Next-generation association studies for complex traits (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: 29 March 2011
Nature Genetics volume 43, pages 287–288 (2011)Cite this article
- 965 Accesses
- 50 Citations
- 5 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
A new study successfully applies complementary whole-genome sequencing and imputation approaches to establish robust disease associations in an isolated population. This strategy is poised to help elucidate the role of variants at the low end of the allele frequency spectrum in the genetic architecture of complex traits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1
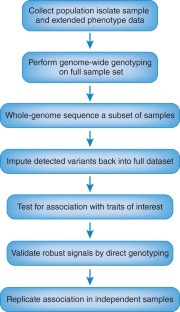
References
- Holm, H. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 316–320 (2011).
Article CAS Google Scholar - 1000 Genomes Project Consortium et al. Nature 467, 1061–1073 (2010).
- Kong, A. et al. Nat. Genet. 40, 1068–1075 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Le, S.Q. & Durbin, R. Genome Res. published online, doi:10.1101/gr.113084.110 (27 October 2010).
- Asimit, J. & Zeggini, E. Annu. Rev. Genet. 44, 293–308 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Peltonen, L., Palotie, A. & Lange, K. Nat. Rev. Genet. 1, 182–190 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Eleftheria Zeggini is at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK.,
Eleftheria Zeggini
Authors
- Eleftheria Zeggini
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toEleftheria Zeggini.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeggini, E. Next-generation association studies for complex traits.Nat Genet 43, 287–288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0411-287
- Published: 29 March 2011
- Issue Date: April 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0411-287