CBD vs. THC (original) (raw)
Evidence Based
This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
CBD vs. THC: What Are the Differences?
March 5, 2019
- The Main Difference Between CBD and THC
- Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
- CBD vs. THC: How They Compare
- Are THC-Free CBD Products Safer?
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide medical advice or to take the place of medical advice or treatment from a personal physician. All viewers of this content are advised to consult their doctors or qualified health professionals regarding specific health questions. Neither Dr. Axe nor the publisher of this content takes responsibility for possible health consequences of any person or persons reading or following the information in this educational content. All viewers of this content, especially those taking prescription or over-the-counter medications, should consult their physicians before beginning any nutrition, supplement or lifestyle program.
One of the biggest concerns among CBD beginners is whether or not it causes a “high.” Many people want to take advantage of the many CBD oil benefits, without feeling “out of it” after using it. Fortunately, and in part explaining the tremendous popularity of CBD, that’s exactly what happens: CBD health benefits, without the unwanted psychoactive or intoxicating side effects.
Indeed, when you look at the components of CBD vs. THC, there’s one major difference — the type of mind-altering effects. That’s not to say that THC doesn’t have health benefits, too. In fact, both compounds show potential benefits.
So when considering CBD vs. THC — you may want to know the main difference between the two.
The Main Difference Between CBD and THC
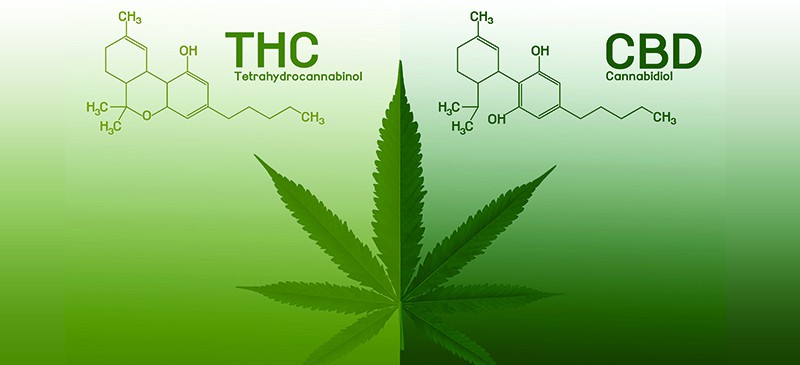
CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are both compounds that come from the ancient plant Cannabis sativa and can be found in cannabis oil. THC is the compound in cannabis that produces intoxicating effects, while CBD is the major non-intoxicating component in the plant species.
Chemical Structure
The chemical composition of CBD and THC are exactly the same, with both containing 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. The major difference between the structure of these compounds is the arrangement of a single atom. Considering that an atom is a very, very tiny particle, this small difference in chemical structure makes a huge impact when it comes to the effects of these compounds.
Psychoactive Effects
Here’s the major difference between THC and CBD: THC has what can be called “unwanted” psychoactive effects that give you that high, euphoric feeling, while CBD has non-intoxicating effects. So while THC contributes the most to cannabis psychoactivity among all cannabinoids, research shows that CBD has certain properties and positive effects against some negative psychological reactions caused by THC.
It’s important to note that CBD is often referred to as “non-psychoactive,” but it turns out that this is a misrepresentation of the cannabinoid. CBD is actually psychoactive. What does this mean? By definition, a psychoactive compound affects the mind and behavior. This means that it has the ability to affect brain function and outlook, perception, cognition and behavior.
Because CBD works on the central nervous system, both directly and indirectly, it does have these effects. So yes, CBD is psychoactive, which is what is thought to also give it its benefits. In fact, all cannabinoids are psychoactive, in different ways and to different degrees.
Both CBD and THC are psychoactive, as they both affect the mind, but there is one major difference in the way they make you feel — unlike THC, CBD is non-intoxicating. Using THC may alter your senses and increase your hunger. It may even make you feel out of control, depending on the way your body reacts to the cannabinoid. With CBD, you will generally not experience noticeable changes, which is what makes it more appealing to so many people.
Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
When scientists started studying the beneficial effects of cannabis, specifically those of THC, they discovered a biochemical communication system in the body — now called the endocannabinoid system. We are just beginning to understand this body system and already it’s believed to be one of the most important physiological systems involved in maintaining our health. It plays a role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that the body has a stable and well-functioning internal environment.
The system is made up of endocannabinoid receptors that respond to cannabinoid compounds the body makes on its own, and also those found in the cannabis plant species and a number of other plants. These receptors are found throughout the brain and body. Of the 100+ cannabinoids that have been identified in the cannabis species, CBD and THC have been studied the most extensively for their effects on the endocannabinoid system.
Researchers have identified two major types of cannabinoid receptors — CB1 and CB2. Plus, additional receptors for cannabinoids are being explored extensively. Receptors respond to environmental stimuli, like chemical messengers, and produce an effect within our cells. CB1 receptors are found in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2 receptors are found in our immune cells. In fact, recent discoveries suggest that more than half of all the receptors in the brain are cannabinoid receptors!
We have what’s called “endogenous cannabinoids,” which are neurotransmitters, or chemical messengers, that bind to cannabinoid receptors. But compounds found in cannabis, like THC, also bind to cannabinoid receptors, mimicking the effects of messengers found within the human body. Receptors react to cannabis compounds and produce a specific effect, which can benefit many body parts and bodily processes.
We know that THC works as a chemical messenger, but the role of CBD is a little less clear. CBD works on the central nervous system, and it modulates several non-cannabinoid receptors and TRPV1.
So what happens when the endocannabinoid system becomes underactive or overactive? The body will begin to become imbalanced and can no longer remain in a homeostatic state. This is being referred to as “endocannabinoid system dysfunction,” and it may lead to an overall imbalance.
Just like any other body system, endocannabinoid system dysfunction can be the result of dietary choices, lifestyle factors and other issues. This is how using CBD and other compounds found in cannabis may come into the picture.
CBD vs. THC: How They Compare
CBD and THC are similar in some ways; however, many people choose to use CBD and avoid THC because they prefer not to feel any intoxicating effects. This THC drawback explains why CBD is gaining popularity among consumers who are looking to take advantage of the properties of cannabis, without feeling high for it.
While more research needs to be conducted, some research shows that CBD generally has a better safety profile than other cannabinoids, including THC. Higher doses seem to be well tolerated in humans and animals.
Are THC-Free CBD Products Safer?
THC-free CBD products are often deemed safe and just as effective as those containing CBD with trace amounts of THC. But as more research is conducted, we are finding out that the two compounds actually have what’s called “complementary effects,” which means that when they are used in combination, it can compound their effects.
The beneficial properties of THC is often downplayed because of the compound’s controversial intoxicating effects. This, combined with the misrepresentation of CBD as a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, tends to make people believe that THC is questionable. This notion has been troublesome for the advancement of whole plant cannabis and it promotes the “othering” of THC.
However, when trace amounts of THC are used in CBD products, the benefits are likely greater.
Some research findings indicate that CBD isolates with no THC may not be as effective as full-spectrum products that contain high amounts of CBD and trace amounts of THC. These very small amounts of THC will not leave you feeling “high” or intoxicated, but will work with CBD and other cannabinoid compounds in the product to have greater beneficial effects.
Related: 10 Herbs and Superfoods with Cannabinoids Similar to Cannabis
Final Thoughts
- CBD and THC are both compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant species. They have similar benefits, but one major difference — THC has greater mind-altering effects, while CBD is non-intoxicating.
- When it comes to their benefits, both CBD and THC work in similar ways.
- What’s next for CBD and THC? Emerging research suggests that a combination of cannabinoids can be even more beneficial than using just one.
Read Next: CBD Oil for Dogs