Population differences in SLE susceptibility genes: STAT4 and BLK, but not PXK, are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese (original) (raw)
- Original Article
- Published: 19 February 2009
- P Ng1,
- M Zhao1,
- N Hirankarn2,
- C S Lau3 nAff8,
- C C Mok4,
- T M Chan3,
- R W S Wong3,
- K W Lee5,
- M Y Mok3,
- S N Wong6,
- Y Avihingsanon7,
- T L Lee1,
- M H K Ho1,
- P P W Lee1,
- W H S Wong1 &
- …
- Y L Lau1
Genes & Immunity volume 10, pages 219–226 (2009)Cite this article
- 2058 Accesses
- 6 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
In this study, we compared the association of several newly discovered susceptibility genes for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) between populations of European origin and two Asian populations. Using 910 SLE patients and 1440 healthy controls from Chinese living in Hong Kong, and 278 SLE patients and 383 controls in Thailand, we studied association of STAT4, BLK and PXK with the disease. Our data confirmed association of STAT4 (rs7574865, odds ratio (OR) =1.71, _P_=3.55 × 10−23) and BLK (rs13277113, OR=0.77, _P_=1.34 × 10−5) with SLE. It was showed that rs7574865 of STAT4 is also linked to hematologic disorders and potentially some other subphenotypes of the disease. More than one genetic variant in STAT4 were found to be associated with the disease independently in our populations (rs7601754, OR=0.59, _P_=1.39 × 10−9, and _P_=0.00034 when controlling the effect of rs7574865). With the same set of samples, however, our study did not detect any significant disease association for PXK, a risk factor for populations of European origin (rs6445975, joint _P_=0.36, OR=1.06, 95% confidence interval: 0.93–1.21). Our study indicates that some of the susceptibility genes for this disease may be population specific.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
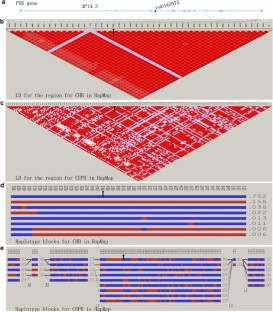
Figure 1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Danchenko N, Satia JA, Anthony MS . Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 2006; 15: 308–318.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Mok CC, Lau CS . Lupus in Hong Kong Chinese. Lupus 2003; 12: 717–722.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Mok CC, Tang SS . Incidence and predictors of renal disease in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 2004; 117: 791–795.
Article Google Scholar - Seligman VA, Lum RF, Olson JL, Li H, Criswell LA . Demographic differences in the development of lupus nephritis: a retrospective analysis. Am J Med 2002; 112: 726–729.
Article Google Scholar - Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW et al. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 977–986.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Nath SK, Han S, Kim-Howard X, Kelly JA, Viswanathan P, Gilkeson GS et al. A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 152–154.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, Taylor KE, Ortmann W, Garnier S et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 900–909.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 204–210.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kobayashi S, Ikari K, Kaneko H, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K, Shimane K et al. Association of STAT4 with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the Japanese population. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 1940–1946.
Article Google Scholar - Palomino-Morales RJ, Rojas-Villarraga A, Gonzalez CI, Ramirez G, Anaya JM, Martin J . STAT4 but not TRAF1/C5 variants influence the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombians. Genes Immun 2008; 9: 379–382.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Taylor KE, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Ortmann WA, Plenge RM, Tian C et al. Specificity of the STAT4 genetic association for severe disease manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000084.
Article Google Scholar - Sigurdsson S, Nordmark G, Garnier S, Grundberg E, Kwan T, Nilsson O et al. A common STAT4 risk haplotype for systemic lupus erythematosus is over-expressed, correlates with anti-dsDNA production and shows additive effects with two IRF5 risk alleles. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 2868–2876.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M . Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 209–213.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lovato P, Brender C, Agnholt J, Kelsen J, Kaltoft K, Svejgaard A et al. Constitutive STAT3 activation in intestinal T cells from patients with Crohn's disease. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 16777–16781.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Martinez A, Varade J, Marquez A, Cenit MC, Espino L, Perdigones N et al. Association of the STAT4 gene with increased susceptibility for some immune-mediated diseases. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 2598–2602.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Korman BD, Alba MI, Le JM, Alevizos I, Smith JA, Nikolov NP et al. Variant form of STAT4 is associated with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Genes Immun 2008; 9: 267–270.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kawasaki A, Ito I, Hikami K, Ohashi J, Hayashi T, Goto D et al. Role of STAT4 polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population: a case–control association study of the STAT1–STAT4 region. Arthritis Res Ther 2008; 10: R113.
Article Google Scholar - Clatworthy MR, Willcocks L, Urban B, Langhorne J, Williams TN, Peshu N et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated defects in the inhibitory receptor FcgammaRIIb reduce susceptibility to malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 7169–7174.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Willcocks LC, Lyons PA, Clatworthy MR, Robinson JI, Yang W, Newland SA et al. Copy number of FCGR3B, which is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, correlates with protein expression and immune complex uptake. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 1573–1582.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hirankarn N, Avihingsanon Y, Wongpiyabovorn J . Genetic susceptibility to SLE is associated with TNF-alpha gene polymorphism −863, but not −308 and −238, in Thai population. Int J Immunogenet 2007; 34: 425–430.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the Shun Tak District Min Yuen Tong of Hong Kong. PN and MZ were supported by Edward Sai Kim Hotung Paediatric Education and Research Fund, and University Postgraduate Studentship. WY acknowledges support from UGC, UHK (200711159155).
Author information
Author notes
- C S Lau
Present address: 8Current address: Division of Medicine & Therapeutics, Ninewells Hospital & Medical School, Dundee, DD1 9SY, Tayside, UK.,
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
W Yang, P Ng, M Zhao, T L Lee, M H K Ho, P P W Lee, W H S Wong & Y L Lau - Department of Microbiology, Lupus Research Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
N Hirankarn - Department of Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
C S Lau, T M Chan, R W S Wong & M Y Mok - Department of Medicine, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China
C C Mok - Department of Medicine, Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Hong Kong, China
K W Lee - Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China
S N Wong - Department of Medicine, Lupus Research Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Y Avihingsanon
Authors
- W Yang
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - P Ng
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - M Zhao
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - N Hirankarn
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - C S Lau
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - C C Mok
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - T M Chan
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - R W S Wong
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - K W Lee
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - M Y Mok
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - S N Wong
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Y Avihingsanon
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - T L Lee
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - M H K Ho
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - P P W Lee
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - W H S Wong
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Y L Lau
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toY L Lau.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Ng, P., Zhao, M. et al. Population differences in SLE susceptibility genes: STAT4 and BLK, but not PXK, are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese.Genes Immun 10, 219–226 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.1
- Received: 16 October 2008
- Revised: 17 December 2008
- Accepted: 18 December 2008
- Published: 19 February 2009
- Issue Date: April 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.1