Two drugs are better than one to start T2DM therapy (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: 08 November 2019
DIABETES
Nature Reviews Endocrinology volume 16, pages 15–16 (2020)Cite this article
- 1331 Accesses
- 21 Citations
- 26 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
Early and intensive glycaemic control protects patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from the development of late cardiovascular complications. The authors of the VERIFY trial now show that a more durable attainment of HbA1c <7% is observed by adding vildagliptin to metformin as starting therapy in newly diagnosed patients with T2DM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
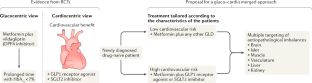
Fig. 1: Proposal for merging the glucocentric and the cardiocentric view of T2DM treatment.
References
- [No authors listed.] Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 352, 837–853 (1998).
- Holman, R. R. et al. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 1577–1589 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Laiteerapong, N. et al. The legacy effect in type 2 diabetes: impact of early glycemic control on future complications (The Diabetes & Aging Study). Diabetes Care 42, 416–426 (2019).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Brown, J. B., Conner, C. & Nichols, G. A. Secondary failure of metformin monotherapy in clinical practice. Diabetes Care 33, 501–506 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Phung, O. J. et al. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 16, 410–417 (2014).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Matthews, D. R. et al. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): a 5-year, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 394, 1519–1529 (2019).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Schnell, O. et al. Report from the 4th Cardiovascular Outcome Trial (CVOT) Summit of the Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease (D&CVD) EASD Study Group. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 18, 30 (2019).
Article Google Scholar - Davies, M. J. et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 41, 2669–2701 (2018).
Article Google Scholar - Cosentino, F. et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486 (2019).
- Abdul-Ghani, M. & DeFronzo, R. A. Is it time to change the type 2 diabetes treatment paradigm? Yes! GLP-1 RAs should replace metformin in the type 2 diabetes algorithm. Diabetes Care 40, 1121–1127 (2017).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Italian Ministry of Health (Ricerca Corrente), who supported part of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Cardiovascular and Dysmetabolic Diseases, IRCCS MultiMedica, Milano, Italy
Francesco Prattichizzo, Lucia La Sala & Antonio Ceriello
Authors
- Francesco Prattichizzo
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Lucia La Sala
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Antonio Ceriello
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toAntonio Ceriello.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prattichizzo, F., La Sala, L. & Ceriello, A. Two drugs are better than one to start T2DM therapy.Nat Rev Endocrinol 16, 15–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0294-3
- Published: 08 November 2019
- Issue Date: January 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0294-3