Beriev Be-6 (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Patrol aircraft in the Soviet Navy
| Be-6 | |
|---|---|
 Be-6 at Ukrainian State Aviation Museum Be-6 at Ukrainian State Aviation Museum |
|
| General information | |
| Type | Maritime reconnaissance and patrol aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Beriev OKB |
| Primary users | Soviet Navy People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force |
| Number built | 123 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1949–57 |
| First flight | 1949 |
| Retired | Late 1960s |
| Developed into | Beriev Be-12 |
The Beriev Be-6 (USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 34",[1] NATO reporting name "Madge"[2]) was a flying boat produced by the Soviet Beriev OKB. It was capable of accomplishing a wide variety of missions, such as long-range maritime reconnaissance, coastal and supply line patrols, torpedo/bombing strikes, mine-laying, and transport operations.
Design and development
[edit]
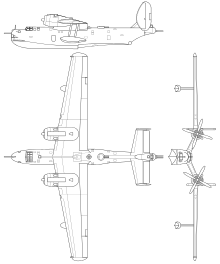
The Be-6 was a gull-winged aircraft with twin oval vertical stabilizers on top of a deep fuselage. The aircraft was of all-metal construction except for fabric covering the rudders and ailerons. The engines were installed in the bends of the wings, with the floats on an underwing cantilever rack. Each float was divided into four watertight compartments.[_citation needed_]
Operational history
[edit]
A U.S. Navy A-4B intercepting a Be-6 off Japan, 1964.
The Be-6 was built from 1949 to 1957 at the Beriev plant in Taganrog. The aircraft had 19 variants through its production cycle, and 123 aircraft were eventually built. Since requirements of Soviet naval aircraft did not change rapidly, the reliable Be-6 remained in service until the late 1960s. Some aircraft ended service as civilian unarmed transports in Arctic regions. One survivor is preserved at the Ukraine State Aviation Museum in Kyiv, Ukraine. Beriev Be-6s operated by the People's Republic of China PLANAF proved useful in patrolling the long coastline and huge territorial waters off China's coast. During the 1970s the original Shvetsov radial engines began to wear out with no replacements available, so several aircraft were re-engined with WoJiang WJ-6 turboprop engines, in new nacelles, for a new lease of life and were redesignated Qing-6.[3]
A Qing-6 (Be-6 conversion) powered by 4,250 hp (3,170 kW) WoJiang WJ-6 turboprop engines driving J17G13 propellers, at the China Aviation Museum, Beijing
- Soviet Naval Aviation
- LL-143: Prototype of Be-6 with Shvetsov ASh-72 radial engines; nose, beam, ventral and tail positions for a total of six 12.7mm UBT machine guns. Maiden Flight in March 1945.
- Be-6: standard production aircraft with Shvetsov ASh-73 radial piston engines.
- Qing-6: Be-6 aircraft of the PLANAF re-engined with Dongan WJ-5 turboprops.[3]
Specifications (Be-6)
[edit]
Data from The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft from 1875–1995 [4]
General characteristics
- Crew: 8
- Length: 23.5 m (77 ft 1 in)
- Wingspan: 33 m (108 ft 3 in)
- Height: 7.64 m (25 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 120 m2 (1,300 sq ft)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 23020; tip: NACA 23010 [5]
- Empty weight: 18,827 kg (41,506 lb)
- Gross weight: 23,456 kg (51,712 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 29,000 kg (63,934 lb)
- Maximum alighting weight: 20,928 kg (46,138 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Shvetsov ASh-73TK 18-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,800 kW (2,400 hp) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed V-3BA-5 constant-speed propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 414 km/h (257 mph, 224 kn) at 1,800 m (5,900 ft)
377 km/h (234 mph; 204 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 280 km/h (170 mph, 150 kn) at 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
- Alighting speed:' 147 km/h (91 mph; 79 kn)
- Range: 4,800 km (3,000 mi, 2,600 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 6,100 m (20,000 ft)
- Time to altitude: 5,000 m (16,000 ft) in 20 minutes
Armament
- Guns: 5 × 23 mm (0.91 in) Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 autocannon in 3 remotely controlled turrets
- Bombs:
- General ordnance, or
- 2×1,000 kg (2,205 lb) torpedoes, or
- 8 mines
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- ^ "Designations of Soviet and Russian Military Aircraft and Missiles". designation-systems.net.
- ^ "Designations of Soviet and Russian Military Aircraft and Missiles".
- ^ a b Gordon,Yefim & Komissarov, Dmitry. Chinese Aircraft. Hikoki Publications. Manchester. 2008. ISBN 978-1-902109-04-6
- ^ Gunston, Bill (1995). The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft from 1875–1995. Osprey Aerospace. ISBN 1-85532-405-9.
- ^ Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- Gunston, Bill. “The Osprey Encyclopaedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995”. London, Osprey. 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9
- Gordon, Yefim & Komissarov, Dmitry. Chinese Aircraft. Hikoki Publications. Manchester. 2008. ISBN 978-1-902109-04-6