Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of some Medicinal Plants Extracts Commonly Used in Algerian Traditional Medicine against some Pathogenic Bacteria (original) (raw)
ArticleView
Abstract
Pharmacognosy Journal,2018,10,3,507-512.
Published:March 2018
Type:Original Article
Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of some Medicinal Plants Extracts Commonly Used in Algerian Traditional Medicine against some Pathogenic Bacteria
Mohamed Senouci Bereksi1*, Hafida Hassaïne2, Chahrazed Bekhechi1, Djamel Eddine Abdelouahid2
1Laboratory of Natural Products, Department of Biology, University of Tlemcen, 13000 Tlemcen, ALGERIA.
2Laboratory of Applied Microbiology in Food, Biomedical and Environment, Department of Biology, University of Tlemcen, 13000 Tlemcen, ALGERIA.
Abstract:
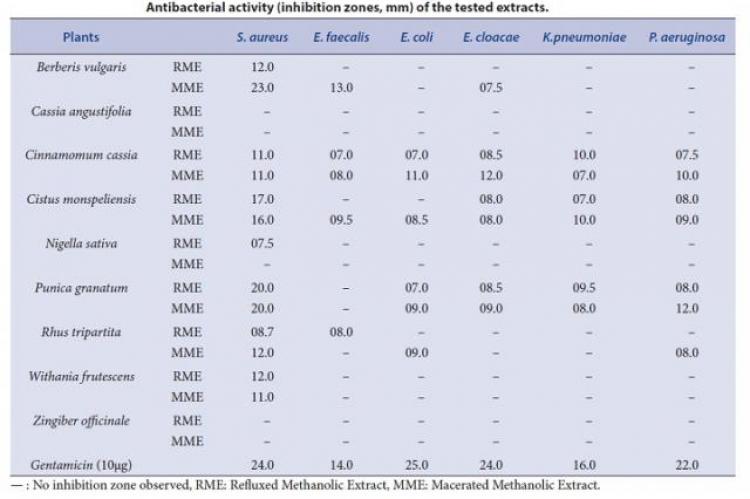
Introduction: The objective of this study was to evaluate the antibacterial activity of hydromethanolic extracts of Berberis vulgaris, Cassia angustifolia, Cinnamomum cassia, Cistus monspeliensis, Nigella sativa, Punica granatum, Rhus tripartata, Withania frutescens and Zingiber officinale against different Gram-positive and Gram-negative reference bacterial strains. Methods: The evaluation of antibacterial activity for different extracts of each plant was carried out using the disc diffusion method and determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Results: The plant extracts showed zone of inhibition ranging from 06.0 to 23.0 mm against one or more tested bacteria, and their efficacy in terms of MICs where ranged from 0.1 to 12.8 mg/mL. The Refluxed and Macerated extracts of these plants have shown relatively similar results in terms of diameters of inhibition and MICs. The extracts of B. vulgaris, C. monspeliensis and P. granatum demonstrated relatively high activity as compared to the other plant extracts mainly against S. aureus, E. faecalis and E. cloacae. Conclusion: Findings of this study indicate that hydromethanolic extracts of these plants have antibacterial activity against the different tested bacterial strains. This activity supports their use in treatment of infections caused by such resistant bacteria.
Images
Antibacterial activity (inhibition zones, mm) of the tested extracts.