MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling (original) (raw)
- Correspondence
- Published: 29 September 2015
- Eric A Franzosa2,3,
- Timothy L Tickle2,3,
- Matthias Scholz1,
- George Weingart2,
- Edoardo Pasolli1,
- Adrian Tett1,
- Curtis Huttenhower2,3 &
- …
- Nicola Segata1
Nature Methods volume 12, pages 902–903 (2015)Cite this article
- 23k Accesses
- 1350 Citations
- 43 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Subjects
An Erratum to this article was published on 30 December 2015
This article has been updated
To the Editor:
MetaPhlAn (metagenomic phylogenetic analysis)1 is a method for characterizing the taxonomic profiles of whole-metagenome shotgun (WMS) samples that has been used successfully in large-scale microbial community studies2,3. This work complements the original species-level profiling method with a system for eukaryotic and viral quantitation, strain-level identification and strain tracking. These and other extensions make the MetaPhlAn2 computational package (http://segatalab.cibio.unitn.it/tools/metaphlan2/ and Supplementary Software) an efficient tool for mining WMS samples.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: MetaPhlAn2 can accurately reconstruct the taxonomic composition of shotgun metagenomes.
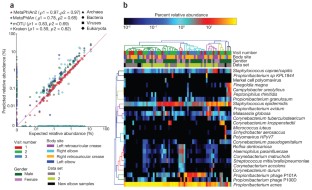
Change history
09 December 2015
In the version of this article initially published, MetaPhlAn was mislabeled as MetaphlAn2 in the key to Figure 1a (blue stars). The error has been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
- Segata, N. et al. Nat. Methods 9, 811–814 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar - The Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Nature 486, 207–214 (2012).
- Scher, J.U. et al. Elife 2, e01202 (2013).
Article Google Scholar - Sunagawa, S. et al. Nat. Methods 10, 1196–1199 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wood, D.E. & Salzberg, S. Genome Biol. 15, R46 (2014).
Article Google Scholar - Grice, E.A. et al. Science 324, 1190–1192 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Farina and M. Cristofolini for skin-sample collection, V. De Sanctis and R. Bertorelli for metagenomic sequencing, B. Ren for help in the generation of the synthetic metagenomes, the Human Microbiome Project Consortium, and the individuals from the Saint Louis, MO, and Houston, TX, areas, whose generous participation made the HMP possible. This work was supported in part by the US National Institutes of Health (grants R01HG005969 and U54DE023798 to C.H.), the US National Science Foundation (grant DBI-1053486 to C.H.), the US Army Research Office (grant W911NF-11-1-0473 to C.H.), Danone Research (grant PLF-5972-GD to G.W.) the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (Marie Curie grant PCIG13-618833 to N.S.), the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (grant FIR RBFR13EWWI to N.S.), Fondazione Caritro (grant Rif.Int.2013.0239 to N.S.) and Terme di Comano (grant to N.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Centre for Integrative Biology, University of Trento, Trento, Italy
Duy Tin Truong, Matthias Scholz, Edoardo Pasolli, Adrian Tett & Nicola Segata - Biostatistics Department, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, USA
Eric A Franzosa, Timothy L Tickle, George Weingart & Curtis Huttenhower - The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
Eric A Franzosa, Timothy L Tickle & Curtis Huttenhower
Authors
- Duy Tin Truong
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Eric A Franzosa
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Timothy L Tickle
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Matthias Scholz
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - George Weingart
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Edoardo Pasolli
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Adrian Tett
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Curtis Huttenhower
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Nicola Segata
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toNicola Segata.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truong, D., Franzosa, E., Tickle, T. et al. MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling.Nat Methods 12, 902–903 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3589
- Published: 29 September 2015
- Issue Date: October 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3589