How to Create an ArrayList in Java (original) (raw)
To store dynamically-sized elements in Java, we used ArrayList. Whenever new elements are added to it, its increase their size automatically. ArrayList implements Java’s List Interface and part of Java’s Collection.
Because of their functionality and flexibility, it is widely used.
Key Points of an ArrayList
- An
ArrayListis a re-sizable array, also known as a dynamic array. It raises its size according to new elements and decreases the size when the elements are removed. - An array is used to store an element in
ArrayListinternally. It allows you to retrieve the elements by their index. - Java
ArrayListclass permits duplicate and null values. - Java
ArrayListclass is a well-ordered collection. It keeps the insertion order of the elements. - In
ArrayList, you cannot create anArrayListof primitive types like int, char, boolean, etc. You must use boxed types like Integer, Character, Boolean etc.
Hierarchy of ArrayList
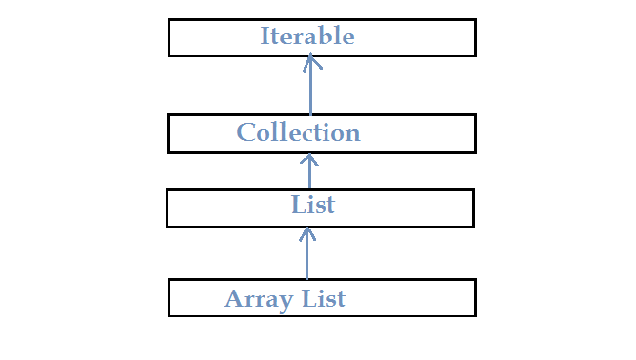
ArrayList implements the List Interface extends Collection extends Iterable.
In Java, we can create ArrayList by creating this simple statement:
ArrayList arlist = new ArrayList( );
In above syntax, list is of “String” type, so the elements are that going to be added to this list will be string type. The type decide which type of elements list will have.
ArrayList arlist = new ArrayList( );
Above syntax, is accepts int elements.
How to Add Elements?
To add an element in ArrayList, we can use add( ) method. This method has variations, which is use depends on requirements.
Syntax
arlist.add(“JavaTpoint”);
Add elements at the particular location, we can write method like this:
arlist.add(2, “JavaTpoint”);
Example 1
class ArrayList1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> ArrayList<String>();
arlist.add("JAVA");
arlist.add("Csharp");
arlist.add("Python");
arlist.add("Php");
arlist.add("Android");
arlist.add("HTML");
//Adding "C++" at the sixth position
arlist.add(5, "C++");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(arlist);
}
}Output:
[JAVA, Csharp, Python, Php, Android, C++, HTML]
How to Remove Elements
To add an element in ArrayList, we can use the remove( ) method. This method also has variations.
class ArrayList1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> ArrayList<String>();
arlist.add("JAVA");
arlist.add("Csharp");
arlist.add("Python");
arlist.add("Php");
arlist.add("Android");
arlist.add("HTML");
//remove "C++" from the sixth position
arlist.remove("C++");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(arlist);
}
}
class ArrayList1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> ArrayList<String>();
arlist.add("JAVA");
arlist.add("Csharp");
arlist.add("Python");
arlist.add("Php");
arlist.add("Android");
arlist.add("HTML");
//remove "C++" from the sixth position
arlist.remove("C++");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(arlist);
}
}Output: [JAVA, Csharp, Python, Php, Android, HTML]
Methods of Java ArrayList
There are many methods in Java ArrayList, but we explain here some main methods:
| Int Siz() | returns the elements present in the list. |
|---|---|
| Void trimToSize( ) | Used to trim the capacity from list’s current size to ArrayList instance. |
| E set(int index, element) | replace the elements with the specified position. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | remove the first instance of the detailed element. |
| set(int index, Object o) | It is used to update an element. Replace the element with object o. |
| Object get(int index) | returns the object of the list |
| boolean isEmpty( ) | returns true if list is empty. |
Constructors of Java ArrayList
| ArrayList( ) | built an empty array list. |
|---|---|
| ArrayList(Collection<? extends E>c ) | built an array list that is initialized with the elements of the collection c |
| ArrayList(int capacity) | built array list that has the specified initial capacity. |
Further Reading
Different Approaches to Sorting Elements of an Arraylist in Java
ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector
If you enjoyed this article and want to learn more about Java Collections, check out this collection of tutorials and articles on all things Java Collections.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.