DNA damage: ubiquitin marks the spot (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: January 2008
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology volume 15, pages 20–22 (2008)Cite this article
- 1111 Accesses
- 71 Citations
- 9 Altmetric
- Metrics details
DNA damage activates signaling cascades driven by the ATM–ATR protein kinases, culminating in the recruitment of repair proteins to the damage site through poorly understood mechanisms. Now a flurry of papers reveals how ATM-dependent phosphorylation of mediator and chromatin-associated proteins at sites of double-strand breaks promotes ubiquitylation of local nucleosomes, thereby eliciting a powerful signal for recruitment of repair complexes to the damage site.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
UBE4B interacts with the ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce Ku70 and c-FLIPL polyubiquitination and enhanced neuroblastoma apoptosis
- Christophe Le Clorennec
- , Divya Subramonian
- … Peter E. Zage
Cell Death & Disease Open Access 13 November 2023
Ubiquitination by HUWE1 in tumorigenesis and beyond
- Shih-Han Kao
- , Han-Tsang Wu
- & Kou-Juey Wu
Journal of Biomedical Science Open Access 04 September 2018
Histone modifications in DNA damage response
- Lin-Lin Cao
- , Changchun Shen
- & Wei-Guo Zhu
Science China Life Sciences Open Access 29 January 2016
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: The hierarchical signaling network within the DDR.

Kim Caesar
Figure 2: Modification of the ubiquitin signal.
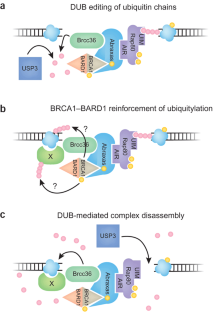
Kim Caesar
References
- Huen, M.S. et al. Cell 131, 901–914 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Kolas, N.K. et al. Science 318, 1637–1640 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Mailand, N. et al. Cell 131, 887–900 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wang, B. & Elledge, S.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, published online 5 December 2007 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0710061104).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Matsuoka, S. et al. Science 316, 1160–1166 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Stucki, M. & Jackson, S.P. DNA Repair (Amst.) 5, 534–543 (2006).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Morris, J.R. & Solomon, E. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 807–817 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Polanowska, J., Martin, J.S., Garcia-Muse, T., Petalcorin, M.I. & Boulton, S.J. EMBO J. 25, 2178–2188 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Ruffner, H., Joazeiro, C.A., Hemmati, D., Hunter, T. & Verma, I.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5134–5139 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Zhao, G.Y. et al. Mol. Cell 25, 663–675 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sobhian, B. et al. Science 316, 1198–1202 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Liu, Z., Wu, J. & Yu, X. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 716–720 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kim, H., Chen, J. & Yu, X. Science 316, 1202–1205 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wang, B. et al. Science 316, 1194–1198 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Bekker-Jensen, S. et al. J. Cell Biol. 173, 195–206 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Bekker-Jensen, S., Lukas, C., Melander, F., Bartek, J. & Lukas, J. J. Cell Biol. 170, 201–211 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Durocher, D. et al. Mol. Cell 6, 1169–1182 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Plans, V. et al. J. Cell. Biochem. 97, 572–582 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bergink, S. et al. Genes Dev. 20, 1343–1352 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Pickart, C.M. & Fushman, D. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 8, 610–616 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bothos, J., Summers, M.K., Venere, M., Scolnick, D.M. & Halazonetis, T.D. Oncogene 22, 7101–7107 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ito, K. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 2725–2732 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Nicassio, F. et al. Curr. Biol. 17, 1972–1977 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chen, X., Arciero, C.A., Wang, C., Broccoli, D. & Godwin, A.K. Cancer Res. 66, 5039–5046 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Dong, Y. et al. Mol. Cell 12, 1087–1099 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Eric J. Bennett and J. Wade Harper are at the Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA. wade_harper@hms.harvard.edu,
Eric J Bennett & J Wade Harper
Authors
- Eric J Bennett
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - J Wade Harper
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, E., Harper, J. DNA damage: ubiquitin marks the spot.Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 20–22 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb0108-20
- Issue Date: January 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb0108-20
This article is cited by
UBE4B interacts with the ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce Ku70 and c-FLIPL polyubiquitination and enhanced neuroblastoma apoptosis
- Christophe Le Clorennec
- Divya Subramonian
- Peter E. Zage
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
E3 ubiquitin ligases in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and implications for therapies
- Zijian Zhou
- Kaifeng Zheng
- Xiaofeng Jin
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
Ubiquitination by HUWE1 in tumorigenesis and beyond
- Shih-Han Kao
- Han-Tsang Wu
- Kou-Juey Wu
Journal of Biomedical Science (2018)
E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer and implications for therapies
- Dong Wang
- Leina Ma
- Wenyi Wei
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2017)
Histone modifications in DNA damage response
- Lin-Lin Cao
- Changchun Shen
- Wei-Guo Zhu
Science China Life Sciences (2016)