Amyloid-lowering isocoumarins are not direct inhibitors of γ-secretase (original) (raw)
- Letters to Editor
- Published: 01 May 2002
- Chittaranjan Das1,
- William A. Campbell1,
- W. Taylor Kimberly1,
- Anna Y. Kornilova1,
- Thekla S. Diehl1,
- Wenjuan Ye1,
- Beth L. Ostaszewski1,
- Weiming Xia1,
- Dennis J. Selkoe1 &
- …
- Michael S. Wolfe1
Nature Cell Biology volume 4, pages E110–E111 (2002)Cite this article
- 208 Accesses
- 34 Citations
- Metrics details
To the Editor
The last step in the production of the amyloid-β protein (Aβ), the major protein component of the cerebral plaques of Alzheimer's disease, is proteolysis within the transmembrane region of the Amyloid-β Precursor Protein (APP) by γ-secretase. The Notch receptor (N) is processed in a similar manner as part of a signalling mechanism essential for metazoan development. Missense mutations in the polytopic presenilins, PS1 and PS2, cause Alzheimer's disease and alter the specificity of γ-secretase to increase production of a much more aggregation-prone form of Aβ1. Knockout studies, site-directed mutagenesis, pharmacological profiling, affinity labelling and biochemical isolation all strongly support the hypothesis that γ-secretase is a complex of integral membrane proteins, an aspartyl protease in which the active site resides between the two subunits of a processed form of PS2,3. As a corollary, PS processes both APP and N.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
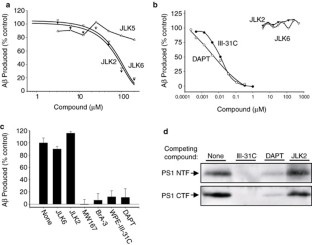
Figure 1: Effect of isocoumarins on γ-secretase and PS.
References
- Hardy, J. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2095–2097 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Esler, W. P. & Wolfe, M. S. Science 293, 1449–1454 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Esler, W. P. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 2720–2725 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Petit, A. et al. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 507–511 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Koo, E. H. & Squazzo, S. L. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 17386–17389 (1994).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Li, Y. M. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6138–6143 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Dovey, H. F. et al. J. Neurochem. 76, 173–181 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Xia, W. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9299–9304 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Li, Y. M. et al. Nature 405, 689–694 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Esler, W. P. et al. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 428–434 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wolfe, M. S. et al. J. Med. Chem. 41, 6–9 (1998)-
Article CAS Google Scholar - Berechid, B. E. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8154–8165 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Center for Neurologic Diseases, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, 77 Avenue Louis Pasteur, Boston, 02115, MA, USA
William P. Esler, Chittaranjan Das, William A. Campbell, W. Taylor Kimberly, Anna Y. Kornilova, Thekla S. Diehl, Wenjuan Ye, Beth L. Ostaszewski, Weiming Xia, Dennis J. Selkoe & Michael S. Wolfe
Authors
- William P. Esler
- Chittaranjan Das
- William A. Campbell
- W. Taylor Kimberly
- Anna Y. Kornilova
- Thekla S. Diehl
- Wenjuan Ye
- Beth L. Ostaszewski
- Weiming Xia
- Dennis J. Selkoe
- Michael S. Wolfe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esler, W., Das, C., Campbell, W. et al. Amyloid-lowering isocoumarins are not direct inhibitors of γ-secretase.Nat Cell Biol 4, E110–E111 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0502-e110b
- Issue date: 01 May 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0502-e110b