The Many Faces of Sirtuins: Sirtuins and the Warburg effect (original) (raw)
- Between Bedside and Bench
- Published: 07 January 2014
Nature Medicine volume 20, pages 24–25 (2014)Cite this article
- 10k Accesses
- 37 Citations
- 13 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
Metabolic regulators that permit adaptation to changes in caloric intake have been shown to be needed to protect from age-related disorders. Sirtuins play a crucial part in this program, impinging on not only aging but also other diseases. New findings are uncovering the multifaceted activity of sirtuins in living organisms and their effects on healthspan. In 'Bedside to Bench', Leonard Guarente discusses how different sirtuins are hindering cancer metabolism through suppression of the Warburg effect. The apparent antitumor effects of several sirtuins through their regulation of different metabolic pathways suggest therapeutic approaches to induce sirtuin function or that of downstream targets may block cancer growth. In 'Bench to Bedside', Eric Verdin peruses a few studies in different animal models showing that increased amounts of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), a cofactor of sirtuins, may have a positive effect in longevity and span of healthy life, or healthspan, by increasing sirtuin enzymatic activity. Whether harnessing NAD therapeutically is a potential way to extend lifespan and ameliorate diseases is still open to debate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Regulation of the Warburg effect by sirtuins.
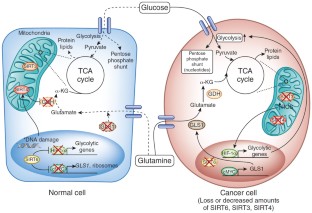
Marina Corral Spence
References
- Warburg, O., Wind, F. & Negelein, E. J. Gen. Physiol. 8, 519–530 (1927).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ward, P.S. & Thompson, C.B. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, a006783 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Guarente, L. Genes Dev. 27, 2072–2085 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Sebastián, C. et al. Cell 151, 1185–1199 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Zhong, L. et al. Cell 140, 280–293 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Haigis, M.C. et al. Cell 126, 941–954 (2006).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Jeong, S.M. et al. Cancer Cell 23, 450–463 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Csibi, A. et al. Cell 153, 840–854 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kim, H.S. et al. Cancer Cell 17, 41–52 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Verdin, E., Hirschey, M.D., Finley, L.W. & Haigis, M.C. Trends Biochem. Sci. 35, 669–675 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bell, E.L., Emerling, B.M., Ricoult, S.J. & Guarente, L. Oncogene 30, 2986–2996 (2011).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Finley, L.W. et al. Cancer Cell 19, 416–428 (2011).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hubbard, B.P. et al. Science 339, 1216–1219 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Feldman, J.L., Baeza, J. & Denu, J.M. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 31350–31356 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wong, K.K., Engelman, J.A. & Cantley, L.C. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 20, 87–90 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Leonard Guarente is at the Department of Biology, Glenn Laboratory for the Science of Aging and Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.,
Leonard Guarente
Corresponding author
Correspondence toLeonard Guarente.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
L.G. has served as a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline and Chronos. He owns stock in Elysium Health and Segterra.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guarente, L. The Many Faces of Sirtuins: Sirtuins and the Warburg effect.Nat Med 20, 24–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3438
- Published: 07 January 2014
- Issue Date: January 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3438