What Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Can Do for You (original) (raw)
Fact Checked
This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Benefits & Techniques
April 30, 2018
- Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Facts About Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- How It Works
- CBT vs. Other Types of Psychotherapy
- Ways to Practice CBT Techniques on Your Own

In today’s society, doctors and psychiatrists are quick to prescribe psychotropic drugs that often come with dangerous side effects for any disorder that stems from thought patterns. But what if I told you there was a better, safer way to manage and treat stress and brain disorders? Enter cognitive behavioral therapy.
According to the National Association of Cognitive Behavioral Therapists, cognitive behavioral therapy (often just called CBT) is a popular form of psychotherapy that emphasizes the importance of underlying thoughts in determining how we feel and act. Considered to be one of the most successful forms of psychotherapy to come around in decades, cognitive behavioral therapy has become the focus of hundreds of research studies. (1)
CBT therapists work with patients to help them uncover, investigate and change their own thought patterns and reactions, since these are really what cause our perceptions and determine our behaviors. Using CBT therapists offers patients valuable perspective, which helps improve their quality of life and manage stress better than patients simply “problem-solving” tough situations on their own.
Something that might surprise you about CBT: A core principle is that external situations, interactions with other people and negative events are not responsible for our poor moods and problem in most cases. Instead, CBT therapists actually view the opposite as being true. It’s, in fact, our own reactions to events, the things we tell ourselves about the events — which are within our control — that wind up affecting our quality of life.
This is great news — because it means we have the power to change. Through cognitive behavioral therapy, we can learn to change the way we think, which changes the way we feel, which in turn changes the way we view and handle tough situations when they arise. We can become better at intercepting disruptive thoughts that make us anxious, isolated, depressed, prone to emotionally eating and unwilling to change negative habits.
Ad
When we can accurately and calmly look at situations without distorting reality or adding additional judgments or fears, we’re better able to know how to react appropriately in a way that makes us feel happiest in the long run.
Related: Operant Conditioning: What Is It and How Does It Work?
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
A 2012 meta-analysis published in the Journal of Cognitive Therapy and Research identified 269 studies that supported the use of CBT for the following problems: (2)
- substance abuse disorders
- schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
- depression and dysthymia
- manic depression/bipolar disorder
- anxiety disorders
- somatoform disorders
- eating disorders
- sleep disorders, including insomnia
- personality disorders
- anger and aggression
- criminal behaviors
- general stress and distress due to general medical conditions
- chronic fatigue syndrome
- muscle pains and tension
- pregnancy complications and female hormonal conditions
Researchers found the strongest support for CBT in treating anxiety disorders, somatoform disorders, bulimia, anger control problems and general stress. After reviewing 11 review studies comparing improvement rates between CBT and other therapy treatments, they found that CBT showed higher response rates than the comparison treatments in seven of the 11 reviews (more than 60 percent). Only one of 11 reviews reported that CBT had lower response rates than comparison treatments, leading researchers to believe that CBT is one of the most effective therapy treatments there is.
Here are some of the major ways cognitive behavioral therapy benefits patients from different walks of life:
1. Lowers Symptoms of Depression
Cognitive behavioral therapy is one of the best-known, empirically supported treatments for depression. Studies show that CBT helps patients overcome symptoms of depression like hopelessness, anger and low motivation, and lowers their risk for relapses in the future.
CBT is believed to work so well for relieving depression because it produces changes in cognition (thoughts) that fuel vicious cycles of negative feelings and rumination. Research published in the journal Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Mood Disorders found that CBT is so protective against acute episodes of depression that it can be used along with, or in place of, antidepressant medications. CBT has also shown promise as an approach for helping handle postpartum depression and as an adjunct to medication treatment for bipolar patients. (3)
Additionally, preventive cognitive therapy (a variant of CBT) paired with antidepressants were found to assist patients who experienced reoccurring depression. The 2018 human study assessed 289 participants then randomly assigned them to PCT and antidepressants, antidepressants alone or PCT with declining use of antidepressants after recovery. The study found that found that preventive cognitive therapy paired with antidepressant treatment was first-rate compared to antidepressant treatment alone. (4)
2. Reduces Anxiety
According to work published in Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, there’s strong evidence regarding CBT treatment for anxiety-related disorders, including panic disorders, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. Overall, CBT demonstrates both efficacy in randomized controlled trials and effectiveness in naturalistic settings between patients with anxiety and therapists. (5)
Researchers have found that CBT works well as a natural remedy for anxiety because it includes various combinations of the following techniques: psycho-education about the nature of fear and anxiety, self-monitoring of symptoms, somatic exercises, cognitive restructuring (for example disconfirmation), image and in vivo exposure to feared stimuli (exposure therapy), weaning from ineffective safety signals, and relapse prevention.
3. Helps Treat Eating Disorders
The Journal of Psychiatric Clinics of North America reports that eating disorders provide one of the strongest indications for cognitive behavioral therapy. CBT has been found to help address the underlying psychopathology of eating disorders and question the over-evaluation of shape and weight. It can also interfere with the maintenance of unhealthy body weights, improve impulse control to help stop binge eating or purging, reduce feelings of isolation, and help patients become more comfortable around “trigger foods” or situations using exposure therapy. (6)
Cognitive therapy has become the treatment of choice for treating bulimia nervosa and “eating disorders not otherwise specified” (EDNOS), the two most common eating disorder diagnoses. There’s also evidence that it can be helpful in treating around 60 percent of patients with anorexia, considered to be one of the hardest mental illnesses to treat and prevent from returning.
4. Reduces Addictive Behaviors and Substance Abuse
Research has shown that CBT is effective for helping treat cannabis and other drug dependencies, such as opioid and alcohol dependence, plus helping people quit smoking cigarettes and gambling. Studies published in the Oxford Journal of Public Health involving treatments for smoking cessation have found that coping skills learned during CBT sessions were highly effective in reducing relapses in nicotine quitters and seem to be superior to other therapeutic approaches. (7) There’s also stronger support for CBT’s behavioral approaches (helping to stop impulses) in the treatment of problematic gambling addictions compared to control treatments. (8)
5. Helps Improve Self-Esteem and Confidence
Even if you don’t suffer from any serious mental problems at all, CBT can help you replace destructive, negative thoughts that lead to low self-esteem with positive affirmations and expectations. This can help open new ways to handle stress, improve relationships and increase motivation to try new things. The Psychology Tools website provides great resources for using CBT worksheets on your own to work on developing affirmative communication skills, healthy relationships and helpful stress-reducing techniques. (9)
Related: What Is Autophobia? How to Treat the Fear of Being Alone
Ad
Related: Benefits of Humanistic Therapy + How It Works
Facts About Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
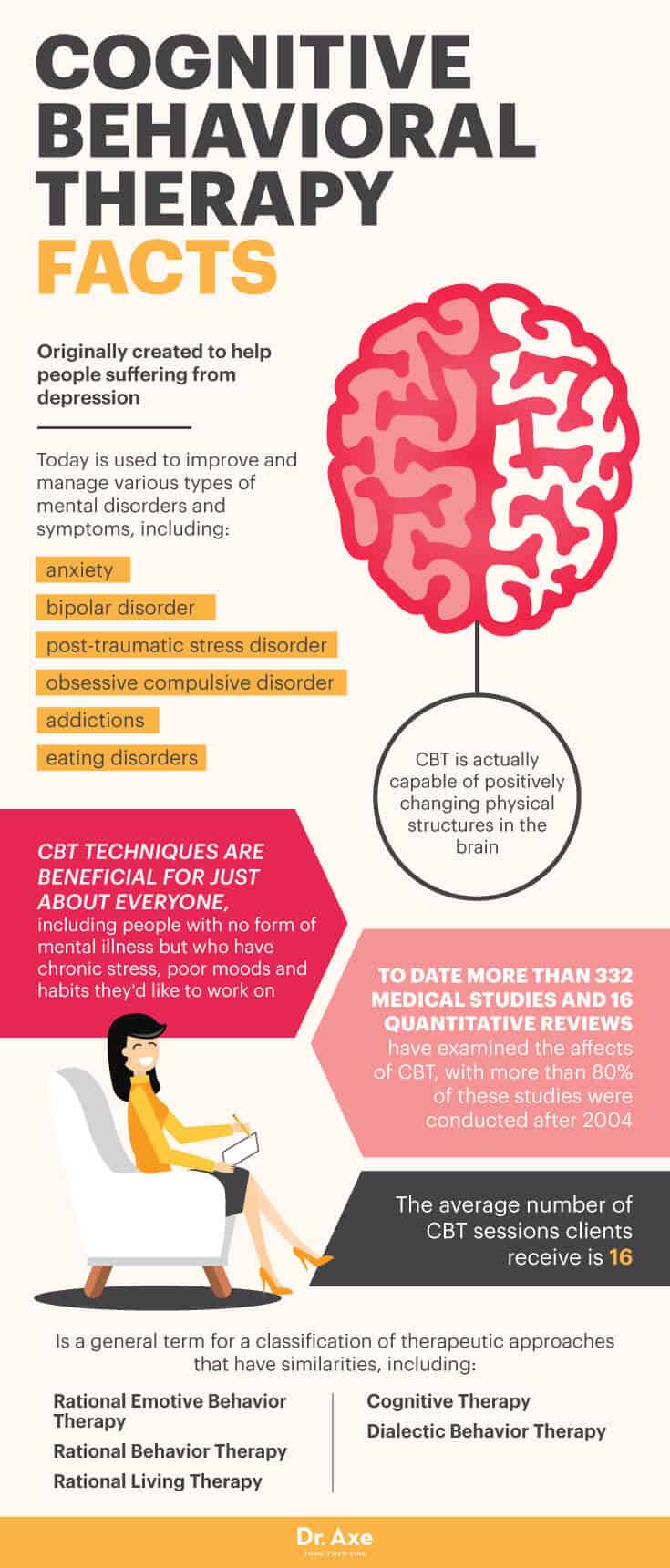
- CBT was originally created to help people suffering from depression, but today it’s used to improve and manage various types of mental disorders and symptoms, including: anxiety, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, addictions and eating disorders. (10)
- CBT techniques are also beneficial for just about everyone else, including people with no form of mental illness but who have chronic stress, poor moods and habits they’d like to work on.
- The term cognitive behavioral therapy is considered a general term for a classification of therapeutic approaches that have similarities, including: rational emotive behavior therapy, rational behavior therapy, rational living therapy, cognitive therapy and dialectical behavior therapy.
- To date, more than 332 medical studies and 16 quantitative reviews have examined the effects of CBT. Interestingly, more than 80 percent of these studies were conducted after 2004. (11)
- Studies have found that in people who have completed CBT programs and then undergone brain scans, CBT is actually capable of positively changing physical structures in the brain. (12)
- CBT can work quickly, helping patients feel better and experience lessened symptoms within a short period of time (several months, for example). While many forms of therapy can take many months or even years to become very helpful, the average number of CBT sessions clients receive is only 16.
- CBT often involves the patient completing “homework” assignments on their own between therapy sessions, which is one of the reasons benefits can be experienced so quickly.
- In addition to homework being done by the patients while they’re alone, cognitive behavioral therapists also use instructions, questioning and “exposure therapy” during sessions. CBT is very interactive and collaborative. The therapist’s role is to listen, teach and encourage, while the patient’s role is to be open and expressive.
- One of the biggest advantages for patients is that CBT can be continued even after formal sessions with a therapist are over. Eventually, formal therapy ends, but at this point the clients can continue to work on exploring CBT concepts, using techniques they’ve learned, journaling and reading to help prolong benefits and manage symptoms.
Related: Aversion Therapy: What Is It, Is It Effective & Why Is It Controversial?
How It Works
CBT works by pinpointing thoughts that continuously rise up, using them as signals for positive action and replacing them with healthier, more empowering alternatives.
The heart of CBT is learning self-coping skills, giving patients the ability to manage their own reactions/responses to situations more skillfully, change the thoughts they tell themselves, and practice “rational self-counseling.” While it definitely helps for the CBT therapist/counselor and patient to build trust and have a good relationship, the power really lies in the patient’s hands. How willing a patient is to explore his or her own thoughts, stay open-minded, complete homework assignments and practice patience during the CBT process all determine how beneficial CBT will be for them.
Some of the characteristics that make cognitive behavioral therapy unique and effective include:
- **Rational approach: CBT theory and techniques are based on rational thinking, meaning they aim to identify and use facts. The “inductive method” of CBT encourages patients to examine their own perceptions and beliefs to see if they are in fact realistic. In CBT, there is an underlying assumption that most emotional and behavioral reactions are learned. Many times with a CBT therapists’s help, patients learn that their long-held assumptions and hypotheses are at least partially incorrect, which causes them unnecessary worrying and suffering. (13)
- Law of entropy and impermanence: CBT rests on scientific assumptions, including the law of entropy, which is essentially the fact that “if you don’t use it, you lose it.” We always have the power to change how we feel because our feelings are rooted in our brains’ chemical interactions, which are constantly evolving. If we break cycles of thought patterns, our brains will adjust for the better. MRI scans show the human brain creates and sustains neural synapses (connections) between frequent thoughts and emotions, so if you practice positive thinking your brain will actually make it easier to feel happier in the future.
- Accepting unpleasant or painful emotions: Many CBT therapists can help patients learn how to stay calm and clear-headed even when they’re faced with undesirable situations. Learning to accept difficult thoughts or emotions as being “simply part of life” is important, because this can help stop a vicious cycle from forming. Often we get upset about our tough feelings and add on even more suffering. Instead of adding self-blame, anger, frustration, sadness or disappointment to already-tough feelings, CBT teaches patients to calmly accept a problem without judgment in order to not make it even worse.
- Questioning and expressing: Cognitive behavioral therapists usually ask patients many questions in order to help them gain a new perspective, see the situation more clearly and realistically, and help them undercover how they really feel.
- Specific agendas and techniques: CBT is usually done in a series of sessions that each have a specific goal, concept or technique to work with. Unlike some other forms of therapy, sessions are not simply for the therapist and patient to talk openly without an agenda in mind. CBT therapists teach their clients how to better handle difficult thoughts and feelings by practicing specific techniques during sessions that can later be applied to life when they’re most needed.
Related: Systematic Desensitization Benefits + How to Do It
CBT vs. Other Types of Psychotherapy
CBT is a type of psychotherapy, which means it involves open talking between patient and therapist. You might have heard of several other forms of psychotherapy in the past and are wondering what makes CBT stand apart. Many times there is some overlap between different forms of psychotherapy. A therapist might use techniques from various psychotherapy approaches to help patients best reach their goals and improve (for example, to help someone with a phobia, CBT might be coupled with exposure therapy).
According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness, here is how CBT differs from other popular forms of therapy: (14)
- CBT vs. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT and CBT are probably the most similar therapeutic approaches, however DBT relies more heavily on validation or accepting uncomfortable thoughts, feelings and behaviors. DBT therapists help patients find balance between acceptance and change by using tools like mindfulness guided meditation.
- CBT vs. Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy that’s often used to help treat eating disorders, phobias and obsessive-compulsive disorder. It teaches patients to practice using calming techniques and small series of “exposures” to triggers (things that are most feared) in order to become less anxious about the outcome.
- CBT vs. Interpersonal Therapy: Interpersonal therapy focuses on the relationships a patient has with his or her family, friends, co-workers, media and community to help evaluate social interactions and recognize negative patterns (such as isolation, blame, jealousy or aggression). CBT can be used with interpersonal therapy to help reveal underlying beliefs and thoughts driving negative behavior toward others.

Related: What Is Art Therapy? Benefits & How It’s Used to Help Heal
Ways to Practice CBT Techniques on Your Own
- Identify your current obstacles: The first step is to identify what’s really causing you stress, unhappiness and unease. Maybe you’re feeling resentful toward someone, fearful of failure or worried about being rejected socially in some way. You might find that you have persistent anxiety, symptoms of depression or are struggling to forgive someone for a past event. Once you can recognize this and become more aware of your primary obstacle, then you have the power to start work on overcoming it.
- Try “thought recording”: You can use a journal or even record your own voice on a tape recorder to help you identify recurring destructive thoughts you frequently tell yourself. Ask yourself questions to dig deeper and form connections you weren’t previously aware of. Then reread your entries as if you were not yourself, but a good friend. What advice would you give yourself? What beliefs of yours can you notice aren’t very accurate, only making matters worse and not overall helpful?
- Form patterns and recognize your triggers: Think about what types of situations make you most likely to feel anxious, upset, critical or sad. Start to form patterns of behaving in certain ways or experiencing certain things (for example, maybe drinking too much alcohol or gossiping behind someone’s back) and how they leave you feeling, so you can start breaking the cycle.
- Notice how things are always changing: Feelings come and go constantly (called impermanence), so knowing that fear, anger or other strongly unpleasant emotions are only temporary can help you stay calm in the moment.
- “Put yourself in their shoes”: It’s important to try and view situations as rationally, clearly and realistically as possible. It helps to consider other people’s perspectives, question your assumptions, and see if there’s something important you might be missing or ignoring.
- Thank yourself and be patient: Even though CBT works quickly for many people, it’s an ongoing process that’s essentially lifelong. There’s always ways to improve, feel happier, and treat others and yourself better, so practice being patient. Remind yourself there is no finish line. Give yourself credit for putting effort into facing your problems directly, and try to view “slip-ups” as inevitable parts of the journey and learning process.
Related: What Is Psychodynamic Therapy? Types, Techniques & Benefits
Final Thoughts
- CBT techniques are also beneficial for just about everyone else, including people with no form of mental illness but who have chronic stress, poor moods and habits they’d like to work on.
- Some of the major ways cognitive behavioral therapy benefits patients from different walks of life includes lowering symptoms of depressions, reducing anxiety, treating eating disorders, reduces addictive behaviors and substance abuse, and helps improve self-esteem and confidence.
- You can practice cognitive behavioral therapy by identifying your current obstacles, trying thought recording, forming patterns and recognizing your triggers, noticing how things are always changing, putting yourself in others’ shoes, and thanking yourself and being patient.

