Software for bead-based registration of selective plane illumination microscopy data (original) (raw)
- Correspondence
- Published: June 2010
Nature Methods volume 7, pages 418–419 (2010)Cite this article
- 10k Accesses
- 279 Citations
- 40 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
To the Editor:
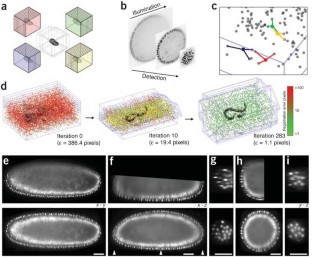
SPIM multiview registration is complicated by degradation of the signal along the illumination as well as detection axes (Fig. 1b), limited overlap between the views, different orientations of the optical sections and development of the specimen during acquisition. We developed a SPIM registration method and implemented it in a plugin for Fiji. The software enables efficient, sample-independent registration of multiview SPIM acquisitions using fluorescent beads in rigid mounting medium as fiduciary markers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
- Seth Donoughe
- , Jordan Hoffmann
- … Cassandra G. Extavour
Nature Communications Open Access 06 July 2022
Detachment mechanism and reduced evaporation of an evaporative NaCl salt crust
- G. Licsandru
- , C. Noiriel
- … M. Prat
Scientific Reports Open Access 06 May 2022
Hand2 delineates mesothelium progenitors and is reactivated in mesothelioma
- Karin D. Prummel
- , Helena L. Crowell
- … Christian Mosimann
Nature Communications Open Access 30 March 2022
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Bead-based registration framework.
References
- Huisken, J., Swoger, J., Del Bene, F., Wittbrodt, J. & Stelzer, E.H. Science 305, 1007–1009 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Huisken, J. & Stainier, D.Y. Development 136, 1963–1975 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lindeberg, T. J. Appl. Stat. 21, 224–270 (1994).
Article Google Scholar - Fischler, M.A. & Bolles, R.C. Commun. ACM 24, 381–395 (1981).
Article Google Scholar - Preibisch, S., Saalfeld, S. & Tomancak, P. Bioinformatics 25, 1463–1465 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Preibisch, S., Rohlfing, T., Hasak M.P. & Tomancak P. SPIE Medical Imaging 2008 (eds., Reinhardt, J.M. & Pluim, J.P.W.) 6914 69140E-69140E-8 (2008).
Google Scholar - Swoger, J. et al. Opt. Express 15, 8029–8042 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank Carl Zeiss Microimaging for access to the SPIM demonstrator; R.K. Ejsmont (Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, Dresden) for His-YFP flies; D. White, E. Dimitrova, M. Sarov and P. Campinho for help with imaging and B. Schmid for help with 3D viewer programming. S.P. and S.S. were supported by a Dresden International Graduate School for Biomedicine and Bioengineering doctorate stipend. J.S. and P.T. acknowledge funding from the Human Frontier Science Program Research grant RGY0084.
Author information
Author notes
- Stephan Preibisch and Stephan Saalfeld: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
- Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, Dresden, Germany
Stephan Preibisch, Stephan Saalfeld, Johannes Schindelin & Pavel Tomancak
Authors
- Stephan Preibisch
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Stephan Saalfeld
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Johannes Schindelin
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Pavel Tomancak
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toPavel Tomancak.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Data (PDF 4604 kb)
Supplementary Software
SPIM registration plugin for Fiji. (ZIP 4350 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Rotation capabilities of the selective plane illumination microscope. (MOV 42 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
Visualization of the global optimization of eight view selective plane illumination microscope acquisition of C. elegans with 40×, 0.8 objective. (MOV 4043 kb)
Supplementary Video 3
Visualization of the global optimization of tiled single-photon confocal acquisition of Drosophila with 40×, 0.8 objective. (MOV 6422 kb)
Supplementary Video 4
Three-dimensional rendering of Drosophila gastrulation time-lapse acquired from seven angles. (MOV 393 kb)
Supplementary Video 5
Three-dimensional rendering of Drosophila embryogenesis time-lapse acquired from five angles. (MOV 5121 kb)
Supplementary Video 6
Three-dimensional rendering of fixed Drosophila reconstructed from multiview spinning disc acquisition. (MOV 1108 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preibisch, S., Saalfeld, S., Schindelin, J. et al. Software for bead-based registration of selective plane illumination microscopy data.Nat Methods 7, 418–419 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0610-418
- Issue Date: June 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0610-418