Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate regulates the formation of the basolateral plasma membrane in epithelial cells (original) (raw)
- Letter
- Published: 20 August 2006
- Wei Yu1,
- Martin ter Beest1 nAff6,
- Fernando Martin-Belmonte1,
- Arlinet Kierbel3,
- Joanne Engel3,4 &
- …
- Keith Mostov1,5
Nature Cell Biology volume 8, pages 963–970 (2006)Cite this article
- 3354 Accesses
- 4 Altmetric
- Metrics details
A Corrigendum to this article was published on 01 October 2006
Abstract
Polarity is a central feature of eukaryotic cells and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) has a central role in the polarization of neurons and chemotaxing cells. In polarized epithelial cells, PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 is stably localized at the basolateral plasma membrane, but excluded from the apical plasma membrane, as shown by localization of GFP fused to the PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-binding pleckstrin-homology domain of Akt (GFP-PH–Akt), a fusion protein that indicates the location of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3. Here, we ectopically inserted exogenous PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 into the apical plasma membrane of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Within 5 min many cells formed protrusions that extended above the apical surface. These protrusions contained basolateral plasma membrane proteins and excluded apical proteins, indicating that their plasma membrane was transformed from apical to basolateral. Addition of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to the basolateral surface of MDCK cells grown as cysts caused basolateral protrusions. MDCK cells grown in the presence of a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor had abnormally short lateral surfaces, indicating that PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 regulates the formation of the basolateral surface.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Exogenous PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 delivered to the apical surface of MDCK cells induces protrusions.

Figure 2: Endogenous Rac1 and Cdc42 are activated by exogenous PtdIns(3,4,5)P3.
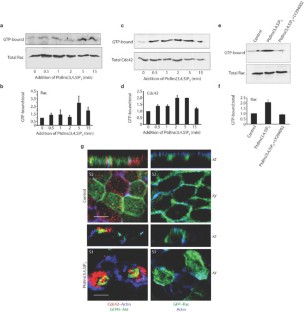
Figure 3: PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 regulates cell polarity.

Figure 4: PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 stimulates transcytosis.
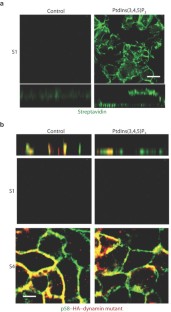
Figure 5: PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 is required for formation and maintenance of the basolateral surface.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Gibson, M. C. & Perrimon, N. Apicobasal polarization: epithelial form and function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 747–752 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Nelson, W. J. Adaptation of core mechanisms to generate cell polarity. Nature 422, 766–774 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Yu, W. et al. β1-integrin orients epithelial polarity via Rac1 and laminin. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 433–445 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wodarz, A. Establishing cell polarity in development. Nature Cell Biol. 4, E39–E44 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ohno, S. Intercellular junctions and cellular polarity: the PAR-aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette playing fundamental roles in cell polarity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 641–648 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Macara, I. G. Par proteins: partners in polarization. Curr. Biol. 14, R160–R162 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Mostov, K., Su, T. & ter Beest, M. Polarized epithelial membrane traffic: conservation and plasticity. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 287–293 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Xu, J. et al. Divergent signals and cytoskeletal assemblies regulate self-organizing polarity in neutrophils. Cell 114, 201–214 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Merlot, S. & Firtel, R. A. Leading the way: Directional sensing through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and other signaling pathways. J. Cell Sci. 116, 3471–3478 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Van Haastert, P. J. & Devreotes, P. N. Chemotaxis: signalling the way forward. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 626–634 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Huang, Y. E. et al. Receptor-mediated regulation of PI3Ks confines PI(3,4,5)P3 to the leading edge of chemotaxing cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 1913–1922 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Meili, R. & Firtel, R. A. Two poles and a compass. Cell 114, 153–156 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Watton, S. J. & Downward, J. Akt/PKB localisation and 3′ phosphoinositide generation at sites of epithelial cell-matrix and cell-cell interaction. Curr. Biol. 9, 433–436 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Yu, W. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor switches orientation of polarity and mode of movement during morphogenesis of multicellular epithelial sructures. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 748–763 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wang, F. et al. Lipid products of PI(3)Ks maintain persistent cell polarity and directed motility in neutrophils. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 513–518 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Weiner, O. D. et al. A PtdInsP(3)- and Rho GTPase-mediated positive feedback loop regulates neutrophil polarity. Nature Cell. Biol. 4, 509–513 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ozaki, S., DeWald, D. B., Shope, J. C., Chen, J. & Prestwich, G. D. Intracellular delivery of phosphoinositides and inositol phosphates using polyamine carriers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11286–11291 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Tian, W., Laffafian, I., Dewitt, S. & Hallett, M. B. Exclusion of exogenous phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate from neutrophil-polarizing pseudopodia: stabilization of the uropod and cell polarity. EMBO Rep. 4, 982–988 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Weiner, O. D. et al. A PtdInsP(3)- and Rho GTPase-mediated positive feedback loop regulates neutrophil polarity. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 509–513 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Etienne-Manneville, S. & Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420, 629–635 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ridley, A. J. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 471–477 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Altschuler, Y. et al. Redundant and distinct functions for dynamin-1 and dynamin-2 isoforms. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1871–1881 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Mostov, K., Apodaca, G., Aroeti, B. & Okamoto, C. Plasma membrane protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 116, 577–583 (1992).
Article CAS Google Scholar - von Stein, W., Ramrath, A., Grimm, A., Muller-Borg, M. & Wodarz, A. Direct association of Bazooka/PAR-3 with the lipid phosphatase PTEN reveals a link between the PAR/aPKC complex and phosphoinositide signaling. Development 132, 1675–1686 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kierbel, A., Gassama-Diagne, A., Mostov, K. & Engel, J. N. The phosphoinositol-3-kinase-protein kinase B/Akt pathway is critical for Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAK internalization. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 2577–2585 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Low, S.-H. et al. Differential localization of syntaxin isoforms in polarized MDCK cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 2007–2018 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Debnath, J., Muthuswamy, S. K. & Brugge, J. S. Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods 30, 256–268 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Apodaca, G., Katz, L. A. & Mostov, K. E. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of IgA in MDCK cells via apical recycling endosomes. J. Cell Biol. 125, 67–86 (1994).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hansen, S. H. et al. Induced expression of Rnd3 is associated with transformation of polarized epithelial cells by the Raf–MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 9364–9375 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lipschutz, J. H. et al. in Current Protocols Cell in Biology (Wiley and Sons.) 15.5 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Matlin, G. Ojakian and B. Stevenson for reagents. We thank H. Bourne, O. Weiner, M. Zegers, P. Brakeman and members of our laboratory for advice and comments on the paper. and D. Mills for help with the manuscript. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants to K.M. and J.E. W.Y. is supported by a fellowship from the National Kidney Foundation. F.M.-B. is supported by the Human Frontiers Science Program (HFSP).
Author information
Author notes
- Martin ter Beest
Present address: The Vontz Center, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, 3125 Eden Avenue, ML0581, Cincinnati, OH 45267-0581, USA
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Anatomy, University of California, San Francisco, 94143, CA, USA
Ama Gassama-Diagne, Wei Yu, Martin ter Beest, Fernando Martin-Belmonte & Keith Mostov - Institut Federatif de Recherche Claude de Preval, IFR30, INSERM Unite 563, Departement Lipoproteines et Mediateurs Lipidiques, Hopital Purpan, Toulouse Cedex, 31059, France
Ama Gassama-Diagne - Departments of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, 94143, CA, USA
Arlinet Kierbel & Joanne Engel - Microbiology and Immunology, University of California, San Francisco, 94143, CA, USA
Joanne Engel - Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of California, San Francisco, 94143, CA, USA
Keith Mostov
Authors
- Ama Gassama-Diagne
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Wei Yu
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Martin ter Beest
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Fernando Martin-Belmonte
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Arlinet Kierbel
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Joanne Engel
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Keith Mostov
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.G. designed, performed and interpreted all of the experiments. W.Y. helped with the design of some experiments. M.t.B. and F.M.-B. made invaluable reagents. A.K. and J.E. helped with the interpretation of data and writing of the paper. K.M. conceived the experiments, helped with interpretation of data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence toAma Gassama-Diagne.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gassama-Diagne, A., Yu, W., ter Beest, M. et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate regulates the formation of the basolateral plasma membrane in epithelial cells.Nat Cell Biol 8, 963–970 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1461
- Received: 24 March 2006
- Accepted: 17 July 2006
- Published: 20 August 2006
- Issue Date: 01 September 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1461