Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 31 March 2003
- Kathleen Szegda1,
- Gregory Campbell2,
- W. David Martin2 &
- …
- Thomas R. Insel1,3 nAff4
Nature Neuroscience volume 6, pages 445–446 (2003)Cite this article
- 2831 Accesses
- 19 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
Inbred mouse strains are classically used to search for the genes associated with behavioral traits, including emotionality. To distinguish genetic and environmental contributions to the expression of adult behavior in mice, we investigated the effects of prenatal (embryo transfer) and postnatal (cross-fostering) environments in two strains of inbred mice with profound and reliable differences in behavior1. Here we report that strain-related behavioral differences may result from environmental factors during development rather than genetic differences between the offspring.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
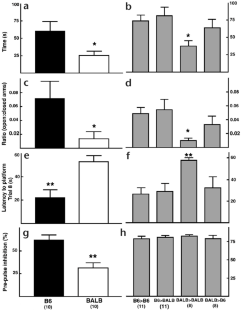
Figure 1: Open-field, elevated-plus maze, water-maze learning and pre-pulse inhibition behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Bucan, M. & Abel, T. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3, 114–123 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Crabbe, J.C., Wahlsten, D. & Dudek, B.C. Science 284, 1670–1672 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Dulawa, S.C. & Geyer, M.A. Neuropharmacology 39, 2170–2179 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Paylor, R. & Crawley, J.N. Psychopharmacology 132, 169–180 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - DeFries, J.C., Thomas, E.A., Hegmann, J.P. & Weir, M.W. Psychon. Sci. 8, 207–208 (1967).
Article Google Scholar - Carlier, M., Roubertoux, P. & Cohen-Salmon, C. Physiol. Behav. 30, 837–844 (1983).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Rhees, B.K., Ernst, C.A., Miao, C.H. & Atchley, W.R. Genetics 153, 905–917 (1999).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Le Roy, I., Carlier, M. & Roubertoux, P.L. Behav. Brain Res. 125, 57–64 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Brown, R.E., Mathieson, W.B., Stapleton, J. & Neumann, P.E. Physiol. Behav. 67, 599–605 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Zaharia, M.D., Kulczycki, J., Shanks, N., Meaney, M.J. & Anisman, H. Psychopharmacology 128, 227–239 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Liu, D. et al. Science 277, 1659–1662 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Liu, D., Diorio, J., Day, J.C., Francis, D.D. & Meaney, M.J. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 799–806 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Francis, D., Diorio, J., Liu, D. & Meaney, M.J. Science 286, 1155–1158 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors thank T. Etzel for assistance with animal care, and Cure Autism Now and the National Science Foundation IBN 9876754 for support.
Author information
Author notes
- Thomas R. Insel
Present address: NIMH, 6001 Executive Blvd. Room 8235, MSC 9669, Bethesda, Maryland, 20892, USA
Authors and Affiliations
- Center for Behavioral Neuroscience, Emory University, Yerkes Research Center, 954 Gatewood Rd., Atlanta, 30329, Georgia, USA
Darlene D. Francis, Kathleen Szegda & Thomas R. Insel - Transgenic Mouse Core, Emory University School of Medicine, Whitehead Research Building, Atlanta, 30329, Georgia, USA
Gregory Campbell & W. David Martin - Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, 30329, Georgia, USA
Thomas R. Insel
Authors
- Darlene D. Francis
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Kathleen Szegda
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Gregory Campbell
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - W. David Martin
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Thomas R. Insel
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toThomas R. Insel.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, D., Szegda, K., Campbell, G. et al. Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice.Nat Neurosci 6, 445–446 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1038
- Received: 05 February 2003
- Accepted: 27 February 2003
- Published: 31 March 2003
- Issue Date: 01 May 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1038