Home – EMIT (original) (raw)

EMIT delivers first-of-a-kind maps of minerals in Earth’s dust-source areas, enabling scientists to model the fine particles’ role in climate change and more. Read More ›

EMIT will be the first instrument to use NASA-invented imaging spectroscopy technology to comprehensively measure the mineral composition of the Earth's arid land dust source regions.

Extended Mission Approved!
In early 2024, EMIT passed into an extended mission phase of operations. This means that the EMIT sensor will continue to collect data from its vantage point on the International Space Station through at least 2026. The EMIT team looks forward to supporting additional data collection, the newly announced ROSES funded Research and Applications Team, and the user community in the coming years.
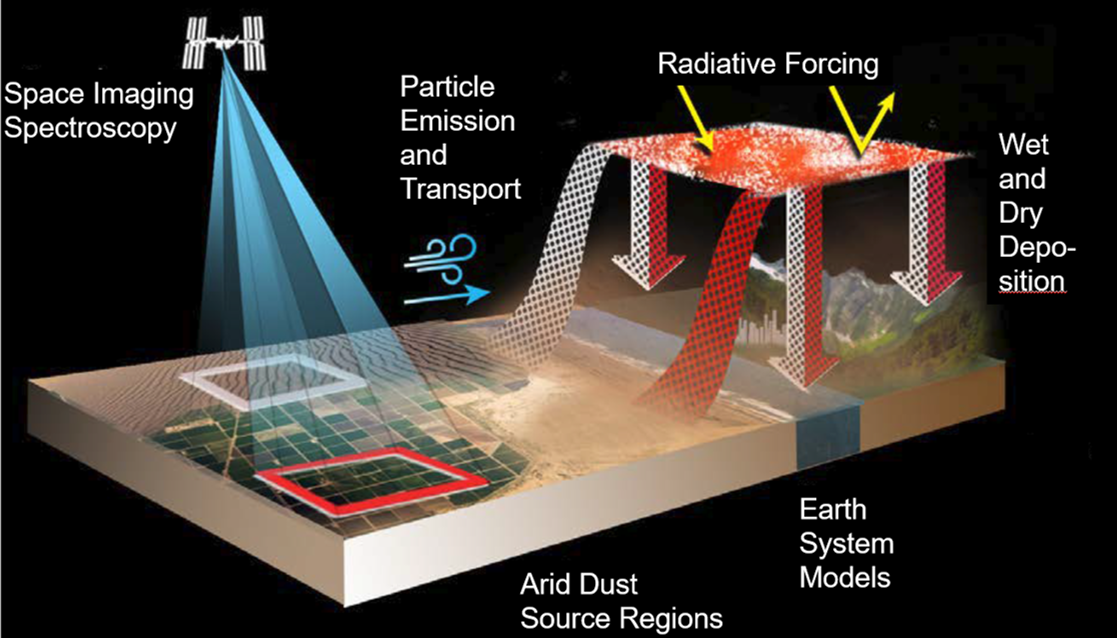
EMIT Mineral Dust Source Measurements Close a Gap in Our Knowledge
Mineral dust blown into the air is an important part of the Earth system. Wind blows dust into the atmosphere from desert regions around the world, and can carry dust across oceans. Dark minerals that absorb sunlight can warm the Earth, while light-colored minerals can cool the Earth. By accurately mapping the composition of areas that produce mineral dust, EMIT will advance our understanding of dust’s effects throughout the Earth system and to human populations now and in the future.
In 2020, winds in Africa blew surface mineral dust into the atmosphere that then crossed the Atlantic Ocean and affected states from Florida to Texas. Mineral dust has many impacts to the Earth. Today we know mineral dust originates in the arid land regions of our planet, but we know very little about the composition. EMIT will make new measurements of the source regions to be used with advanced Earth system models to close this knowledge gap and answer key science questions.
Meet the Team
The EMIT Science Team is comprised of leaders in the fields of Earth System Modeling, mineral dust aerosols, surface geology, and imaging spectroscopy.
About the Instrument
Imaging Spectroscopy
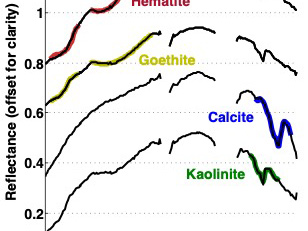
The EMIT instrument is an imaging spectrometer — a NASA invention widely used in the agency’s space missions — that will measure light in visible and infrared wavelengths. When the various wavelengths of light – the spectrum – are distributed across the instrument’s detector, they display unique spectral signatures indicating the mineral composition of the surface. EMIT will acquire over 100,000 such spectra every second, mapping the composition of minerals on Earth’s surface.
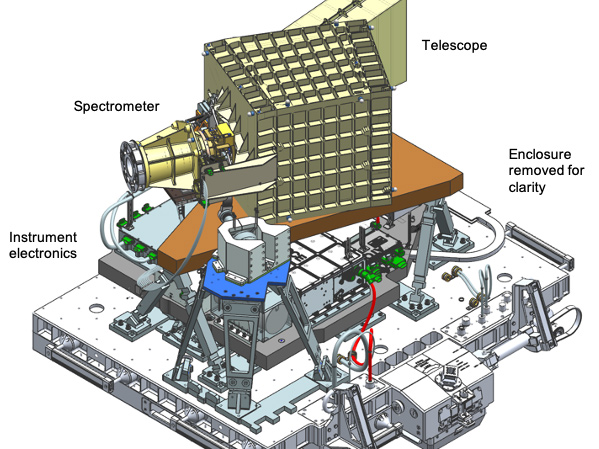
Inside EMIT
EMIT incorporates multiple advanced new technologies. Its Dyson spectrometer optical layout provides exceptionally high photon throughput, meaning the optics maximize the light reaching the detector. The detector array uses new custom coatings to maximize sensitivity over the full EMIT wavelength range. Across EMIT’s 39-mile (72-kilometer) field of view, the instrument has a uniform spectral response. This allows use of the most advanced data processing algorithms.
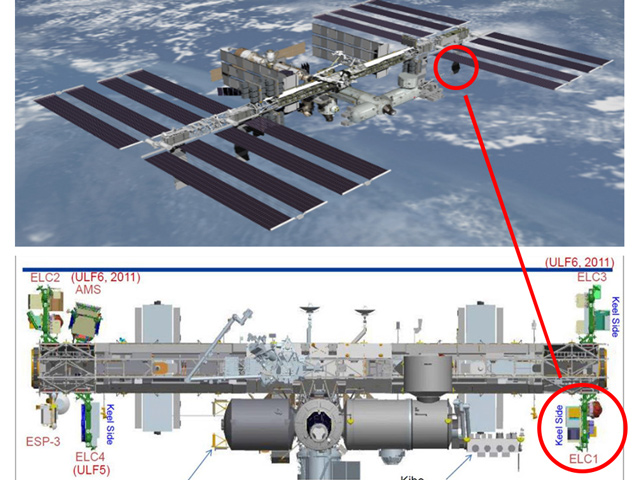
Destination
EMIT was launched with a SpaceX rocket to its destination on the International Space Station (ISS).