A histone-H3-like protein in C. elegans (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 07 October 1999
Cell division
Nature volume 401, pages 547–548 (1999)Cite this article
- 1335 Accesses
- 213 Citations
- Metrics details
Abstract
The segregation of a chromosome during mitosis is mediated by a region of the chromosome known as the centromere, which organizes the kinetochore, to which the spindle microtubules attach. Many organisms have monocentric chromosomes, in which the centromeres map to single loci, whereas others, including the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, have holocentric chromosomes, in which non-localized kinetochores extend along the length of each chromosome1,2. The centromeres of monocentric chromosomes use specialized nucleosomes containing histone-H3-like proteins (known as CENP-A in mammals3,4,5,6 and Cse4 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae7,8). Here we show that a C. elegans histone-H3-like protein is necessary for the proper segregation of chromosomes during mitosis and identifies the centromeres of these holocentric chromosomes, indicating that both holocentric and monocentric chromosomes use centromeric histone-H3-like proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
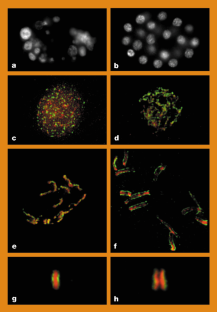
Figure 1: A centromeric histone-H3-like protein from Caenorhabditis elegans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Albertson, D. G., Rose, A. M. & Villeneuve, A. M. in C. elegans, Vol. II (eds Riddle, D. L. et al.) 47–78 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, New York, 1997).
Google Scholar - Albertson, D. G., & Thomson, J. N. Chromosoma 86, 409–428 (1982).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Earnshaw, W. C., & Rothfield, N. Chromosoma 91, 313–321 (1985).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Palmer, D. K. et al. J. Cell Biol. 104, 805–815 (1987).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Palmer, D. K. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 3734–3738 (1991).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Sullivan, K. F., Hechenberger, M. & Masri, K. J. Cell Biol. 127, 581–592 (1994).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Stoler, S. et al. Genes Dev. 9, 573–586 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Meluh, P. B. et al. Cell 94, 607–613 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wilson, R. et al. Nature 368, 32–38 (1994).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Fire, A. et al. Nature 391, 806–811 (1998).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Zinkowski, R. P., Meyne, J., & Brinkley, B. R. J. Cell Biol. 113, 1091–1110 (1991).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Division of Basic Sciences, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, Seattle, 98109, Washington, USA
Kami Ahmad & Landon L. Moore - Molecular and Cellular Biology Program, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, Seattle, 98109, Washington, USA
Brian J. Buchwitz, Mark B. Roth & Steven Henikoff - Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, Seattle, 98109, Washington, USA
Steven Henikoff
Authors
- Brian J. Buchwitz
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Kami Ahmad
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Landon L. Moore
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Mark B. Roth
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Steven Henikoff
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toMark B. Roth.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchwitz, B., Ahmad, K., Moore, L. et al. A histone-H3-like protein in C. elegans.Nature 401, 547–548 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/44062
- Issue Date: 07 October 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/44062