Pharmacological prevention of Parkinson disease in Drosophila (original) (raw)
- Letters to the Editor
- Published: 01 November 2002
Nature Medicine volume 8, pages 1185–1186 (2002)Cite this article
- 2400 Accesses
- 14 Altmetric
- Metrics details
To the editor
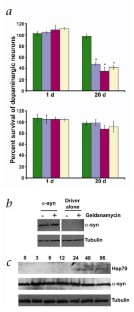
Geldanamycin is a naturally occurring benzoquinone ansamycin that specifically binds to and interferes with the activity of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 (ref. 6), a negative regulator of heat-shock factor7. Treating mammalian cells in culture with geldanamycin activates a stress response8. We hypothesized that feeding flies geldanamycin might protect against α-synuclein toxicity through the modulation of stress response pathways. A concentration of 3 μg/ml geldanamycin effectively inhibits Hsp90 activity in Drosophila9, thus we used this concentration in our study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Geldanamycin treatment prevents dopaminergic cell loss in α-synuclein transgenic flies.
References
- Polymeropoulos, M.H. et al. Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276, 2045–2047 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kruger, R. et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nature Genet. 18, 106–108 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Spillantini, M.G. et al. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Feany, M.B. & Bender, W.W. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 404, 394–398 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Auluck, P.K., Chan, H.Y., Trojanowski, J.Q., Lee, V.M.-Y. & Bonini, N.M. Chaperone suppression of α-synuclein toxicity in a Drosophila model for Parkinson's disease. Science 295, 865–868 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Whitesell, L., Mimnaugh, E.G., De Costa, B., Myers, C.E. & Neckers, L.M. Inhibition of heat shock protein Hsp90-pp60v-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone ansamycins: Essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 8324–8328 (1994).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Zou, J., Guo, Y., Guettouche, T., Smith, D.F. & Voellmy, R. Repression of heat shock transcription factor HSF1 activation by Hsp90 (Hsp90 complex) that forms a stress-sensitive complex with HSF1. Cell 94, 471–480 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Sittler, A. et al. Geldanamycin activates a heat shock response and inhibits huntingtin aggregation in a cell culture model of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 1307–1315 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Rutherford, S.L. & Lindquist, S. Hsp90 as a capacitor for morphological evolution. Nature 396, 336–342 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lang, A.E. & Lozano, A.M. Parkinson's disease. Second of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 1130–1143 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Neuroscience, University of Pennsylvania and University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Pavan K. Auluck & Nancy M. Bonini - Department of Biology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute University of Pennsylvania and University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Nancy M. Bonini
Authors
- Pavan K. Auluck
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Nancy M. Bonini
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toNancy M. Bonini.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auluck, P., Bonini, N. Pharmacological prevention of Parkinson disease in Drosophila.Nat Med 8, 1185–1186 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1102-1185
- Issue Date: 01 November 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1102-1185