Improved whole-chromosome phasing for disease and population genetic studies (original) (raw)
- Correspondence
- Published: 01 January 2013
Nature Methods volume 10, pages 5–6 (2013)Cite this article
- 12k Accesses
- 972 Citations
- 30 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
To the Editor:
Methods that can accurately estimate haplotypes from single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotype data are important because they are widely used in many areas of genetic analysis. Examples include the creation of haplotype reference panels, pre-phasing1 before genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and population genetic analysis. The task is an inverse problem in which we observe a set of SNP genotypes in a sample, typically using a genome-wide SNP microarray, and wish to infer the underlying haplotypes carried by the study individuals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
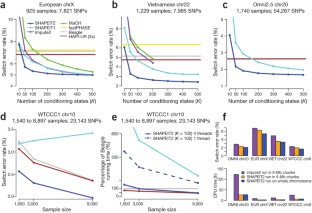
Figure 1: Accuracy and computational performance.
References
- Howie, B. et al. Nat. Genet. 44, 955–959 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Delaneau, O., Marchini, J. & Zagury, J.F. Nat. Methods 9, 179–181 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Howie, B.N., Marchini, J. & Stephens, M. G3 1, 457–470 (2011).
Article Google Scholar - Williams, A.L. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 91, 238–251 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Browning, S.R. & Browning, B.L. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 1084–1097 (2007).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Li, Y. et al. Genet. Epidemiol. 34, 816–834 (2010).
Article Google Scholar - Scheet, P. & Stephens, M. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78, 629–644 (2006).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
J.M. and O.D. acknowledge support from the Medical Research Council (G0801823). O.D. acknowledges support from Peptinov SAS (France). Thanks to B. Howie, C. Churchhouse and J. O'Connell for comments on this paper and to A. Cox (Illumina Cambridge Ltd) for providing the high-coverage trio sequence data set. The Vietnamese cohort was provided by A. Alcais (Institut National de la Santé de la Recherche Médicale, Paris, France) and E. Schurr (McGill Centre for the Study of Host Resistance, Montreal, Canada). This study uses data from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium.
Author information
Author notes
- Jean-Francois Zagury and Jonathan Marchini: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Statistics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Olivier Delaneau & Jonathan Marchini - Chaire de Bioinformatique, Laboratoire Génomique, Bioinformatique, et Applications (EA 4627), Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers, Paris, France
Jean-Francois Zagury - Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Jonathan Marchini
Authors
- Olivier Delaneau
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Jean-Francois Zagury
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Jonathan Marchini
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence toJean-Francois Zagury or Jonathan Marchini.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delaneau, O., Zagury, JF. & Marchini, J. Improved whole-chromosome phasing for disease and population genetic studies.Nat Methods 10, 5–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2307
- Published: 01 January 2013
- Issue Date: January 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2307