Effect of Substrate Temperature on the Selectivity in Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition of Aluminum (original) (raw)
© 1992 ECS - The Electrochemical Society
Journal of The Electrochemical Society,Volume 139,Number 12Citation K. Lee I. et al 1992 J. Electrochem. Soc. 139 3578DOI 10.1149/1.2069125
Article metrics
7 Total downloads
0 Video abstract views
1945-7111/139/12/3578
Abstract
Selective deposition of aluminum was carried out by the low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) method. Selectivity between silicon and silicon dioxide was investigated in a cold wall LPCVD system with tri‐isobutyl‐aluminum (TIBA) source. It has been found that the substrate temperature is the most important variable in determining the selectivity among other variables such as TIBA flow rate and TIBA pressure. Growth activation energy 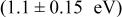 and nucleation activation energy
and nucleation activation energy 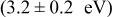 for the aluminum deposition were determined from Arrhenius plot, and it could be concluded that the temperature dependence of the selectivity of aluminum between Si and
for the aluminum deposition were determined from Arrhenius plot, and it could be concluded that the temperature dependence of the selectivity of aluminum between Si and 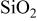 came from the large difference (∼1 eV) in nucleation activation energies. It was suggested that topology improvement in chemically vapor deposited films could be made by pretreatment of the substrate which reduces the nucleation activation energy.
came from the large difference (∼1 eV) in nucleation activation energies. It was suggested that topology improvement in chemically vapor deposited films could be made by pretreatment of the substrate which reduces the nucleation activation energy.
Export citation and abstractBibTeXRIS
Access this article
The computer you are using is not registered by an institution with a subscription to this article. Please choose one of the options below.
Login
Rent from
Make a recommendation
To gain access to this content, please complete the Recommendation Form and we will follow up with your librarian or Institution on your behalf.
For corporate researchers we can also follow up directly with your R&D manager, or the information management contact at your company. Institutional subscribers have access to the current volume, plus a 10-year back file (where available).