Half-awake to the risk of predation (original) (raw)
- Scientific Correspondence
- Published: 04 February 1999
Nature volume 397, pages 397–398 (1999)Cite this article
- 2254 Accesses
- 176 Citations
- 582 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
Birds have overcome the problem of sleeping in risky situations by developing the ability to sleep with one eye open and one hemisphere of the brain awake1. Such unihemispheric slow-wave sleep is in direct contrast to the typical situation in which sleep and wakefulness are mutually exclusive states of the whole brain. We have found that birds can detect approaching predators during unihemispheric slow-wave sleep, and that they can increase their use of unihemispheric sleep as the risk of predation increases. We believe this is the first evidence for an animal behaviourally controlling sleep and wakefulness simultaneously in different regions of the brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
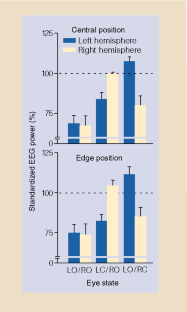
Figure 1: The relation between eye state and standardized EEG power (1-6 Hz) for the left and right hemispheres of birds occupying central and edge positions.
References
- Ball, N. J., Amlaner, C. J., Shaffery, J. P. & Opp, M. R. in Sleep '86 (eds Koella, W. P., Obál, F., Schulz, H. & Visser, P.) 151-153 (Fischer, New York, 1988).
- Oleksenko, A. I., Mukhametov, L. M., Polyakova, I. G., Supin, A. Y. & Kovalzon, V. M. J. Sleep Res. 1, 40–44 (1992).
Google Scholar - Lima, S. L. Adv. Study Behav. 27, 215–290 (1998).
Google Scholar - Elgar, M. A. Biol. Rev. 64, 13–33 (1989).
Google Scholar - Amlaner, C. J. & Ball, N. J. in Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine 2nd edn (eds Kryger, M. H., Roth, T. & Dement, W. C.) 81-94 (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994).
- Hoffmann, R. F., Moffitt, A. R., Shearer, J. C., Sussman, P. S. & Wells, R. B. Waking Sleeping. 3, 1–16 (1979).
Google Scholar - Schaeffel, F., Howland, H. C. & Farkas, L. Vision Res. 26, 1977–1993 (1986).
Google Scholar - Bredenkötter, M. & Bischof, H. -J. Vis. Neurosci. 5, 155–163 (1990).
Google Scholar - Rechtschaffen, A., Gilliland, M. A., Bergmann, B. M. & Winter, J. B. Science 221, 182–184 (1983).
Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Life Sciences, Indiana State University, Terre Haute, 47809, Indiana, USA
Niels C. Rattenborg, Steven L. Lima & Charles J. Amlaner
Authors
- Niels C. Rattenborg
- Steven L. Lima
- Charles J. Amlaner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rattenborg, N., Lima, S. & Amlaner, C. Half-awake to the risk of predation.Nature 397, 397–398 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/17037
- Issue Date: 04 February 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/17037