Dermatologists Often Fail to Treat These Root Causes of Eczema (original) (raw)
This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
What Are Eczema Symptoms? Plus 5 Natural Treatments
November 19, 2016
- What Is Eczema?
- Common Eczema Symptoms and Signs
- Eczema Causes and Risk Factors
- Eczema vs. Psoriasis
- How Common Is Eczema?
- Conventional Treatments for Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis
- 5 Natural Eczema Treatments

Eczema symptoms, which commonly include skin dryness and itchiness, affect about 20 percent of children (roughly one in five) and up to 4 percent of adults. Eczema, along with related skin conditions like dermatitis and allergies, tends to develop most often among people who already have very dry, sensitive skin or a rundown immune system. In adults, symptoms are usually recurrent and more severe than in children, and research shows that infants and children can normally overcome eczema within the first several years of life.
While dermatologists normally choose to treat eczema symptoms with prescription topical creams and sometimes medications used to kill bacteria or alter immune responses, there are also natural treatments for eczema available. These include applying essential oils, reducing food allergies, making dietary improvements, and avoiding irritating skin care or beauty products.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is not one specific condition, but rather a collective term for a group of related skin disorders that cause symptoms like inflammation, redness, dryness and scaling. A diagnoses of eczema can be used to describe any type of dermatitis or “itchy rash.”
While about 2 percent to 4 percent of all adults develop eczema, it’s much more common in babies and children, who tend to already have sensitive skin. Eczema symptoms are all related to inflammation that occurs on the very top layer of the skin. Once the barrier of the skin becomes damaged and dry, due to factors like loss of moisture or allergies that lead to an immune response, sensitivity and irritation can be hard to control.
Several common types of eczema, which develop for various reasons and therefore might be treated in different ways, include:
Ad
- Hand eczema
- Atopic dermatitis (related to allergies)
- Contact dermatitis (mostly caused from irritants)
- Seborrheic dermatitis (mostly causes a dry scalp)
- Dyshidrotic eczema (causes fluid-filled blisters)
- Nummular eczema (causes a rash with coin-shaped blisters, looks similar to ringworm)
- Neurodermatitis (long term itching due to scratching)
- Stasis dermatitis (occurs on the lower extremities)
Common Eczema Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms of eczema can either be short-term (acute) or chronic. Symptoms like itching or peeling tend to come and go, periodically causing flare-ups in response to things like stress and low immune function. Although signs of skin inflammation might clear up for periods of time, most patients experience recurrent symptoms, sometimes over the course of many years if the underlying causes are left untreated. Depending on the specific type of eczema someone has, eczema symptoms and signs can include: (1)
- Inflamed skin, such as skin that appears red and swollen. The hands are the most likely body part to develop eczema symptoms in adults.
- Itchiness. If itching becomes very bad, it’s tempting to scratch the skin, but this actually makes irritation worse (known as the “itch-scratch cycle”).
- Blisters or crusty patches of skin that can crack open, ooze and become scaly
- Peeling, flaking skin due to severe dryness. When eczema develops on the scalp (called seborrheic dermatitis), dandruff is common.
- Developing cuts and cracks in the skin due to severe dryness, which can sometimes lead to bacterial infections
- Changes in skin color and texture, such as skin becoming rougher, darker and thicker
- Sensitivity to products like shampoo, lotion and cleansers
- Burning due to irritation or exposed, raw skin
- If itchiness and other symptoms become very severe, sometimes patients experience other secondary problems like increased stress, trouble sleeping, embarrassment, and difficulty concentrating at work or school
- Atopic eczema, caused by allergies, can sometimes occur along with other symptoms like a fever, fatigue, asthma or respiratory issues
- Eczema has also been found to be common among people with other skin conditions, making treatment complicated, such as herpes or warts
Eczema symptoms in babies and children:
- When babies or children develop eczema, they’re most likely to have redness and dryness on their cheeks, head (known as cradle cap) or chin, in addition to the backs of their arms and legs, chest, stomach, or parts of the back.
- Like in adults, children and babies are susceptible to forming eczema patches of red, sensitive skin on areas of the body that are usually rougher and dryer to begin with. If symptoms last into the teen years or adulthood, they’re likely to affect the palms, hands, elbows, feet or knees.
- Eczema is most likely to develop in babies within the first six months of life but usually clears up on its own as the immune system learns to adapt to and overcome skin inflammation.
- In about 50 percent to 70 percent of all young children or teens with eczema, symptoms will either greatly reduce or completely go away before the age of 15.

Eczema Causes and Risk Factors
Eczema affects the visible, very outer part of the skin called the corneal layer. The corneal layer belongs to part of the skin called the epidermis, which sits on top of the middle layer (called the dermis) and the innermost layer (called the subcutaneous layer).
The corneal layer is important for keeping the body protected from things like microbes or harmful bacteria that can enter through cuts and penetrate into deeper layers of the skin. Because it’s a protective layer, the corneal is constantly renewing itself, shedding old damaged cells and growing new, healthy ones in their place. This process helps keep the barrier of the skin strong and resilient in healthy people without eczema but becomes disrupted in those with eczema due to inflammation.
When someone has eczema, the process of shedding and renewing corneal skin cells becomes disrupted. Reasons for this include: (2)
- Genetic factors, including having a mutated gene that results in reduced production of the protein called filaggrin, which normally helps maintain the corneal layer.
- Reduced serum (oil) production, resulting in very dry skin. This can also be due to genetics or changes in the immune system.
- Low immune function, which leads to inflammation in response to things like yeasts and bacteria that live on the skin. Low immune function can be due to factors like medications, autoimmune disorders, untreated infections, nutrient deficiencies or poor gut health. Sometimes cracks in the skin caused by eczema can lead to infections when a common type of bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, which is found on a high percentage of even healthy adults’ skin, triggers an inflammatory response in susceptible individuals.
- Allergies (called atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema), which cause the release of antibodies and a harmful immune response. Allergic responses can be due to things like consuming certain foods, chemical exposure or contact with other harsh toxins/substances, such as chemical perfumes or soaps. Surprisingly, atopic dermatitis is not linked to things like pet or fur exposure. In fact, the opposite is true: Eczema has been found to be less common in children who have many siblings or dogs or who spend time in day care settings or around other children from a young age. This causes a stronger immune system and built-up protection.
- Toxicity, including from smoking or exposure to high amounts of pollution. “Over-cleanliness” and antibiotic use are other contributors, which negatively affect the immune system.
- People who live in developed countries or colder climates seem to develop eczema more often, due to dry and cold climates or factors like pollution and poor diet.
- In children, being formula-fed seems to raise the risk for eczema. Research shows that breastfed babies have increased protection against allergies that can affect the immune system and skin.
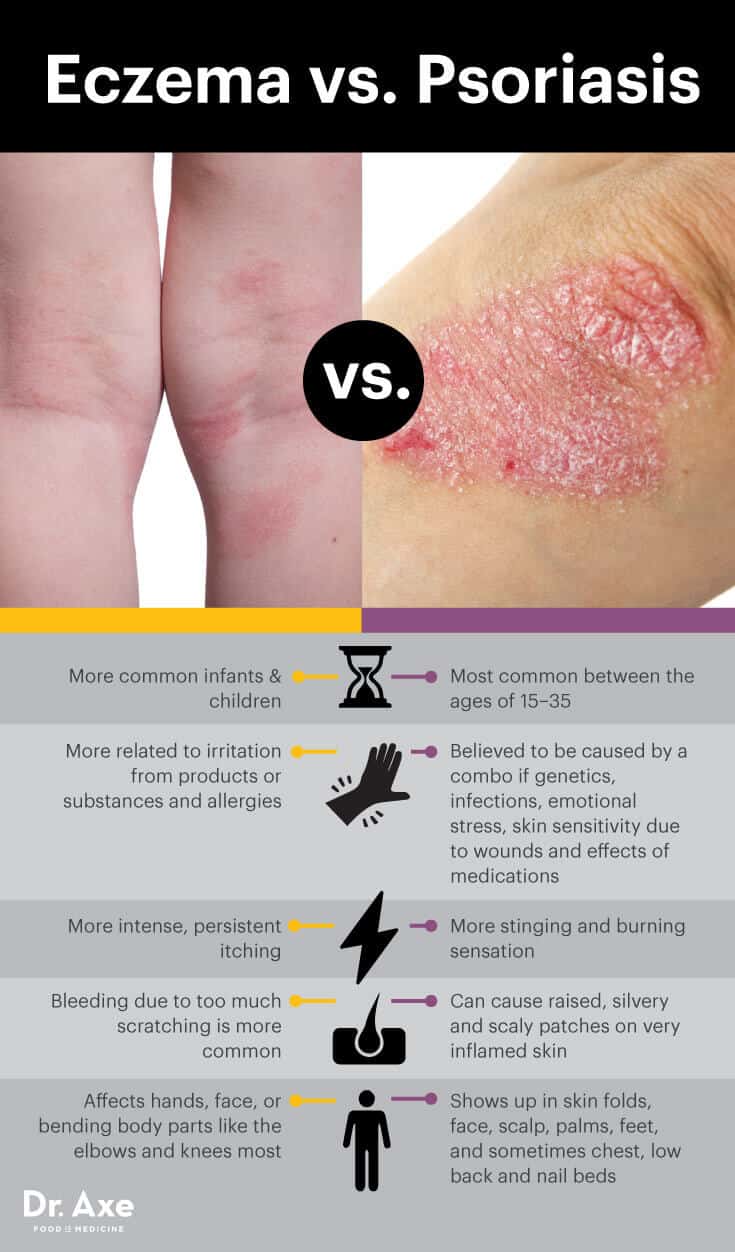
Eczema vs. Psoriasis
- Both psoriasis and eczema cause similar types of skin irritation, including symptoms like itching and redness. Eczema is more common in infants and children, while psoriasis is most common between the ages of 15–35.
- Both conditions can be triggered by low immune function or stress. However, eczema is more related to irritation (from things like skin care products) and allergies. The exact cause of psoriasis remains controversial but is believed to be a combination of genetics, infections, emotional stress, skin sensitivity due to wounds and sometimes effects of taking medications.
- Compared to psoriasis, eczema tends to cause intense, persistent itching that can be very hard to stop scratching. Bleeding due to over-itching is more common with eczema than with psoriasis. (4)
- Although itching and even self-wounding the skin are more common with eczema, psoriasis usually causes more stinging or burning. Burning can occur due to eczema too, but the desire to scratch is usually much more intense.
- In addition to burning, psoriasis can cause raised, silvery and scaly patches to form on very inflamed skin.
- There are also some differences in terms of where symptoms tend to show up. Eczema most commonly causes symptoms on the hands, face, or parts of the body that bend like the elbows and knees. Psoriasis often shows up in skin folds or on places like the face and scalp, palms and feet, and sometimes the chest, low back and nail beds.
How Common Is Eczema?
- Eczema affects about 15 percent to 20 percent of all young children and about 2 percent to 4 percent of adults. Approximately 31.6 million Americans have at least one form of eczema, about 17.8 million of which have allergic (atopic) dermatitis that can be severe.
- Eczema occurs in both men and women, but men seem to be at a greater risk. (5)
- Eczema has been found to be associated with allergies, especially in children. About one in three children who have eczema also develop allergy-related symptoms like asthma or hay fever. (6)
- About 70 percent of eczema cases in children begin before the age of 5.
- 60 percent of infants or children with eczema continue to have symptoms at least periodically during adulthood.
- In American adults, it’s estimated that about 80 percent of contact dermatitis is due to chemical exposure/irritation and about 20 percent is related to allergies.
- At least 11 different disorders related to immune function and allergies can cause eczema symptoms.
- The hands are most commonly affected by eczema. Hand dermatitis accounts for 20 percent to 35 percent of all eczema cases in the U.S.
- Only about 35 percent to 37 percent of people with eczema visit a doctor for a diagnoses.
Conventional Treatments for Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis
There is currently no “cure” for eczema, only ways to help manage eczema symptoms. Dermatologists recommend cleansing affected skin gently, avoiding irritating products, and sometimes talking to a doctor about dietary interventions or medications if necessary. When prescriptions are necessary to control eczema symptoms, treatments normally include some combination of:
- Skin ointments or cream: These are used to add more moisture to dry skin and usually generously applied at least twice a day.
- Soaps and shampoos for sensitive skin: Because many commercial beauty or cleansing products contain irritating synthetic scents and additives that dry skin, special kinds can be given out by dermatologists that cause less reactions.
- Medicated steroid creams: Steroid creams (called corticosteroids) help reduce inflammation and therefore can lower itching or swelling. Because steroid creams can cause side effects at times and cannot be used by all patients, sometimes other ointments called pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are used as alternatives.
- Recently, researchers have been developing treatments that address underlying immune responses that cause skin inflammation. These target specific molecules in the origin or development of eczema, including immune antagonists called interleukin 4 receptors.
5 Natural Eczema Treatments
1. Leave the Skin Alone (Don’t Scratch, Just Soothe!)
Itching caused by eczema can make it very tempting to scratch dry or peeling skin. But scratching has been found to lead to complications because it can cause open cracks or wounds that allow bacteria in. This sometimes causes infections, especially if the immune system is already weakened. It’s safer to try and leave the skin alone while you treat the underlying source of eczema. Applying a salve or moist towel to dry skin can keep you from picking at it.
Instead of scratching, other tips for protecting sensitive, healing skin include avoiding too much UV light/sun exposure, talking to your doctor if you take any medications that might worsen symptoms, keeping skin away from very hot water or very dry, cold temperatures (which can increase irritation), and changing the products you apply to your skin.
2. Reduce Allergies and Inflammation
Food, environmental factors and skin care products can all cause allergic reactions that trigger eczema symptoms. Allergies can be triggered in those with eczema by things like:
Ad
- Chemical-containing soaps, lotions, detergents, disinfectants, etc.
- Dust, pollen, mold, pet hair or debris
- Foods like synthetic additives or preservatives found in packaged products, gluten, dairy, shellfish or peanuts.
- Inflammatory foods like sugar and refined oils might also contribute to symptoms.
3. Breastfeeding and a Healthy Diet
Research suggests that a child’s risk for developing eczema is reduced when the child is breastfed. Into childhood and adulthood, a healthy diet with anti-inflammatory foods can help boost immunity. Foods that might be able to help reduce eczema symptoms are:
- Essential fatty acids — These fats are found in things like wild-caught fish, nuts and seeds.
- Probiotic foods — These include cultured veggies, yogurt, kefir and amasai.
- High-fiber foods — Aim for at least 30 grams of fiber per day to improve gut health from vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, coconut and sprouted grains/legumes.
- High-antioxidant foods — Consume more fresh, brightly colored plant foods to reduce inflammation and get plenty vitamins, minerals and electrolytes.
4. Supplement to Improve Immune Function
Supplements that might be able to help control eczema irritation are:
- Probiotics (25–100 billion organisms daily): Research shows that probiotic supplements can have protective and preventive effects when it comes to skin health. They’re linked with improved gut health and immune function, along with other related factors like decreased allergies.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (1,000 milligrams daily): Help lower inflammation.
- Antioxidants (such as vitamins E, C and A): Antioxidants can help prevent skin damage, reduce inflammation and promote wound healing.
- Vitamin D3 (2,000–5,000 IU daily): The “sunshine vitamin” helps regulate immune functions and is a very common deficiency.
5. Applying Healing Oils to the Skin
Certain natural essential oils, such as lavender essential oil, which has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, might help keep sensitive skin from flaring up. Make your own homemade eczema cream by combining hydrating, antibacterial ingredients like**lavender oil,** tea tree, raw honey, coconut or shea butter. You can also use products like probiotics, geranium essential oil and/or myrrh essential oil on sensitive skin.
Precautions When Experiencing Eczema Symptoms
Complications can sometimes develop due to eczema, especially when symptoms become very severe and scratching is continuous. This can lead to wounds, infections, scarring and spreading of symptoms. If you notice eczema symptoms for the first time and aren’t sure of the cause, talk to your doctor. It’s important to distinguish between different skin conditions in order to control symptoms and treat the underlying cause.
Final Thoughts on Eczema Symptoms
- Eczema is a collective term for a group of related skin disorders that cause symptoms like skin itching, redness, dryness and scaling.
- Causes of eczema include allergies, irritation from products, low immune function, stress and very cold, dry climates that irritate skin.
- Natural treatments for eczema symptoms can include applying coconut oil and essential oils, using a warm towel to soothe skin, reducing allergies, and taking supplements to improve gut health and immunity.

