magnet survey (original) (raw)
ABOUT
USERS
RESEARCH
INDUSTRY
MEDIA LIBRARY
NEWS-EVENTS
-
- Project
- Consortium
- Novel access modes
* Dual Access
* Fast-track access
* First time access
* Long-term access
* Technical development access - EMFL future magnet survey
- Workshops
* Laboratory High Energy Density Plasmas (LaB)
* Perspectives with High Magnetic Fields at Neutron Source
* Free Electron Lasers & High Magnetic Fields
* Frontiers of Synchrotron & XFEL research - Events
- News
- Documents
- Intranet
* Intranet Register
* Intranet Login
magnet surveyEva Bezgousko2023-01-12T13:15:53+00:00
What are the objectives of this survey ?
Our aim is to establish a roadmap for the development of new magnets based on the needs of our users.
How long is the survey and what if I am only interested in very specific magnet types ?
There are no mandatory parts. Participants may skip magnets and magnet categories at their convenience. Navigation buttons and intermediate tables of contents are provided to facilitate a rapid completion of relevant parts.
How is the survey organized ?
The survey lists potentially interesting magnets organized in 4 categories. Participants are invited to choose magnets that are essential for their research and rate the importance of specific parameter values by selecting one of the options; useful, important or extremely important.
What if the magnet I want doesn’t appear in the list ?
A text field at the end of the survey permits additional suggestions. Alternatively, participants may send their ideas tomagnets.survey@lncmi.cnrs.fr
Is the survey anonymous ?
Participants are asked to enter their scientific domain at the end of the document. It is also possible to leave your name, institution and e-mail address but there is no obligation to do so. This survey does not contain any trackers, please make sure to press the "submission" button in order to save your answers.
Table of contents
- Standard geometry magnets at the EMFL facilities
- Facility magnets with specific experimental access or geometry
- Facility magnets with specific time dependence
- Mobile installations
PART 1 : STANDARD GEOMETRY MAGNETS AT THE EMFL FACILITIES
CATEGORIES
- DC Magnets : 30-60 T
- Pulsed magnets: 60 - 100 T with 10-100 ms duration
- Megagauss magnets > 100 T with sub-millisecond duration
DC Magnets: 30 - 60 T
Required maximum field
Additional information
- 30-40 T: target range for standard resistive or superconducting user magnets with normal access capacity.
- 40-50 T: target range of current hybrid projects; limited access capacity for users (1 magnet per facility).
- > 50 T: possible future project requiring a multi-national effort; limited access capacity for users (1 or 2 magnets worldwide).
Required temperature
Required sample space
Additional information
Specifications for sample space and temperature are used to estimate the smallest winding / bore diameter that the magnet can have. If you are not sure about sample space, please use the comment box below to let us know about the experiments you want to perform.
Special requirements
Persistent mode operation
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform with DC magnets with standard geometry ;
- ... specifications for homogeneity, noise level, fast ramping, persistent mode operation (if applicable) ;
- ... any other requirement for this class of magnets.
Pulsed Magnets : 60 - 100 T with 10 - 100ms duration
Required maximum field
Additional information
- 60-70 T: standard monolithic magnets with smooth profile (sinusoidal rise, exponential decay) in the 100 ms range.
- 70-90 T: multi-coil magnets with ∼10 ms useful pulse duration around Bmax ; the superposition of pulses from nested magnets creates discontinuities in B(t).
- >90 T: multi-coil magnets with ∼10 ms useful pulse duration around Bmax ; the superposition of pulses from nested magnets creates discontinuities in B(t) (kinks) and dB/dt (jumps); shots above 90 T may require special justification to protect coils from unnecessary fatigue.
Required temperature
Required sample space
Additional information
Specifications for sample space and temperature are used to estimate the smallest winding / bore diameter that the magnet can have. If you are not sure about sample space, please use the comment box below to let us know about the experiments you want to perform.
Special requirements
Additional information
Short- and long-pulse magnets are important for certain measurements where dB/dt is either beneficial (e.g. inductive measurements) or problematic (e.g. specific heat). Note that longer pulse durations result in substantially longer cool-down times.
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform in pulsed magnets with standard geometry ;
- ... specifications for homogeneity or pulse duration (if applicable) ;
- ... any other requirements for this class of magnets.
Megagauss magnets: > 100 T with sub-millisecond duration
Required maximum field
Additional information
- 100-120 T, 100 µs: possible future non-destructive insert-outsert type magnet ; the development would requires investments in both new coils and generators.
- 150-200 T, 10 µs: disposable single-turn coils ; possibility to perform repeated measurements with specific experimental techniques (VIS-MIR optics, magnetization).
- 1000 T, 10 µs: electromagnetic flux compression at the ISSP Kashiwa ; integration into the EMFL user access scheme under discussion ; single-shot experiments only. All magnets are limited in bore diameter to less than 10 mm.
Required temperature
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform in Megagauss fields ;
- ... your technical requirements for these experiments.
PART 2 : FACILITY MAGNETS WITH SPECIFIC EXPERIMENTAL ACCESS OR GEOMETRY
CATEGORIES
- Magnets with extra-wide bore
- Transverse-access magnets (split coils)
- More magnets with specific experimental access or geometry
Magnets with extra-wide bore
Field-bore preference for DC wide-bore magnets
Additional information
Indicate here the maximum field and the room temperature bore diameter that are closest to your needs. (The room-temperature bore takes into account space occupied by equipment used for cooling the magnet but not any cryostats or furnaces necessary for the experiment.) Magnets with 370, 600 and 800 mm refer to the possible use of the outer coils of hybrid magnet systems that are currently under construction ; other magnets would require separate developments ; a magnet producing 30 T in 50 mm bore exists.
Field-bore preference for pulsed wide-bore magnets
Additional information
Indicate here the maximum field and the room-temperature bore diameter that are closest to your needs. (The room-temperature bore takes into account space occupied by equipment used for cooling the magnet but not any cryostats or furnaces necessary for the experiment.). Note that pulsed wide-bore magnets have longer pulse durations (>100 ms) and substantially longer cool-down times.
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you want to perform with wide-bore magnets ;
- ... any other requirements for this class of magnets.
Transverse-access magnets (split coils)
Importance rating
Additional information
Rate here the importance of this type of magnet for your research.
Required temperature
Preferred field-bore-split optimization for DC magnets
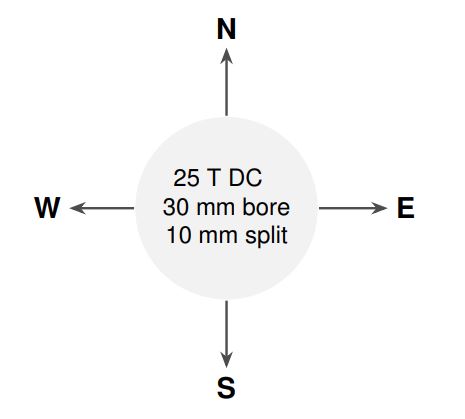
N : Go for more field, less bore
S : Go for more bore, less field
E : Go for more field, less split
W : Go for more split, less field
Additional information
The center of the wind rose contains a likely compromise of parameters for a DC split coil. Indicate in which direction the parameters in the center of the wind rose for DC magnets should be changed in order to suit your needs (for example, indicate N and E to obtain more field in exchange for a reduced bore and/or split).
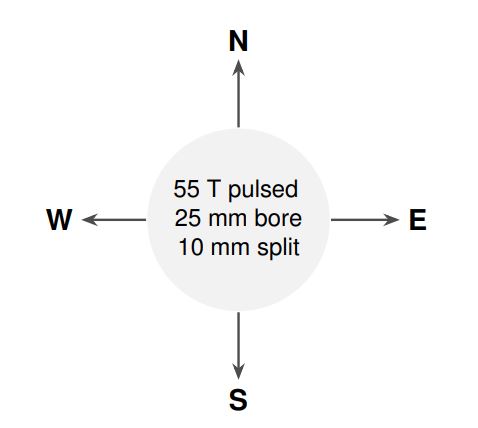
N : Go for more field, less bore
S : Go for more bore, less field
E : Go for more field, less split
W : Go for more split, less field
Additional information
The center of the wind rose contains a likely compromise of parameters for a pulsed split coil. Indicate in which direction and to what degree the parameters should be changed in order to better suit your needs (for example, indicate N and E to obtain more field in exchange for a reduced bore and/or split).
Tell us more about...
- ...the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform with split-coils (DC or pulsed);
- ...specifications for the required experimental access and sample space ;
- ...any other requirements for this class of magnets.
More magnets with specific experimental access or geometry
More possibilites...
Conical bore magnet: pulsed or DC magnet with up to 30◦ opening angle of the bore.
Levitation magnet/large gradient magnet: magnet designed to optimize the volume both the magnetic field and its gradient are simultaneously large
Dipole magnet: accelerator-type magnet designed to extend the lateral distance over which a substantial perpendicular field is obtained (see figure on the right).

Additional information
Note that special magnet geometries imply substantially lower fields than those available in conventional magnets.
Tell us more about...
- ... your technical requirements for the listed magnets ;
- ... specifications for the specific experimental access and geometry ;
- ...the type(s) of experiment(s) you want to perform with them and other possible comments.
PART 3 : FACILITY MAGNETS WITH SPECIFIC TIME DEPENDENCE
CATEGORIES
- DC outsert, pulsed insert
- Flat-top pulsed magnets
- More magnets with specific time dependence
DC outsert, pulsed insert
Required total maximum field (DC & pulsed)
Additional information
DC-outsert-pulsed-insert magnets are useful for applications requiring pre-polarization or the alignment of magnetic sub-systems.
Required DC background field
Required temperature
Required sample space
Additional information
Specifications for sample space and temperature are used to estimate the smallest winding / bore diameter that the magnet can have. If you are not sure about sample space, please use the comment box below to let us know about the experiments you want to perform.
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform in DC-outsert, pulsed-insert magnets ;
- ... any other requirements for this class of magnets.
Flat-top pulsed magnets
Required peak field and plateau width
Additional information
Flat-top magnets provide a plateau with typically ≃1% flatness for constant-field measurements ; implementing a flat-top magnet requires substantial infrastructure investments for developing an auxiliary capacitor bank and inductive coupler.
Required temperature
Required sample space
Additional information
Specifications for sample space and temperature are used to estimate the bore diameter. If you are not sure about sample space, please use the comment box below to let us know about the experiments you want to perform.
Special requirements
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform in flat-top pulsed magnets;
- ... specifications for homogeneity and flatness (if applicable) ;
- ... any other requirements for this class of magnets.
More magnets with specific time dependence
More possibilities
Oscillating-field magnet: pulsed magnet driven by a generator resembling a serial RLC circuit ; field reversals of 80-95% between the first and second maximum are feasible depending on bore diameter, pulse duration and peak field ; reducing either parameter also reduces the decay ; technical development requiring additional investments due to the need of capacitors with enhanced tolerance towards voltage reversal.
Slow-start magnet: pulsed magnet providing a smoother onset of the magnetic field in order to reduce eddy currents, noise and heating effects associated with the initial rise.
Tell us more about...
- ... your technical requirements for oscillating-field magnets;
- ...your ideas for more magnets with specific time-dependence;
- ...the type(s) of experiment(s) you want to perform and other possible comments.
PART 4 : MOBILE INSTALLATIONS
CATEGORIES
- Mobile infrastructure specifications
- Mobile magnets for uses outside the EMFL facilities
Mobile infrastructure specifications
Preferred infrastructure size
Conventional pulsed generator
Upscaled pulsed generator
Downscaled pulsed generator
Additional information
- Conventional pulsed generator: 30-60 T depending on coil type in ≃20 mm, ≃10 ms ; one shot at full field approximately every 10 minutes ; pallet-sized modules requiring 12-15 m2 in the host facility ; 24 kV operating voltage and possible violent coil failures.
- Upscaled installations: larger useful volumes, large pulse duration, smaller duty cycle ; installation mounted in containers that have to be stored at, or connected to, the measurement site ; enhanced security requirements due to the additional stored energy.
- Downscaled installations: higher duty cycle, less pulse duration for a useful diameters <5 mm ; installation mounted on a single pallet.
Alternative installations
Additional information
Mobile Megagauss generators provide 100 T in 8 mm / 5 µs approximately once every hour ; installation mounted on a single pallet; enhanced security requirements due to the use of 50-60 kV and the coil explosion ; provisions for electromagnetic shielding and evacuating metallic vapors necessary.
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform with a mobile generator;
- ...the type of facility where the experiment would be installed;
- ...any other requirements for mobile generators.
Mobile magnets for uses outside the EMFL facilities
Required coil geometry
Required temperature
Required sample space
Special requirements
Variable coil orientation
Advanced vibration damping
Tell us more about...
- ... the type(s) of experiment(s) you intend to perform with mobile magnets ;
- ... the type of facility where the experiment would be installed ;
- ... why your experiment requires a special coil-geometry (if applicable) ;
- ... specifications for coil orientation, vibration damping or UHV compatibility (if applicable) ;
- ... any other requirement for this class of magnets.
FINAL INFORMATION
Please provide below some keywords to describe your scientific domain, specific research interests.
We would also like to know more about the type of institution you are working in (university, public or private research institute, industry ...).
If you are willing to help us further in establishing this road map, we suggest you to leave your contact details. We will only contact you to obtain further precisions regarding your needs in terms of magnet technology and will not distribute any personal information outside this project.
Your e-mail address (optional) ...
Please do not forget to press the submit button below to save your answers.
Thank you for participating in this survey !
Thank you for your participation! Your form has been submitted successfully.
There was an error trying to send the form. Please try again and be patient after sumitting >5s.
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.