Trans-histone regulatory pathway in chromatin (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 14 July 2002
Gene silencing
- Tiaojiang Xiao2,
- Zu-Wen Sun1,
- Jennifer A. Caldwell3,
- Jeffrey Shabanowitz3,
- Donald F. Hunt3,
- C. David Allis1 &
- …
- Brian D. Strahl2
Nature volume 418, page 498 (2002)Cite this article
- 3965 Accesses
- 461 Citations
- 1 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
The fundamental unit of eukaryotic chromatin, the nucleosome, consists of genomic DNA wrapped around the conserved histone proteins H3, H2B, H2A and H4, all of which are variously modified at their amino- and carboxy-terminal tails to influence the dynamics of chromatin structure and function1,2 — for example, conjugation of histone H2B with ubiquitin controls the outcome of methylation at a specific lysine residue (Lys 4) on histone H3, which regulates gene silencing in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae3. Here we show that ubiquitination of H2B is also necessary for the methylation of Lys 79 in H3, the only modification known to occur away from the histone tails, but that not all methylated lysines in H3 are regulated by this '_trans_-histone' pathway because the methylation of Lys 36 in H3 is unaffected. Given that gene silencing is regulated by the methylation of Lys 4 and Lys 79 in histone H3, we suggest that H2B ubiquitination acts as a master switch that controls the site-selective histone methylation patterns responsible for this silencing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
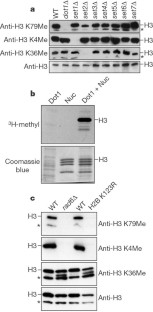
Figure 1: Regulation of Lys-79 methylation on histone H3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Kornberg, R. D. & Lorch, Y. Cell 98, 285–294 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Strahl, B. D. & Allis, C. D. Nature 403, 41–45 (2000).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Sun, Z. W. & Allis, C. D. Nature 418, 104–108 (2002).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - van Leeuwen, F., Gafken, P. R. & Gottschling, D. E. Cell 109, 745–756 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ng, H. H. et al. Genes Dev. 16, 1518–1527 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Feng, Q. et al. Curr. Biol. 12, 1052–1058 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Dlakic, M. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 26, 405–407 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Robzyk, K., Recht, J. & Osley, M. A. Science 287, 501–504 (2000).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar - Briggs, S. D. et al. Genes Dev. 15, 3286–3295 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bryk, M. et al. Curr. Biol. 12, 165–170 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Strahl, B. D. et al. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 1298–1306 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, 22908, Virginia, USA
Scott D. Briggs, Zu-Wen Sun & C. David Allis - Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, 27599, North Carolina, USA
Tiaojiang Xiao & Brian D. Strahl - Departments of Chemistry and Pathology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, 22908, Virginia, USA
Jennifer A. Caldwell, Jeffrey Shabanowitz & Donald F. Hunt
Authors
- Scott D. Briggs
- Tiaojiang Xiao
- Zu-Wen Sun
- Jennifer A. Caldwell
- Jeffrey Shabanowitz
- Donald F. Hunt
- C. David Allis
- Brian D. Strahl
Corresponding author
Correspondence toBrian D. Strahl.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
This advance online publication (AOP) Nature paper should be as “Author(s) Nature, 14 July 2002 (doi:10.1038/nature00970)”. Once the print version (identical to the AOP) is published, the citation becomes “Author(s) Nature volume, page (year); advance online publication 14 July 2002 (doi: 10.1038/nature00970)”.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briggs, S., Xiao, T., Sun, ZW. et al. _Trans_-histone regulatory pathway in chromatin.Nature 418, 498 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00970
- Received: 30 May 2002
- Accepted: 01 July 2002
- Published: 14 July 2002
- Issue Date: 01 August 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00970