Modulation of Fos-mediated AP-1 transcription by the promyelocytic leukemia protein (original) (raw)
- Original Paper
- Published: 09 June 1998
- Joop A Gäken2,
- Elliot B Gingold2,
- Tony Kouzarides3,
- Kun-Sang Chang1 &
- …
- Farzin Farzaneh2
Oncogene volume 16, pages 2843–2853 (1998)Cite this article
Abstract
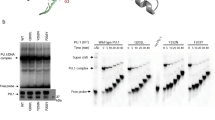
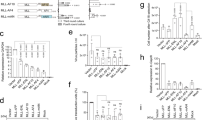
The growth and transformation suppressor function of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein are disrupted in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) as a result of its fusion to the **RAR**α gene by t(15;17) translocation. There is significant sequence homology between the dimerization domain of PML and the Fos family of proteins, which imply that PML may be involved in AP-1 activity. Here we show that PML can cooperate with Fos to stimulate its AP-1-mediated transcriptional activity. Cotransfection of PML with GAL4/Fos strongly induced Fos-mediated activation of GAL4-responsive reporters, indicating a functional interaction between Fos and PML in vivo. Deletion analysis of Fos and PML demonstrated that the intact C-terminal domain of Fos (containing the dimerization domain), and the RING-finger, B1 box and nuclear localization domains of PML are involved in the cooperative activity of Fos and PML. Immunoprecipitation and electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that PML is associated with the AP-1 complex. PMLRARα was also found to enhance the transcriptional activity of GAL4/Fos. The addition of retinoic acid abrogated the PMLRARα, but not PML-induced stimulation of GAL4/Fos activity in a dose-dependent manner. This study demonstrated that PML is involved in the AP-1 complex and can modulate Fos-mediated transcriptional activity, which may contribute to its growth suppressor function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Similar content being viewed by others
Role of Fra-2 in cancer
Article Open access 16 December 2023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Division of Laboratory Medicine, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, 77030, Texas, USA
Sadeq Vallian & Kun-Sang Chang - Department of Molecular Medicine, King's College School of Medicine and Dentistry, London, SE5 9NU, UK
Joop A Gäken, Elliot B Gingold & Farzin Farzaneh - Wellcome/CRC Institute, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, CB2 1QR, UK
Tony Kouzarides
Authors
- Sadeq Vallian
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Joop A Gäken
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Elliot B Gingold
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Tony Kouzarides
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Kun-Sang Chang
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Farzin Farzaneh
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallian, S., Gäken, J., Gingold, E. et al. Modulation of Fos-mediated AP-1 transcription by the promyelocytic leukemia protein.Oncogene 16, 2843–2853 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201837
- Received: 21 November 1997
- Revised: 09 January 1998
- Accepted: 12 January 1998
- Published: 09 June 1998
- Issue Date: 04 June 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201837