The Supplement for Osteoarthritis Pain (original) (raw)
Evidence Based
This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Chondroitin Benefits for Osteoarthritis & Joint Pain
May 24, 2023
- What Is Chondroitin?
- How Chondroitin Works
- Benefits
- Chondroitin with Glucosamine
- Supplements and Dosage
- Risks and Side Effects

Chondroitin is one of the most sought after joint supplements available on the market today, due to how it helps rebuild cartilage naturally and boosts recovery of tissue after injury or exercise.
As an important structural component of cartilage and one of the key substances that allows joints to withstand pressure, chondroitin is taken by many people with joint pain, osteoarthritis, and other signs of “wear and tear” due to aging. It’s commonly available in formulas containing similar and complimentary supplements, especially glucosamine and methylsulfonylmethane (MSM).
Although not every study has shown that chondroitin is capable of helping everyone who experiences joint pain, many studies do show support for its effectiveness and also safety.
Aside from offering relief to those with arthritis, chondroitin (and glucosamine) may help people dealing with conditions like chronic knee pain or sacroiliac pain (SI joint pain) that causes upper leg and lower back pain discomfort.
What Is Chondroitin?
Chondroitin is a natural substance found in the human body and a major component of cartilage. Drinking bone broth is probably the greatest way to obtain both glucosamine and chondroitin at home from a real food source, which is why it’s recommend as part of any arthritis diet plan. When found in supplement form, chondroitin can either be derived naturally from the cartilage of animals (including cows, pigs or sharks) or man-made.
The form of chondroitin made in laboratory settings is called chondroitin sulfate, which is a combination of chondroitin and mineral salts that help improve its absorption.
What do chondroitin supplements do? Both natural and laboratory-made chondroitin help build connective tissue throughout the body, including those that form joints and the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Because it works by retaining water, chondroitin benefits include helping to add lubrication and flexibility to stiff or damaged tissues and joints.
How Chondroitin Works
Chondroitin is a major component of the human extracellular matrix (ECM), which is a component present within all tissues and organs that provides physical “scaffolding” for tissues. The ECM is composed of water, proteins and polysaccharides.
Chondroitin helps link together sugar and protein molecules and serves an important role in maintaining the structural integrity of tissue. Its primary benefit and mechanism of action is stimulating regeneration of cartilage, which is the connective tissue that cushions the ends of bones within joints.
Within chondroitin are tightly packed sulfate groups that form a barrier that can withstand compression, shock and even electrostatic charges that damage tissue. Chondroitin is technically a form of a complex carbohydrate, giving it shock and water-absorbing capabilities and making it crucial for allowing joint/bone movement without friction. This is why the loss of chondroitin from cartilage is a major cause of osteoarthritis that degenerates joints.
It’s also important for forming tissue elsewhere in the body, including the skin, GI tract and the brain. In regard to the the brain’s extracellular matrix, it helps stabilize normal brain synapses and protects the brain from injury. Following trauma to the brain, levels of chondroitin are increased rapidly to help regenerate new tissue in order to replace damaged nerve endings.
Benefits
1. Helps Treat Osteoarthritis Joint Pain
Estimates show that over 27 million adults in the U.S. live with osteoarthritis, which is the most common type of arthritis and degenerative joint disease that’s characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and increased joint pain. Chondroitin sulfate is commonly used to treat pains associated with osteoarthritis, especially forms that affect very susceptible body parts like the knees and hands.
Overall, studies have shown that use of chondroitin tends to cause modest improvements in joint pain over the course of several months, although some people experience even more benefits and more quickly — especially when combining several supplements together and making other changes like eating an arthritis diet to treat symptoms.
The University of Utah’s School of Medicine conducted the largest-ever clinical study investigating the effects of chondroitin and glucosamine, called “The Glucosamine/Chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial (GAIT).” According to reports released by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, GAIT is the first large-scale, multicenter clinical trial in the U.S. to test the effects of the dietary supplements glucosamine hydrochloride (glucosamine) and sodium chondroitin sulfate (chondroitin sulfate) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
- The GAIT study compared the effects of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate (used separately and also in combination) to effects of a placebo and also a prescription drug.
- 16 rheumatology research centers across the U.S. and over 1,500 patients participated in the study, which lasted six months.
- Patients received one of five treatments over the course of six months, including the use of glucosamine and chondroitin, celecoxib (a popular prescription drug used for managing osteoarthritis pain) or a placebo. A positive response to any treatment was defined as a 20 percent or greater reduction in pain after six months compared to the start of the study.
- Results of the GAIT study showed that for participants with moderate to severe pain, glucosamine combined with chondroitin sulfate provided statistically significant pain relief compared with the placebo — about 79 percent had a 20 percent or greater reduction in pain versus about 54 percent for placebo group.
- Chondroitin and glucosamine actually worked for more people than the prescription did — 70 percent of participants in the celecoxib group experienced pain relief compared to placebo.
- However, for participants in the mild pain subset, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate seemed to do less to reduce their pain. These participants on average didn’t experience statistically significant pain relief like those with more severe pain did.
Results from another randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that appeared in Arthritis and Rheumatism tested the effects of chondroitin taken by 162 symptomatic patients with osteoarthritis of the hand. The results showed that patients who experienced chronic hand pain and took 800 milligrams of chondroitin sulfate (CS) daily experienced on average modest pain relief, reduced morning stiffness and improvements in overall functionality within three to six months of regular use.
Researchers also found that the majority of patients experienced no adverse side effects due to chondroitin, which often can’t be said of other painkilling medications that can cause adverse effects like stomach ulcers, dependence, digestive issues, blood pressure problems and more. The researchers’ conclusion was that “CS improves hand pain and function in patients with symptomatic OA of the hand and shows a good safety profile.”
2. Helps with Injury and Exercise Recovery
Even for people without osteoarthritis, there’s evidence suggesting that chondroitin used with glucosamine helps preserve valuable cartilage, decreases pain, increases physical function and enhances self-care activities.
It can reduce joint stress following exercise or injury by helping the body synthesize new cartilage, keeping joints flexible and controlling the body’s natural inflammatory responses.
3. Improves Wound Healing and Skin Health
Chondroitin and glucosamine are also used together to help heal wounds, skin-related defects, inflammation of the skin and even in veterinary medicine. Chondroitin can help the body produce collagen, which is essential for skin health, healing and fighting the effects of aging on the skin.
Treatments made using chondroitin and glucosamine are often used for wound dressing even for severe wounds, plus applied over scrapes, burns and lesions to keep wounds moist and promote faster recovery. Some studies have even found that in patients with burns requiring skin grafting, the use of chondroitin in treatment gels can speed up healing time and help control inflammation significantly.
Another substance/supplement that chondroitin may be combined with to improve skin health is hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid is found in skin, eye sockets, all bones, connective tissue, joints, tendons and cartilage structures throughout the body — especially a type called hyaline cartilage, which covers the ends of bones and provides cushioning. It’s a lubricating, clear substance that’s produced by the body naturally to increase moisture and provide elasticity and flexibility.
The primary way in which hyaluronic acid helps improve appearance of “chronoaged skin” (skin aged due to sun exposure) is by reducing water loss and therefore dryness, dandruff, drooping eyes or lips, and sagginess/loss of volume. You can find hyaluronic acid lotions, creams, serums and supplements sold in health food stores, plus it’s also a naturally occurring ingredient in bone broth,
Because it helps form synovial fluid and can buffer bones while providing resistance to wear and tear, hyaluronic acid is also useful for lowering pains and tenderness associated with degenerative joint diseases.
Chondroitin with Glucosamine
Chondroitin and glucosamine are often used together because they have similar mechanisms of lowering inflammation and treating pain — plus they’re considered very safe and pose little risk for side effects. You might also find formulas made with glucosamine, chondroitin and MSM.
What is glucosamine, and how is it different than chondroitin? Like chondroitin, glucosamine is a natural anti-inflammatory compound found in human cartilage and connective tissue. Technically, glucosamine is an amino sugar that the body produces and distributes wherever tissue is located. It’s naturally abundant in fluids that surround joints and in supplement form is sold for the same purposes as chondroitin sulfate.
Studies have found that glucosamine has cartilage-regenerating effects and boosts the strength and flexibility of joints. Glucosamine sulfate is the form most often used today to treat joint pains and osteoarthritis, which is a combination of glucosamine and mineral salts that the body can absorb easily.
What is glucosamine and chondroitin used for? Chondroitin used with glucosamine can help lower symptoms associated with loss of collagen and cartilage, which are found in tendons, joints, ligaments, skin and the digestive tract. These conditions can include tendonitis, bursitis and so on.
In healthy people, when cartilage becomes damaged due to overuse, injury or inflammation, new cartilage is normally produced to take its place. Unfortunately, as we get older our ability to regenerate lost cartilage and repair damaged connective tissue becomes less efficient.
In both humans and animals, glucosamine and chondroitin stimulate the production of new cartilage and can also help reduce inflammation in the process. Is glucosamine and chondroitin effective? To date, more research has been done in regard to glucosamine’s benefits, although the two are very often combined for better results. When taken together benefits include:
- reduced joint pain
- improvement in functionality for patients with arthritis
- improved skin health
- better digestive function
- bone healing
- faster wound healing
Supplements and Dosage
Supplements containing chondroitin can go by many different names depending on the product’s specific formula: chondroitin glucosamine, glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate are all names you might encounter, for example. While the terminology might seem confusing, the various forms available can mostly all be used in same way.
Look for chondroitin supplements in health food stores, major details that sell supplements, or online. If you’re unsure about whether chondroitin or glucosamine are right for you to take, ask your healthcare provider first — especially if you take other medications, such as pain killers.
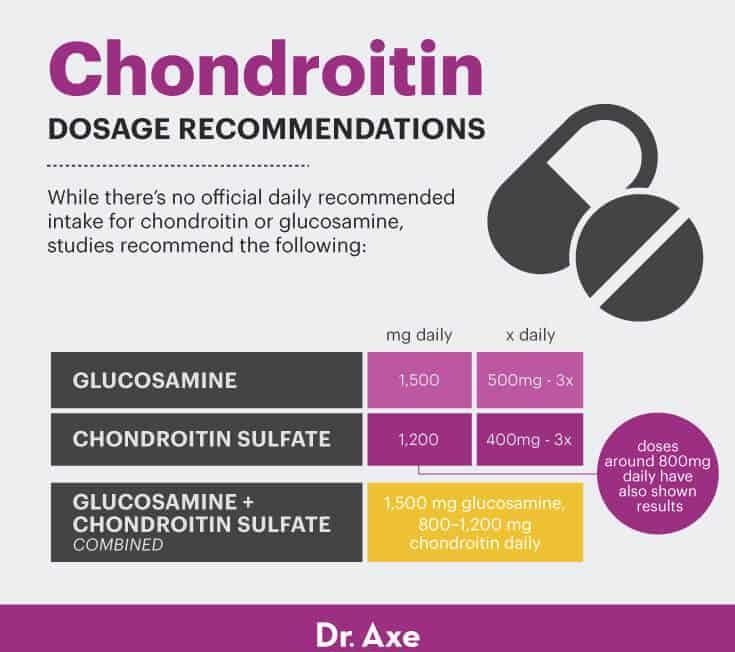
At this time, there isn’t a daily recommended intake for chondroitin or glucosamine. The GAIT study used these supplements in the following dosages:
- Glucosamine when used alone: 1,500 milligrams daily, taken as 500 milligrams three times a day.
- Chondroitin sulfate dosage when used alone: 1,200 milligrams daily, taken as 400 milligrams three times a day. Other studies have used doses around 800 milligrams daily and still seen some results.
- Glucosamine plus chondroitin sulfate combined: same doses — 1,500 milligrams and 800–1,200 milligrams daily.
- All participants in the GAIT study also look an over-the-counter painkiller (acetaminophen) regardless of which treatment group they were in. Over-the-counter painkillers have been found to be safe with use of these two supplements, so participants were allowed to take up to 4,000 milligrams (500-milligram tablets) per day to control pain except for the 24 hours before pain was assessed.
Risks and Side Effects
What are the side effects of taking glucosamine and chondroitin? Both glucosamine and chondroitin have been found to be as safe as placebo (fake pills or sugar pills used in “blind studies”) and cause fewer side effects than some other medicines. Today, these supplements are available in tablet, capsule, powder or liquid form and can be safely consumed with most medications or other dietary supplements.
However, chondroitin may interact with the anticoagulant (blood-thinning) drug warfarin (Coumadin), so check wit your healthcare provider before taking this supplement if you’re using that drug.
Although these supplements are unlikely to cause strong side effects and can help control your pain naturally, they won’t necessarily work for every person. Therefore, they shouldn’t take the place of your other medications unless you’ve discussed this with your healthcare provider. It seems like these supplements are most helpful when used long term and in combination with other lifestyle factors — like an anti-inflammatory diet, exercise, stretching and stress reduction.
For the most effectiveness, a brand of high-quality chondroitin that combines several substances together should be taken for at least three months and used in proper doses. You’re more likely to experience chondroitin side effects if you take very high doses, so always read dosage directions carefully.
The good news is that these supplements are safe to take even if you’ve had problems with other painkillers. Studies show that using these supplements regularly for up to three years poses little risk for side effects.
How much benefit you get from taking them ultimately depends on your starting level of inflammation, the amount of joint deterioration you’ve experienced, your medical history and other lifestyle choices. Some studies have reported potential chondroitin side effects (or those from glucosamine-chondroitin combinations) that include: abdominal pain, heartburn, drowsiness, headaches and allergic reactions (especially if you have an allergy to shellfish).
Final Thoughts
- Chondroitin is a natural substance that helps build cartilage which helps cover the ends of bones and allows them to glide and move smoothly.
- What is chondroitin sulfate used for? Chondroitin benefits include supporting joints’ flexibility and lubrication, which aids in exercise recovery and helps fights inflammation, stiffness and pain. It can be used in place of NSAIDs in patients who need long-term treatment and help with pain management, including those dealing with arthritis/osteoarthritis or chronic injuries.
- Glucosamine, chondroitin and MSM are often used together to support joint health. Chondroitin and glucosamine are both considered to be very safe and effective ways to lower joint pain, plus they are associated with less side effects then most pain-killing medications.
- Most people do not experience chondroitin side effects, however, some will not notice significant improvements in pain when using these products.