Effect of plant sterols and endurance training on LDL particle size and distribution in previously sedentary hypercholesterolemic adults (original) (raw)
- Original Communication
- Published: 26 January 2005
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition volume 59, pages 518–525 (2005)Cite this article
- 1120 Accesses
- 29 Citations
- Metrics details
Abstract
Background:
Plant sterols and exercise favourably alter lipid profiles in a way that protect against future coronary heart disease (CHD). However, their effects on other indicators of CHD risk, such as LDL particle size, still need further clarification.
Objective:
This study examined the effect of plant sterols, exercise, and the combination of plant sterols and exercise, on LDL particle size and distribution in previously sedentary, hypercholesterolemic adults.
Design:
In an 8-week, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm clinical trial, 84 subjects were randomized to one of four intervention groups: (1) combination of sterols and exercise, (2) exercise, (3) sterol, or (4) control.
Results:
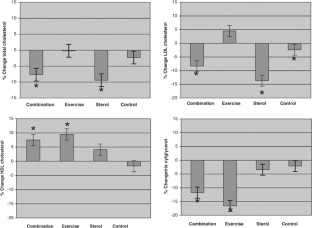
Exercise significantly (P<0.05) reduced post-treatment LDL peak particle size from 255 to 253 Å. Additionally, exercise significantly (P<0.05) decreased the proportion of large LDL particles within plasma. Sterol supplementation significantly (P<0.05) decreased the estimated cholesterol concentrations within small, medium, and large LDL particles by 13.4, 13.5, and 14.4%, respectively, yet had no effect on the distribution of cholesterol among various LDL particle sizes. Furthermore, decreased body weight post-training was associated with increased cholesterol in small LDL particles (_r_=−0.52, P<0.0001). Decrease in body fat percent (BF%) post-training was associated with increased cholesterol concentrations in small LDL particles (_r_=−0.29, P<0.01).
Conclusion:
On the basis of modulating LDL electrophoretic characteristics, the present study demonstrates that plant sterols have no effect on CHD risk, while short-term exercise may potentially increase CHD risk by decreasing LDL peak particle size.
Sponsorship:
This study was sponsored by The Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Beard CM, Barnard RJ, Robbins DC, Ordovas JM & Schaefer EJ (1996): Effects of diet and exercise on qualitative and quantitative measures of LDL and its susceptibility to oxidation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16, 201–207.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bourque C, St-Onge MP, Papamandjaris AA, Cohn JS & Jones PJ (2003): Consumption of an oil composed of medium chain triacyglycerols, phytosterols, and _n_-3 fatty acids improves cardiovascular risk profile in overweight women. Metabolism 52, 771–777.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Charest A, Desroches S, Vanstone CA, Jones PJ & Lamarche B (2004): Unesterified plant sterols and stanols do not affect LDL electrophoretic characteristics in hypercholesterolemic subjects. J. Nutr. 134, 592–595.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Deurenberg P, Andreoli A, Borg P, Kukkonen-Harjula K, de Lorenzo A, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Testolin G, Vigano R & Vollaard N (2001): The validity of predicted body fat percentage from body mass index and from impedance in samples of five European populations. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 973–979.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Elosua R, Molina L, Fito M, Arquer A, Sanchez-Quesada JL, Covas MI, Ordonez-Llanos J & Marrugat J (2003): Response of oxidative stress biomarkers to a 16-week aerobic physical activity program, and to acute physical activity, in healthy young men and women. Atherosclerosis 167, 327–334.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Fahlman MM, Boardley D, Lambert CP & Flynn MG (2002): Effects of endurance training and resistance training on plasma lipoprotein profiles in elderly women. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 57, 54–60.
Article Google Scholar - Festa A (2001): Small, dense low density lipoprotein and the insulin resistance syndrome. Clin. Lab. 47, 111–118.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Fletcher GF (1997): How to implement physical activity in primary and secondary prevention: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Task Force on Risk Reduction, American Heart Association. Circulation 96, 355–357.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Halle M, Berg A, Garwers U, Baumstark MW, Knisel W, Grathwohl D, Konig D & Keul J (1999): Influence of 4 weeks' intervention by exercise and diet on low-density lipoprotein subfractions in obese men with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 48, 641–644.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Jafari M, Leaf DA, Macrae H, Kasem J, O'conner P, Pullinger C, Malloy M & Kane JP (2003): The effects of physical exercise on plasma prebeta-1 high-density lipoprotein. Metabolism 52, 437–442.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Kang HS, Gutin B, Barbeau P, Owens S, Lemmon CR, Allison J, Litaker MS & Le NA (2002): Physical training improves insulin resistance syndrome markers in obese adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 34, 1920–1927.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Katan MB, Grundy SM, Jones P, Law M, Miettinen T & Paoletti R (2003): Efficacy and safety of plant stanols and sterols in the management of blood cholesterol levels. Mayo Clin. Proc. 78, 965–978.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Koba S, Hirano T, Kondo T, Shibata M, Suzuki H, Murakami M, Geshi E & Katagiri T (2002): Significance of small dense low-density lipoproteins and other risk factors in patients with various types of coronary heart disease. Am. Heart J. 144, 1026–1035.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Leon AS & Sanchez OA (2001): Response of blood lipids to exercise training alone or combined with dietary intervention. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 33, 502–515.
Article Google Scholar - Markovic TP, Campbell LV, Balasubramanian S, Jenkins AB, Fleury AC, Simons LA & Chisholm DJ (1998): Beneficial effect on average lipid levels from energy restriction and fat loss in obese individuals with or without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 21, 695–700.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Matvienko OA, Lewis DS, Swanson M, Arndt B, Rainwater DL, Stewart J & Alekel DL (2002): A single daily dose of soybean phytosterols in ground beef decreases serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in young, mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 76, 57–64.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Montoye HJ, Kemper HC, Saris WH & Washburn RA (1996): Measuring Physical Activity and Energy Expenditure. Champaign, IL: Braun-Brumfield.
Google Scholar - Parks EJ, German JB, Davis PA, Frankel EN, Kappagoda CT, Rutledge JC, Hyson DA & Schneeman BO (1998): Reduced oxidative susceptibility of LDL from patients participating in an intensive atherosclerosis treatment program. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68, 778–785.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Purnell JQ, Kahn SE, Albers JJ, Nevin DN, Brunzell JD & Schwartz RS (2000): Effect of weight loss with reduction of intra-abdominal fat on lipid metabolism in older men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 977–982.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sacks FM & Campos H (2003): Clinical Review 163: cardiovascular endocrinology: low-density lipoprotein size and cardiovascular disease: a reappraisal. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 4525–4532.
Article CAS Google Scholar - St-Pierre AC, Ruel IL, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Bernard PM, Despres JP & Lamarche B (2001): Comparison of various electrophoretic characteristics of LDL particles and their relationship to the risk of ischemic heart disease. Circulation 104, 2295–2299.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Tanaka H, Monahan KD & Seals DR (2001): Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 37, 153–156.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Varady KA, Ebine N, Vanstone CA, Parsons WE & Jones PJH. (2004): Plant sterols and endurance training combine to favourably alter plasma lipid profiles in previously sedentary hypercholesterolemic adults after 8 weeks. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 80, 1159–1166.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Welty FK, Stuart E, O'Meara M & Huddleston J (2002): Effect of addition of exercise to therapeutic lifestyle changes diet in enabling women and men with coronary heart disease to reach Adult Treatment Panel III low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal without lowering high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am. J. Cardiol. 89, 1201–1204.
Article Google Scholar - Williams PT, Krauss RM, Vranizan KM & Wood PD (1990): Changes in lipoprotein subfractions during diet-induced and exercise-induced weight loss in moderately overweight men. Circulation 81, 1293–1304.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants who contributed their time and effort, and Dr William Parsons who aided with the physical examinations during the screening phase of the trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- School of Dietetics and Human Nutrition, McGill University, Ste. Anne de Bellevue, Québec, Canada
K A Varady & P J H Jones - Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods Institute, Université Laval, Ste. Foy, Québec, Canada
A C St-Pierre & B Lamarche
Authors
- K A Varady
- A C St-Pierre
- B Lamarche
- P J H Jones
Corresponding author
Correspondence toP J H Jones.
Additional information
Guarantor: PJH Jones.
Contributors: KAV conducted the human trial, analysed the data, and wrote the manuscript. ACS and BL assisted in the data analyses, and were involved in the final approval of the manuscript. PJHJ designed the study and aided in the preparation of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varady, K., St-Pierre, A., Lamarche, B. et al. Effect of plant sterols and endurance training on LDL particle size and distribution in previously sedentary hypercholesterolemic adults.Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 518–525 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602106
- Received: 25 May 2004
- Revised: 27 August 2004
- Accepted: 11 November 2004
- Published: 26 January 2005
- Issue Date: 01 April 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602106