Maturation of mouse fetal germ cells in vitro (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 01 August 2002
Oogenesis
Nature volume 418, page 497 (2002)Cite this article
- 2373 Accesses
- 89 Citations
- Metrics details
Even immature oocytes can eventually be fertilized after some skilful manipulation.
Abstract
Nuclear reprogramming is essential during gametogenesis for the production of totipotent zygotes. Here we show that premeiotic female germ cells derived from mouse fetuses as early as 12.5 days post coitum are able to complete meiosis and genomic imprinting in vitro and that these matured oocytes are highly competent in supporting development to full term after nuclear transfer and in vitro fertilization. To our knowledge, this is the first time that complete oogenesis has been successfully accomplished in vitro.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
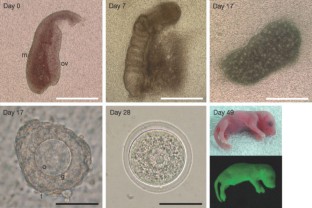
Figure 1: Development of premeiotic female germ cells in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Buehr, M. & McLaren, A. Gamete Res. 11, 271–281 (1985).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Eppig, J. J. & O'Brien, M. J. Biol. Reprod. 54, 197–207 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Cortvrindt, R., Smitz, J. & Van Steirteghem, A. C. Hum. Reprod. 11, 2656–2666 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bao, S., Obata, Y., Carroll, J., Domeki, I. & Kono, T. Biol. Reprod. 62, 616–621 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kono, T., Obata, Y., Yoshimzu, T., Nakahara, T. & Carroll, J. Nature Genet. 13, 91–94 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Obata, Y. et al. Development 125, 1553–1560 (1998).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Obata, Y. & Kono, T. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 5285–5289 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wutz, A. et al. Nature 389, 745–749 (1997).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Bourc'his, D., Xu, G. L., Lin, C. S., Bollman, B. & Bestor, T. H. Science 294, 2536–2539 (2001).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Lucifero, D., Mertineit, C., Clarke, H. J., Bestor, T. H. & Trasler, J. M. Genomics 79, 530–538 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Okabe, M., Ikawa, M., Kominami, K., Nakanishi, T. & Nishimune, Y. FEBS Lett. 407, 313–319 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Gene Research Center, Gunma University, 3-39-22 Showa-machi, Maebashi, 371-8511, Gunma, Japan
Yayoi Obata & Izuho Hatada - Department of Bioscience, Tokyo University of Agriculture, 1-1-1 Sakuragaoka, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo, 156-8502, Japan
Tomohiro Kono
Authors
- Yayoi Obata
- Tomohiro Kono
- Izuho Hatada
Corresponding author
Correspondence toIzuho Hatada.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obata, Y., Kono, T. & Hatada, I. Maturation of mouse fetal germ cells in vitro.Nature 418, 497 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/418497a
- Issue Date: 01 August 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/418497a