These phenotypes extend the catalogue of trypanosome flagellar RNAi mutants, which have all been made in the procyclic form16,17,18,19, and show that motility can be severely compromised while proliferation remains unaffected. We extended our functional interrogation by carrying out RNAi against five proteins in our TbFP validation set in bloodstream-form trypanosomes (Supplementary Fig. 3a). Unexpectedly, we found that all five RNAi analyses resulted in bloodstream-form trypanosomes that did not complete cytokinesis, yielding monstrous cells with an inability to proliferate (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. 3b–h). This striking contrast to the viable RNAi phenotypes produced in procyclic cells is shown in Fig. 3a–c. In each case, RNAi induction led to an inhibition of cytokinesis.
Figure 3: Flagellar motility is essential for bloodstream trypanosomes.
a–c, Ablation of PFR2 and TAX-1 affects growth in bloodstream (b, c), but not procyclic (a), forms. d, Numbers of cells with multiple nuclei and kinetoplasts increase after ablation of TAX-1 in bloodstream forms. e–h, Scanning electron micrograph showing bloodstream-form morphogenesis before (e) and after (f–h) ablation of PFR2 and TAX-1 flagellar proteins. i, j, Transmission electron microscopy analysis of PFR2 (i) and TAX-1 (j) ablation in bloodstream forms. Arrows denote axonemes; asterisks denote flagellar pockets (i, j). Scale bar, 1 µm.
Trypanosomes have one kinetoplast (mitochondrial DNA) and one nucleus (1K1N), and replicate these once during a cell cycle20; on RNAi induction, however, bloodstream cells ceased dividing but continued to progress through the cell cycle. Cells initiated new rounds of S phase and mitosis, leading to large contorted cells containing multiple kinetoplasts and nuclei (Fig. 3d, i, j). At 24 h after induction, the RNAi-induced population of ‘monsters’ contained large numbers of 4K4N and 8K8N cells (Fig. 3d).
Included in the bloodstream RNAi set were newly identified flagellar proteins such as TAX-1, TbPACRGA and DIGIT in addition to an orthologue (TbMBO2) of a Chlamydomonas protein known to regulate motility21. Given the implications of these observations, we tested whether the well-characterized procyclic snl mutant phenotype17,18 (paralysed but viable) of the T. brucei specific PFR2 protein was different in the bloodstream form. We found that this mutant also produced a rapid, lethal and unusual phenotype with production of monstrous cells. Notably, the same construct expressed in procyclic cells reproduced the published paralysed, but viable, phenotype (Fig. 2a).
A very particular phenotype led to the death of bloodstream cells. Uninduced cells had a normal morphology (Fig. 3e), producing a new flagellum during the cell cycle before cytokinesis, with the flagellum emerging from the flagellar pocket and extending along the trypanosome. On RNAi induction, cells produced new flagella but did not complete division and lost all normal morphogenetic axes, becoming monstrously contorted and multiflagellated (Fig. 3f–h). Thin-section electron microscopy showed that the cell periphery was highly convoluted; multiple nuclei were present and some flagella were attached to the outside of the cell, while others were located in a highly enlarged flagellar pocket (Fig. 3i, j and Supplementary Fig. 3b, c, f, g). There were also many flagella with two axonemes, which could be either parallel or antiparallel, indicative of a total loss of morphogenetic patterning (Supplementary Fig. 3d, e). These characteristics are also found in the TbMBO2 and DIGIT phenotypes (Supplementary Fig. 3f, g). Examination of the flagellar pockets indicated that although large they still showed clathrin-coated pits, suggesting that endocytotic processes were operating to some extent (for example, in the TAX-1 phenotype; Supplementary Fig. 3h).
The explanation for the lethal phenotype in bloodstream cells is that cytokinesis fails as a primary event in the absence of correct flagellar motility. Subsequent rounds of the cell cycle compound these events as new flagella and pockets are formed at inappropriate locations. The lack of precise morphogenetic axes in the resulting ‘monstrous cells’ leads to pleiotropic effects compromising membrane–cytoskeletal balance during morphogenesis of the pocket structure. Examination of endocytosis shows that the multiple pockets are active and can facilitate entry of antibodies and lectins. However, there is much variation in their individual capacity for vectorial internalization to nearby endomembrane compartments (Supplementary Fig. 4). An imbalance in the known high flux of endocytosis in the bloodstream form22, coupled with a focus of the secretory pathway on particular pockets in a multiflagellated cell, will lead to the large flagellar pocket phenotype as a secondary event.
In summary, we have shown that flagellum function cannot be compromised and is essential in the bloodstream trypanosome. The severity of the phenotype, its rapid onset, its lethality and its occurrence after the ablation of proteins of diverse function and location in either the axoneme or the trypanosome-specific PFR is highly significant. Coupled with our identification of a set of trypanosome-specific proteins in the TbFP, this suggests that impairment of flagellar function may provide an avenue for disease control in African sleeping sickness.