Elliptic curve (original) (raw)
Algebraic curve
Not to be confused with Ellipse.
This article is about the mathematical curve. For the cryptography technique, see Elliptic-curve cryptography.
A catalog of elliptic curves. The region shown is x, y ∈ [−3,3].
(For (a, b) = (0, 0) the function is not smooth and therefore not an elliptic curve.)
In mathematics, an elliptic curve is a smooth, projective, algebraic curve of genus one, on which there is a specified point O. An elliptic curve is defined over a field K and describes points in _K_2, the Cartesian product of K with itself. If the field's characteristic is different from 2 and 3, then the curve can be described as a plane algebraic curve which consists of solutions (x, y) for:
y 2 = x 3 + a x + b {\displaystyle y^{2}=x^{3}+ax+b}
for some coefficients a and b in K. The curve is required to be non-singular, which means that the curve has no cusps or self-intersections. (This is equivalent to the condition 4_a_3 + 27_b_2 ≠ 0, that is, being square-free in x.) It is always understood that the curve is really sitting in the projective plane, with the point O being the unique point at infinity. Many sources define an elliptic curve to be simply a curve given by an equation of this form. (When the coefficient field has characteristic 2 or 3, the above equation is not quite general enough to include all non-singular cubic curves; see § Elliptic curves over a general field below.)
An elliptic curve is an abelian variety – that is, it has a group law defined algebraically, with respect to which it is an abelian group – and O serves as the identity element.
If _y_2 = P(x), where P is any polynomial of degree three in x with no repeated roots, the solution set is a nonsingular plane curve of genus one, an elliptic curve. If P has degree four and is square-free this equation again describes a plane curve of genus one; however, it has no natural choice of identity element. More generally, any algebraic curve of genus one, for example the intersection of two quadric surfaces embedded in three-dimensional projective space, is called an elliptic curve, provided that it is equipped with a marked point to act as the identity.
Using the theory of elliptic functions, it can be shown that elliptic curves defined over the complex numbers correspond to embeddings of the torus into the complex projective plane. The torus is also an abelian group, and this correspondence is also a group isomorphism.
Elliptic curves are especially important in number theory, and constitute a major area of current research; for example, they were used in Andrew Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem. They also find applications in elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) and integer factorization.
An elliptic curve is not an ellipse in the sense of a projective conic, which has genus zero: see elliptic integral for the origin of the term. However, there is a natural representation of real elliptic curves with shape invariant j ≥ 1 as ellipses in the hyperbolic plane H 2 {\displaystyle \mathbb {H} ^{2}} 


Topologically, a complex elliptic curve is a torus, while a complex ellipse is a sphere.
Elliptic curves over the real numbers
[edit]
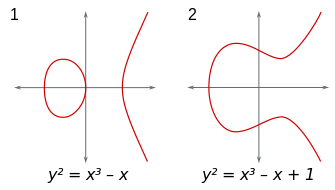
Graphs of curves _y_2 = _x_3 − x and _y_2 = _x_3 − x + 1
Although the formal definition of an elliptic curve requires some background in algebraic geometry, it is possible to describe some features of elliptic curves over the real numbers using only introductory algebra and geometry.
In this context, an elliptic curve is a plane curve defined by an equation of the form
y 2 = x 3 + a x + b {\displaystyle y^{2}=x^{3}+ax+b}
after a linear change of variables (a and b are real numbers). This type of equation is called a Weierstrass equation, and said to be in Weierstrass form, or Weierstrass normal form.
The definition of elliptic curve also requires that the curve be non-singular. Geometrically, this means that the graph has no cusps, self-intersections, or isolated points. Algebraically, this holds if and only if the discriminant, Δ {\displaystyle \Delta } 
Δ = − 16 ( 4 a 3 + 27 b 2 ) ≠ 0 {\displaystyle \Delta =-16\left(4a^{3}+27b^{2}\right)\neq 0}
The discriminant is zero when a = − 3 k 2 , b = 2 k 3 {\displaystyle a=-3k^{2},b=2k^{3}} 
(Although the factor −16 is irrelevant to whether or not the curve is non-singular, this definition of the discriminant is useful in a more advanced study of elliptic curves.)[2]
The real graph of a non-singular curve has two components if its discriminant is positive, and one component if it is negative. For example, in the graphs shown in figure to the right, the discriminant in the first case is 64, and in the second case is −368.
When working in the projective plane, the equation in homogeneous coordinates becomes :
Y 2 Z 2 = X 3 Z 3 + a X Z + b {\displaystyle {\frac {Y^{2}}{Z^{2}}}={\frac {X^{3}}{Z^{3}}}+a{\frac {X}{Z}}+b}
This equation is not defined on the line at infinity, but we can multiply by Z 3 {\displaystyle Z^{3}} 
Z Y 2 = X 3 + a Z 2 X + b Z 3 {\displaystyle ZY^{2}=X^{3}+aZ^{2}X+bZ^{3}}
This resulting equation is defined on the whole projective plane, and the curve it defines projects onto the elliptic curve of interest. To find its intersection with the line at infinity, we can just posit Z = 0 {\displaystyle Z=0} 




![{\displaystyle O=[0:1:0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/18273b8a82c7523639ad09fbbd45bd749d2fdb14)
Since the curve is smooth, hence continuous, it can be shown that this point at infinity is the identity element of a group structure whose operation is geometrically described as follows:
Since the curve is symmetric about the x-axis, given any point P, we can take −P to be the point opposite it. We then have − O = O {\displaystyle -O=O} 



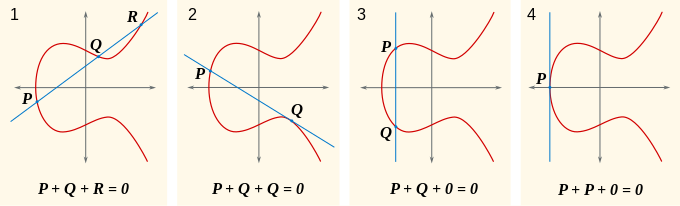
If P and Q are two points on the curve, then we can uniquely describe a third point P + Q in the following way. First, draw the line that intersects P and Q. This will generally intersect the cubic at a third point, R. We then take P + Q to be −R, the point opposite R.
This definition for addition works except in a few special cases related to the point at infinity and intersection multiplicity. The first is when one of the points is O. Here, we define P + O = P = O + P, making O the identity of the group. If P = Q we only have one point, thus we cannot define the line between them. In this case, we use the tangent line to the curve at this point as our line. In most cases, the tangent will intersect a second point R and we can take its opposite. If P and Q are opposites of each other, we define P + Q = O. Lastly, If P is an inflection point (a point where the concavity of the curve changes), we take R to be P itself and P + P is simply the point opposite itself, i.e. itself.
Let K be a field over which the curve is defined (that is, the coefficients of the defining equation or equations of the curve are in K) and denote the curve by E. Then the K-rational points of E are the points on E whose coordinates all lie in K, including the point at infinity. The set of K-rational points is denoted by E(K). E(K) is a group, because properties of polynomial equations show that if P is in E(K), then −P is also in E(K), and if two of P, Q, R are in E(K), then so is the third. Additionally, if K is a subfield of L, then E(K) is a subgroup of E(L).
Algebraic interpretation
[edit]
The above groups can be described algebraically as well as geometrically. Given the curve _y_2 = _x_3 + bx + c over the field K (whose characteristic we assume to be neither 2 nor 3), and points P = (xP, yP) and Q = (xQ, yQ) on the curve, assume first that xP ≠ xQ (case 1). Let y = sx + d be the equation of the line that intersects P and Q, which has the following slope:
s = y P − y Q x P − x Q {\displaystyle s={\frac {y_{P}-y_{Q}}{x_{P}-x_{Q}}}}
The line equation and the curve equation intersect at the points xP, xQ, and xR, so the equations have identical y values at these values.
( s x + d ) 2 = x 3 + b x + c {\displaystyle \left(sx+d\right)^{2}=x^{3}+bx+c}
which is equivalent to
x 3 − s 2 x 2 − 2 s d x + b x + c − d 2 = 0 {\displaystyle x^{3}-s^{2}x^{2}-2sdx+bx+c-d^{2}=0}
Since xP, xQ, and xR are solutions, this equation has its roots at exactly the same x values as
( x − x P ) ( x − x Q ) ( x − x R ) = x 3 + ( − x P − x Q − x R ) x 2 + ( x P x Q + x P x R + x Q x R ) x − x P x Q x R {\displaystyle (x-x_{P})(x-x_{Q})(x-x_{R})=x^{3}+(-x_{P}-x_{Q}-x_{R})x^{2}+(x_{P}x_{Q}+x_{P}x_{R}+x_{Q}x_{R})x-x_{P}x_{Q}x_{R}}
and because both equations are cubics they must be the same polynomial up to a scalar. Then equating the coefficients of _x_2 in both equations
− s 2 = ( − x P − x Q − x R ) {\displaystyle -s^{2}=(-x_{P}-x_{Q}-x_{R})}
and solving for the unknown xR.
x R = s 2 − x P − x Q {\displaystyle x_{R}=s^{2}-x_{P}-x_{Q}}
yR follows from the line equation
y R = y P − s ( x P − x R ) {\displaystyle y_{R}=y_{P}-s(x_{P}-x_{R})}
and this is an element of K, because s is.
If xP = xQ, then there are two options: if yP = −yQ (case 3), including the case where yP = yQ = 0 (case 4), then the sum is defined as 0; thus, the inverse of each point on the curve is found by reflecting it across the x-axis.
If yP = yQ ≠ 0, then Q = P and R = (x R, y R) = −(P + P) = −2_P_ = −2_Q_ (case 2 using P as R). The slope is given by the tangent to the curve at (x P, y P).
s = 3 x P 2 + b 2 y P x R = s 2 − 2 x P y R = y P − s ( x P − x R ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}s&={\frac {3{x_{P}}^{2}+b}{2y_{P}}}\\x_{R}&=s^{2}-2x_{P}\\y_{R}&=y_{P}-s(x_{P}-x_{R})\end{aligned}}}
A more general expression for s {\displaystyle s} 
s = x P 2 + x P x Q + x Q 2 + b y P + y Q {\displaystyle s={\frac {{x_{P}}^{2}+x_{P}x_{Q}+{x_{Q}}^{2}+b}{y_{P}+y_{Q}}}}
where equality to yP − yQ/xP − _xQ_ relies on P and Q obeying _y_2 = _x_3 + bx + c.
Non-Weierstrass curves
[edit]
For the curve _y_2 = _x_3 + _ax_2 + bx + c (the general form of an elliptic curve with characteristic 3), the formulas are similar, with s = _xP_2 + xP xQ + _xQ_2 + axP + axQ + b/yP + _yQ_ and xR = _s_2 − a − xP − xQ.
For a general cubic curve not in Weierstrass normal form, we can still define a group structure by designating one of its nine inflection points as the identity O. In the projective plane, each line will intersect a cubic at three points when accounting for multiplicity. For a point P, −P is defined as the unique third point on the line passing through O and P. Then, for any P and Q, P + Q is defined as −R where R is the unique third point on the line containing P and Q.
For an example of the group law over a non-Weierstrass curve, see Hessian curves.
Elliptic curves over the rational numbers
[edit]
A curve E defined over the field of rational numbers is also defined over the field of real numbers. Therefore, the law of addition (of points with real coordinates) by the tangent and secant method can be applied to E. The explicit formulae show that the sum of two points P and Q with rational coordinates has again rational coordinates, since the line joining P and Q has rational coefficients. This way, one shows that the set of rational points of E forms a subgroup of the group of real points of E.
This section is concerned with points P = (x, y) of E such that x is an integer.
For example, the equation _y_2 = _x_3 + 17 has eight integral solutions with y > 0:[3][4]
(x, y) = (−2, 3), (−1, 4), (2, 5), (4, 9), (8, 23), (43, 282), (52, 375), (5234, 378661).
As another example, Ljunggren's equation, a curve whose Weierstrass form is _y_2 = x_3 − 2_x, has only four solutions with y ≥ 0 :[5]
(x, y) = (0, 0), (−1, 1), (2, 2), (338, 6214).
The structure of rational points
[edit]
Rational points can be constructed by the method of tangents and secants detailed above, starting with a finite number of rational points. More precisely[6] the Mordell–Weil theorem states that the group E(Q) is a finitely generated (abelian) group. By the fundamental theorem of finitely generated abelian groups it is therefore a finite direct sum of copies of Z and finite cyclic groups.
The proof of the theorem[7] involves two parts. The first part shows that for any integer m > 1, the quotient group E(Q)/mE(Q) is finite (this is the weak Mordell–Weil theorem). Second, introducing a height function h on the rational points E(Q) defined by h(_P_0) = 0 and h(P) = log max(|p|, |q|) if P (unequal to the point at infinity _P_0) has as abscissa the rational number x = p/q (with coprime p and q). This height function h has the property that h(mP) grows roughly like the square of m. Moreover, only finitely many rational points with height smaller than any constant exist on E.
The proof of the theorem is thus a variant of the method of infinite descent[8] and relies on the repeated application of Euclidean divisions on E: let P ∈ E(Q) be a rational point on the curve, writing P as the sum 2_P_1 + _Q_1 where Q_1 is a fixed representant of P in E(Q)/2_E(Q), the height of _P_1 is about 1/4 of the one of P (more generally, replacing 2 by any m > 1, and 1/4 by 1/_m_2). Redoing the same with _P_1, that is to say _P_1 = 2_P_2 + _Q_2, then _P_2 = 2_P_3 + _Q_3, etc. finally expresses P as an integral linear combination of points Qi and of points whose height is bounded by a fixed constant chosen in advance: by the weak Mordell–Weil theorem and the second property of the height function P is thus expressed as an integral linear combination of a finite number of fixed points.
The theorem however doesn't provide a method to determine any representatives of E(Q)/mE(Q).
The rank of E(Q), that is the number of copies of Z in E(Q) or, equivalently, the number of independent points of infinite order, is called the rank of E. The Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture is concerned with determining the rank. One conjectures that it can be arbitrarily large, even if only examples with relatively small rank are known. The elliptic curve with the currently largest exactly-known rank is
_y_2 + xy + y = _x_3 − x_2 − 244537673336319601463803487168961769270757573821859853707_x + 961710182053183034546222979258806817743270682028964434238957830989898438151121499931
It has rank 20, found by Noam Elkies and Zev Klagsbrun in 2020. Curves of rank higher than 20 have been known since 1994, with lower bounds on their ranks ranging from 21 to 29, but their exact ranks are not known and in particular it is not proven which of them have higher rank than the others or which is the true "current champion".[9]
As for the groups constituting the torsion subgroup of E(Q), the following is known:[10] the torsion subgroup of E(Q) is one of the 15 following groups (a theorem due to Barry Mazur): Z/NZ for N = 1, 2, ..., 10, or 12, or Z/2Z × Z/2_N_Z with N = 1, 2, 3, 4. Examples for every case are known. Moreover, elliptic curves whose Mordell–Weil groups over Q have the same torsion groups belong to a parametrized family.[11]
The Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture
[edit]
The Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture (BSD) is one of the Millennium problems of the Clay Mathematics Institute. The conjecture relies on analytic and arithmetic objects defined by the elliptic curve in question.
At the analytic side, an important ingredient is a function of a complex variable, L, the Hasse–Weil zeta function of E over Q. This function is a variant of the Riemann zeta function and Dirichlet L-functions. It is defined as an Euler product, with one factor for every prime number p.
For a curve E over Q given by a minimal equation
y 2 + a 1 x y + a 3 y = x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 4 x + a 6 {\displaystyle y^{2}+a_{1}xy+a_{3}y=x^{3}+a_{2}x^{2}+a_{4}x+a_{6}}
with integral coefficients a i {\displaystyle a_{i}} 
The zeta function of an elliptic curve over a finite field Fp is, in some sense, a generating function assembling the information of the number of points of E with values in the finite field extensions Fpn of Fp. It is given by[12]
Z ( E ( F p ) , T ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ # [ E ( F p n ) ] T n n ) {\displaystyle Z(E(\mathbf {F} _{p}),T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\#\left[E({\mathbf {F} }_{p^{n}})\right]{\frac {T^{n}}{n}}\right)}
The interior sum of the exponential resembles the development of the logarithm and, in fact, the so-defined zeta function is a rational function in T:
Z ( E ( F p ) , T ) = 1 − a p T + p T 2 ( 1 − T ) ( 1 − p T ) , {\displaystyle Z(E(\mathbf {F} _{p}),T)={\frac {1-a_{p}T+pT^{2}}{(1-T)(1-pT)}},}
where the 'trace of Frobenius' term[13] a p {\displaystyle a_{p}} 



a p = p + 1 − # E ( F p ) {\displaystyle a_{p}=p+1-\#E(\mathbb {F} _{p})}
or equivalently,
E ( F p ) = p + 1 − a p {\displaystyle \#E(\mathbb {F} _{p})=p+1-a_{p}}  .
.
We may define the same quantities and functions over an arbitrary finite field of characteristic p {\displaystyle p} 


The L-function of E over Q is then defined by collecting this information together, for all primes p. It is defined by
L ( E ( Q ) , s ) = ∏ p ∤ N ( 1 − a p p − s + p 1 − 2 s ) − 1 ⋅ ∏ p ∣ N ( 1 − a p p − s ) − 1 {\displaystyle L(E(\mathbf {Q} ),s)=\prod _{p\not \mid N}\left(1-a_{p}p^{-s}+p^{1-2s}\right)^{-1}\cdot \prod _{p\mid N}\left(1-a_{p}p^{-s}\right)^{-1}}
where N is the conductor of E, i.e. the product of primes with bad reduction ( Δ ( E mod p ) = 0 {\displaystyle (\Delta (E\mod p)=0} 
For example E : y 2 = x 3 + 14 x + 19 {\displaystyle E:y^{2}=x^{3}+14x+19} 


This product converges for Re(s) > 3/2 only. Hasse's conjecture affirms that the _L_-function admits an analytic continuation to the whole complex plane and satisfies a functional equation relating, for any s, L(E, s) to L(E, 2 − s). In 1999 this was shown to be a consequence of the proof of the Shimura–Taniyama–Weil conjecture, which asserts that every elliptic curve over Q is a modular curve, which implies that its _L_-function is the _L_-function of a modular form whose analytic continuation is known. One can therefore speak about the values of L(E, s) at any complex number s.
At s=1 (the conductor product can be discarded as it is finite), the L-function becomes
L ( E ( Q ) , 1 ) = ∏ p ∤ N ( 1 − a p p − 1 + p − 1 ) − 1 = ∏ p ∤ N p p − a p + 1 = ∏ p ∤ N p # E ( F p ) {\displaystyle L(E(\mathbf {Q} ),1)=\prod _{p\not \mid N}\left(1-a_{p}p^{-1}+p^{-1}\right)^{-1}=\prod _{p\not \mid N}{\frac {p}{p-a_{p}+1}}=\prod _{p\not \mid N}{\frac {p}{\#E(\mathbb {F} _{p})}}}
The Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture relates the arithmetic of the curve to the behaviour of this _L_-function at s = 1. It affirms that the vanishing order of the _L_-function at s = 1 equals the rank of E and predicts the leading term of the Laurent series of L(E, s) at that point in terms of several quantities attached to the elliptic curve.
Much like the Riemann hypothesis, the truth of the BSD conjecture would have multiple consequences, including the following two:
Elliptic curves over finite fields
[edit]
Set of affine points of elliptic curve _y_2 = _x_3 − x over finite field F61.
Let K = Fq be the finite field with q elements and E an elliptic curve defined over K. While the precise number of rational points of an elliptic curve E over K is in general difficult to compute, Hasse's theorem on elliptic curves gives the following inequality:
| # E ( K ) − ( q + 1 ) | ≤ 2 q {\displaystyle |\#E(K)-(q+1)|\leq 2{\sqrt {q}}}
In other words, the number of points on the curve grows proportionally to the number of elements in the field. This fact can be understood and proven with the help of some general theory; see local zeta function and étale cohomology for example.
Set of affine points of elliptic curve _y_2 = _x_3 − x over finite field F89.
The set of points E(Fq) is a finite abelian group. It is always cyclic or the product of two cyclic groups. For example,[17] the curve defined by
y 2 = x 3 − x {\displaystyle y^{2}=x^{3}-x}
over F71 has 72 points (71 affine points including (0,0) and one point at infinity) over this field, whose group structure is given by Z/2Z × Z/36Z. The number of points on a specific curve can be computed with Schoof's algorithm.
Set of affine points of elliptic curve _y_2 = _x_3 − x over finite field F71.
Studying the curve over the field extensions of Fq is facilitated by the introduction of the local zeta function of E over Fq, defined by a generating series (also see above)
Z ( E ( K ) , T ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ # [ E ( K n ) ] T n n ) {\displaystyle Z(E(K),T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\#\left[E(K_{n})\right]{T^{n} \over n}\right)}
where the field Kn is the (unique up to isomorphism) extension of K = Fq of degree n (that is, K n = F q n {\displaystyle K_{n}=F_{q^{n}}} 
The zeta function is a rational function in T. To see this, consider the integer a {\displaystyle a} 
E ( K ) = 1 − a + q {\displaystyle \#E(K)=1-a+q} 
There is a complex number α {\displaystyle \alpha } 
1 − a + q = ( 1 − α ) ( 1 − α ¯ ) {\displaystyle 1-a+q=(1-\alpha )(1-{\bar {\alpha }})}
where α ¯ {\displaystyle {\bar {\alpha }}} 
α + α ¯ = a {\displaystyle \alpha +{\bar {\alpha }}=a}
α α ¯ = q {\displaystyle \alpha {\bar {\alpha }}=q}
We choose α {\displaystyle \alpha } 




α {\displaystyle \alpha } 

E ( K n ) = 1 − a n + q n {\displaystyle \#E(K_{n})=1-a_{n}+q^{n}} 
Using the Taylor series for the natural logarithm,
Z ( E ( K ) , T ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( 1 − α n − α ¯ n + q n ) T n n ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ T n n − ∑ n = 1 ∞ α n T n n − ∑ n = 1 ∞ α ¯ n T n n + ∑ n = 1 ∞ q n T n n ) = exp ( − ln ( 1 − T ) + ln ( 1 − α T ) + ln ( 1 − α ¯ T ) − ln ( 1 − q T ) ) = exp ( ln ( 1 − α T ) ( 1 − α ¯ T ) ( 1 − T ) ( 1 − q T ) ) = ( 1 − α T ) ( 1 − α ¯ T ) ( 1 − T ) ( 1 − q T ) {\displaystyle {\begin{alignedat}{2}Z(E(K),T)&=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\left(1-\alpha ^{n}-{\bar {\alpha }}^{n}+q^{n}\right){T^{n} \over n}\right)\\&=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{T^{n} \over n}-\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\alpha ^{n}{T^{n} \over n}-\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\bar {\alpha }}^{n}{T^{n} \over n}+\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }q^{n}{T^{n} \over n}\right)\\&=\exp \left(-\ln(1-T)+\ln(1-\alpha T)+\ln(1-{\bar {\alpha }}T)-\ln(1-qT)\right)\\&=\exp \left(\ln {\frac {(1-\alpha T)(1-{\bar {\alpha }}T)}{(1-T)(1-qT)}}\right)\\&={\frac {(1-\alpha T)(1-{\bar {\alpha }}T)}{(1-T)(1-qT)}}\\\end{alignedat}}}
Then ( 1 − α T ) ( 1 − α ¯ T ) = 1 − a T + q T 2 {\displaystyle (1-\alpha T)(1-{\bar {\alpha }}T)=1-aT+qT^{2}} 
Z ( E ( K ) , T ) = 1 − a T + q T 2 ( 1 − q T ) ( 1 − T ) {\displaystyle Z(E(K),T)={\frac {1-aT+qT^{2}}{(1-qT)(1-T)}}}
For example,[18] the zeta function of E : _y_2 + y = _x_3 over the field F2 is given by
1 + 2 T 2 ( 1 − T ) ( 1 − 2 T ) {\displaystyle {\frac {1+2T^{2}}{(1-T)(1-2T)}}}
which follows from:
| E ( F 2 r ) | = { 2 r + 1 r odd 2 r + 1 − 2 ( − 2 ) r 2 r even {\displaystyle \left|E(\mathbf {F} _{2^{r}})\right|={\begin{cases}2^{r}+1&r{\text{ odd}}\\2^{r}+1-2(-2)^{\frac {r}{2}}&r{\text{ even}}\end{cases}}}
as q = 2 {\displaystyle q=2} 


The functional equation is
Z ( E ( K ) , 1 q T ) = 1 − a 1 q T + q ( 1 q T ) 2 ( 1 − q 1 q T ) ( 1 − 1 q T ) = q 2 T 2 − a q T + q ( q T − q ) ( q T − 1 ) = Z ( E ( K ) , T ) {\displaystyle Z\left(E(K),{\frac {1}{qT}}\right)={\frac {1-a{\frac {1}{qT}}+q\left({\frac {1}{qT}}\right)^{2}}{(1-q{\frac {1}{qT}})(1-{\frac {1}{qT}})}}={\frac {q^{2}T^{2}-aqT+q}{(qT-q)(qT-1)}}=Z(E(K),T)}
As we are only interested in the behaviour of a n {\displaystyle a_{n}} 
Z ( a , T ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ − a n T n n ) {\displaystyle Z(a,T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }-a_{n}{T^{n} \over n}\right)}
Z ( a , T ) = exp ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ − α n T n n − α ¯ n T n n ) {\displaystyle Z(a,T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }-\alpha ^{n}{T^{n} \over n}-{\bar {\alpha }}^{n}{T^{n} \over n}\right)}
and so
Z ( a , T ) = exp ( ln ( 1 − α T ) + ln ( 1 − α ¯ T ) ) {\displaystyle Z(a,T)=\exp \left(\ln(1-\alpha T)+\ln(1-{\bar {\alpha }}T)\right)}
which leads directly to the local L-functions
L ( E ( K ) , T ) = 1 − a T + q T 2 {\displaystyle L(E(K),T)=1-aT+qT^{2}}
The Sato–Tate conjecture is a statement about how the error term 2 q {\displaystyle 2{\sqrt {q}}} 
Elliptic curves over finite fields are notably applied in cryptography and for the factorization of large integers. These algorithms often make use of the group structure on the points of E. Algorithms that are applicable to general groups, for example the group of invertible elements in finite fields, F*q, can thus be applied to the group of points on an elliptic curve. For example, the discrete logarithm is such an algorithm. The interest in this is that choosing an elliptic curve allows for more flexibility than choosing q (and thus the group of units in Fq). Also, the group structure of elliptic curves is generally more complicated.
Elliptic curves over a general field
[edit]
Elliptic curves can be defined over any field K; the formal definition of an elliptic curve is a non-singular projective algebraic curve over K with genus 1 and endowed with a distinguished point defined over K.
If the characteristic of K is neither 2 nor 3, then every elliptic curve over K can be written in the form
y 2 = x 3 − p x − q {\displaystyle y^{2}=x^{3}-px-q}
after a linear change of variables. Here p and q are elements of K such that the right hand side polynomial _x_3 − px − q does not have any double roots. If the characteristic is 2 or 3, then more terms need to be kept: in characteristic 3, the most general equation is of the form
y 2 = 4 x 3 + b 2 x 2 + 2 b 4 x + b 6 {\displaystyle y^{2}=4x^{3}+b_{2}x^{2}+2b_{4}x+b_{6}}
for arbitrary constants _b_2, _b_4, _b_6 such that the polynomial on the right-hand side has distinct roots (the notation is chosen for historical reasons). In characteristic 2, even this much is not possible, and the most general equation is
y 2 + a 1 x y + a 3 y = x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 4 x + a 6 {\displaystyle y^{2}+a_{1}xy+a_{3}y=x^{3}+a_{2}x^{2}+a_{4}x+a_{6}}
provided that the variety it defines is non-singular. If characteristic were not an obstruction, each equation would reduce to the previous ones by a suitable linear change of variables.
One typically takes the curve to be the set of all points (x,y) which satisfy the above equation and such that both x and y are elements of the algebraic closure of K. Points of the curve whose coordinates both belong to K are called _K_-rational points.
Many of the preceding results remain valid when the field of definition of E is a number field K, that is to say, a finite field extension of Q. In particular, the group E(K) of _K_-rational points of an elliptic curve E defined over K is finitely generated, which generalizes the Mordell–Weil theorem above. A theorem due to Loïc Merel shows that for a given integer d, there are (up to isomorphism) only finitely many groups that can occur as the torsion groups of E(K) for an elliptic curve defined over a number field K of degree d. More precisely,[20] there is a number B(d) such that for any elliptic curve E defined over a number field K of degree d, any torsion point of E(K) is of order less than B(d). The theorem is effective: for d > 1, if a torsion point is of order p, with p prime, then
p < d 3 d 2 {\displaystyle p<d^{3d^{2}}}
As for the integral points, Siegel's theorem generalizes to the following: Let E be an elliptic curve defined over a number field K, x and y the Weierstrass coordinates. Then there are only finitely many points of E(K) whose _x_-coordinate is in the ring of integers O K.
The properties of the Hasse–Weil zeta function and the Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture can also be extended to this more general situation.
Elliptic curves over the complex numbers
[edit]
An elliptic curve over the complex numbers is obtained as a quotient of the complex plane by a lattice Λ, here spanned by two fundamental periods _ω_1 and _ω_2. The four-torsion is also shown, corresponding to the lattice 1/4Λ containing Λ.
The formulation of elliptic curves as the embedding of a torus in the complex projective plane follows naturally from a curious property of Weierstrass's elliptic functions. These functions and their first derivative are related by the formula
℘ ′ ( z ) 2 = 4 ℘ ( z ) 3 − g 2 ℘ ( z ) − g 3 {\displaystyle \wp '(z)^{2}=4\wp (z)^{3}-g_{2}\wp (z)-g_{3}}
Here, _g_2 and _g_3 are constants; ℘(z) is the Weierstrass elliptic function and ℘′(z) its derivative. It should be clear that this relation is in the form of an elliptic curve (over the complex numbers). The Weierstrass functions are doubly periodic; that is, they are periodic with respect to a lattice Λ; in essence, the Weierstrass functions are naturally defined on a torus T = C/Λ. This torus may be embedded in the complex projective plane by means of the map
z ↦ [ 1 : ℘ ( z ) : 1 2 ℘ ′ ( z ) ] {\displaystyle z\mapsto \left[1:\wp (z):{\tfrac {1}{2}}\wp '(z)\right]}
This map is a group isomorphism of the torus (considered with its natural group structure) with the chord-and-tangent group law on the cubic curve which is the image of this map. It is also an isomorphism of Riemann surfaces from the torus to the cubic curve, so topologically, an elliptic curve is a torus. If the lattice Λ is related by multiplication by a non-zero complex number c to a lattice _c_Λ, then the corresponding curves are isomorphic. Isomorphism classes of elliptic curves are specified by the j-invariant.
The isomorphism classes can be understood in a simpler way as well. The constants _g_2 and _g_3, called the modular invariants, are uniquely determined by the lattice, that is, by the structure of the torus. However, all real polynomials factorize completely into linear factors over the complex numbers, since the field of complex numbers is the algebraic closure of the reals. So, the elliptic curve may be written as
y 2 = x ( x − 1 ) ( x − λ ) {\displaystyle y^{2}=x(x-1)(x-\lambda )}
One finds that
g 2 ′ = 4 3 3 ( λ 2 − λ + 1 ) g 3 ′ = 1 27 ( λ + 1 ) ( 2 λ 2 − 5 λ + 2 ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}g_{2}'&={\frac {\sqrt[{3}]{4}}{3}}\left(\lambda ^{2}-\lambda +1\right)\\[4pt]g_{3}'&={\frac {1}{27}}(\lambda +1)\left(2\lambda ^{2}-5\lambda +2\right)\end{aligned}}}
and
j ( τ ) = 1728 g 2 ′ 3 g 2 ′ 3 − 27 g 3 ′ 2 = 256 ( λ 2 − λ + 1 ) 3 λ 2 ( λ − 1 ) 2 {\displaystyle j(\tau )=1728{\frac {{g_{2}'}^{3}}{{g_{2}'}^{3}-27{g_{3}'}^{2}}}=256{\frac {\left(\lambda ^{2}-\lambda +1\right)^{3}}{\lambda ^{2}\left(\lambda -1\right)^{2}}}}
with j-invariant j(τ) and λ(τ) is sometimes called the modular lambda function. For example, let τ = 2_i_, then λ(2_i_) = (−1 + √2)4 which implies _g_′2, _g_′3, and therefore g_′23
− 27_g_′32
of the formula above are all algebraic numbers if τ involves an imaginary quadratic field. In fact, it yields the integer j(2_i) = 663 = 287496.
In contrast, the modular discriminant
Δ ( τ ) = g 2 ( τ ) 3 − 27 g 3 ( τ ) 2 = ( 2 π ) 12 η 24 ( τ ) {\displaystyle \Delta (\tau )=g_{2}(\tau )^{3}-27g_{3}(\tau )^{2}=(2\pi )^{12}\,\eta ^{24}(\tau )}
is generally a transcendental number. In particular, the value of the Dedekind eta function η(2_i_) is
η ( 2 i ) = Γ ( 1 4 ) 2 11 8 π 3 4 {\displaystyle \eta (2i)={\frac {\Gamma \left({\frac {1}{4}}\right)}{2^{\frac {11}{8}}\pi ^{\frac {3}{4}}}}}
Note that the uniformization theorem implies that every compact Riemann surface of genus one can be represented as a torus. This also allows an easy understanding of the torsion points on an elliptic curve: if the lattice Λ is spanned by the fundamental periods _ω_1 and _ω_2, then the n-torsion points are the (equivalence classes of) points of the form
a n ω 1 + b n ω 2 {\displaystyle {\frac {a}{n}}\omega _{1}+{\frac {b}{n}}\omega _{2}}
for integers a and b in the range 0 ≤ (a, b) < n.
If
E : y 2 = 4 ( x − e 1 ) ( x − e 2 ) ( x − e 3 ) {\displaystyle E:y^{2}=4(x-e_{1})(x-e_{2})(x-e_{3})}
is an elliptic curve over the complex numbers and
a 0 = e 1 − e 3 , b 0 = e 1 − e 2 , c 0 = e 2 − e 3 , {\displaystyle a_{0}={\sqrt {e_{1}-e_{3}}},\qquad b_{0}={\sqrt {e_{1}-e_{2}}},\qquad c_{0}={\sqrt {e_{2}-e_{3}}},}
then a pair of fundamental periods of E can be calculated very rapidly by
ω 1 = π M ( a 0 , b 0 ) , ω 2 = π M ( c 0 , i b 0 ) {\displaystyle \omega _{1}={\frac {\pi }{\operatorname {M} (a_{0},b_{0})}},\qquad \omega _{2}={\frac {\pi }{\operatorname {M} (c_{0},ib_{0})}}}
M(w, z) is the arithmetic–geometric mean of w and z. At each step of the arithmetic–geometric mean iteration, the signs of zn arising from the ambiguity of geometric mean iterations are chosen such that |wn − zn| ≤ |wn + zn| where wn and zn denote the individual arithmetic mean and geometric mean iterations of w and z, respectively. When |wn − zn| = |wn + zn|, there is an additional condition that Im(zn/_wn_) > 0.[21]
Over the complex numbers, every elliptic curve has nine inflection points. Every line through two of these points also passes through a third inflection point; the nine points and 12 lines formed in this way form a realization of the Hesse configuration.
Given an isogeny
f : E → E ′ {\displaystyle f:E\rightarrow E'}
of elliptic curves of degree n {\displaystyle n} 
f ^ : E ′ → E {\displaystyle {\hat {f}}:E'\rightarrow E}
of the same degree such that
f ∘ f ^ = [ n ] . {\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n].}
Here [ n ] {\displaystyle [n]} ![{\displaystyle [n]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a26847bfc29bbeb4d6ef62ac3fd076378c0fd1db)



Construction of the Dual Isogeny
[edit]
Often only the existence of a dual isogeny is needed, but it can be explicitly given as the composition
E ′ → Div 0 ( E ′ ) → Div 0 ( E ) → E {\displaystyle E'\rightarrow {\mbox{Div}}^{0}(E')\to {\mbox{Div}}^{0}(E)\rightarrow E\,}
where D i v 0 {\displaystyle {\mathrm {Div} }^{0}} 






To see that f ∘ f ^ = [ n ] {\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n]} ![{\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1b3abeb3d135c6c7ac30f660bc8eb29930af3d63)

E → Div 0 ( E ) → Div 0 ( E ′ ) → E ′ {\displaystyle E\rightarrow {\mbox{Div}}^{0}(E)\to {\mbox{Div}}^{0}(E')\to E'\,}
and that since f {\displaystyle f} 




Alternatively, we can use the smaller Picard group P i c 0 {\displaystyle {\mathrm {Pic} }^{0}} 



E ′ → Pic 0 ( E ′ ) → Pic 0 ( E ) → E {\displaystyle E'\to {\mbox{Pic}}^{0}(E')\to {\mbox{Pic}}^{0}(E)\to E\,}
Note that the relation f ∘ f ^ = [ n ] {\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n]} ![{\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1b3abeb3d135c6c7ac30f660bc8eb29930af3d63)
![{\displaystyle {\hat {f}}\circ f=[n].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/db9b4cff65c3c9027f5bc75a4aefebe3110726d9)

![{\displaystyle \phi \circ {\hat {f}}={\hat {f}}\circ [n]=[n]\circ {\hat {f}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/82b6080d67f899f96c9bfaae4f531c7df81a957e)

![{\displaystyle \phi =[n].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e9e3f6a2c5064d9fd024a8b2c6609d2638012b10)
Algorithms that use elliptic curves
[edit]
Elliptic curves over finite fields are used in some cryptographic applications as well as for integer factorization. Typically, the general idea in these applications is that a known algorithm which makes use of certain finite groups is rewritten to use the groups of rational points of elliptic curves. For more see also:
- Elliptic curve cryptography
- Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman key exchange (ECDH)
- Supersingular isogeny key exchange
- Elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA)
- EdDSA digital signature algorithm
- Dual EC DRBG random number generator
- Lenstra elliptic-curve factorization
- Elliptic curve primality proving
Alternative representations of elliptic curves
[edit]
- Hessian curve
- Edwards curve
- Twisted curve
- Twisted Hessian curve
- Twisted Edwards curve
- Doubling-oriented Doche–Icart–Kohel curve
- Tripling-oriented Doche–Icart–Kohel curve
- Jacobian curve
- Montgomery curve
- Arithmetic dynamics
- Elliptic algebra
- Elliptic surface
- Comparison of computer algebra systems
- Isogeny
- j-line
- Level structure (algebraic geometry)
- Modularity theorem
- Moduli stack of elliptic curves
- Nagell–Lutz theorem
- Riemann–Hurwitz formula
- Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem
- ^ Sarli, J. (2012). "Conics in the hyperbolic plane intrinsic to the collineation group". J. Geom. 103: 131–148. doi:10.1007/s00022-012-0115-5. S2CID 119588289.
- ^ Silverman 1986, III.1 Weierstrass Equations (p.45)
- ^ T. Nagell, L'analyse indéterminée de degré supérieur, Mémorial des sciences mathématiques 39, Paris, Gauthier-Villars, 1929, pp. 56–59.
- ^ OEIS: https://oeis.org/A029728
- ^ Siksek, Samir (1995), Descents on Curves of Genus 1 (Ph.D. thesis), University of Exeter, pp. 16–17, hdl:10871/8323.
- ^ Silverman 1986, Theorem 4.1
- ^ Silverman 1986, pp. 199–205
- ^ See also J. W. S. Cassels, Mordell's Finite Basis Theorem Revisited, Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 100, 3–41 and the comment of A. Weil on the genesis of his work: A. Weil, Collected Papers, vol. 1, 520–521.
- ^ Dujella, Andrej. "History of elliptic curves rank records". University of Zagreb.
- ^ Silverman 1986, Theorem 7.5
- ^ Silverman 1986, Remark 7.8 in Ch. VIII
- ^ The definition is formal, the exponential of this power series without constant term denotes the usual development.
- ^ see for example Silverman, Joseph H. (2006). "An Introduction to the Theory of Elliptic Curves" (PDF). Summer School on Computational Number Theory and Applications to Cryptography. University of Wyoming.
- ^ https://www.lmfdb.org/knowledge/show/ec.bad_reduction
- ^ Koblitz 1993
- ^ Heath-Brown, D. R. (2004). "The Average Analytic Rank of Elliptic Curves". Duke Mathematical Journal. 122 (3): 591–623. arXiv:math/0305114. doi:10.1215/S0012-7094-04-12235-3. S2CID 15216987.
- ^ See Koblitz 1994, p. 158
- ^ Koblitz 1994, p. 160
- ^ Harris, M.; Shepherd-Barron, N.; Taylor, R. (2010). "A family of Calabi–Yau varieties and potential automorphy". Annals of Mathematics. 171 (2): 779–813. doi:10.4007/annals.2010.171.779.
- ^ Merel, L. (1996). "Bornes pour la torsion des courbes elliptiques sur les corps de nombres". Inventiones Mathematicae (in French). 124 (1–3): 437–449. Bibcode:1996InMat.124..437M. doi:10.1007/s002220050059. S2CID 3590991. Zbl 0936.11037.
- ^ Wing Tat Chow, Rudolf (2018). "The Arithmetic-Geometric Mean and Periods of Curves of Genus 1 and 2" (PDF). White Rose eTheses Online. p. 12.
Serge Lang, in the introduction to the book cited below, stated that "It is possible to write endlessly on elliptic curves. (This is not a threat.)" The following short list is thus at best a guide to the vast expository literature available on the theoretical, algorithmic, and cryptographic aspects of elliptic curves.
- Ian Blake; Gadiel Seroussi; Nigel Smart (2000). Elliptic Curves in Cryptography. LMS Lecture Notes. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-65374-6.
- Brown, Ezra (2000). "Three Fermat Trails to Elliptic Curves". The College Mathematics Journal. 31 (3): 162–172. doi:10.1080/07468342.2000.11974137. S2CID 5591395., winner of the MAA writing prize the George Pólya Award
- Richard Crandall; Carl Pomerance (2001). "Chapter 7: Elliptic Curve Arithmetic". Prime Numbers: A Computational Perspective (1st ed.). Springer-Verlag. pp. 285–352. ISBN 0-387-94777-9.
- Cremona, John (1997). Algorithms for Modular Elliptic Curves (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-59820-6.
- Darrel Hankerson, Alfred Menezes and Scott Vanstone (2004). Guide to Elliptic Curve Cryptography. Springer. ISBN 0-387-95273-X.
- Hardy, G. H.; Wright, E. M. (2008) [1938]. An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers. Revised by D. R. Heath-Brown and J. H. Silverman. Foreword by Andrew Wiles. (6th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-921986-5. MR 2445243. Zbl 1159.11001. Chapter XXV
- Hellegouarch, Yves (2001). Invitation aux mathématiques de Fermat-Wiles. Paris: Dunod. ISBN 978-2-10-005508-1.
- Husemöller, Dale (2004). Elliptic Curves. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 111 (2nd ed.). Springer. ISBN 0-387-95490-2.
- Kenneth Ireland; Michael I. Rosen (1998). "Chapters 18 and 19". A Classical Introduction to Modern Number Theory. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 84 (2nd revised ed.). Springer. ISBN 0-387-97329-X.
- Knapp, Anthony W. (2018) [1992]. Elliptic Curves. Mathematical Notes. Vol. 40. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691186900.
- Koblitz, Neal (1993). Introduction to Elliptic Curves and Modular Forms. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 97 (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97966-2.
- Koblitz, Neal (1994). "Chapter 6". A Course in Number Theory and Cryptography. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 114 (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-94293-9.
- Serge Lang (1978). Elliptic curves: Diophantine analysis. Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften. Vol. 231. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-08489-4.
- Henry McKean; Victor Moll (1999). Elliptic curves: function theory, geometry and arithmetic. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-65817-9.
- Ivan Niven; Herbert S. Zuckerman; Hugh Montgomery (1991). "Section 5.7". An introduction to the theory of numbers (5th ed.). John Wiley. ISBN 0-471-54600-3.
- Silverman, Joseph H. (1986). The Arithmetic of Elliptic Curves. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 106. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-96203-4.
- Joseph H. Silverman (1994). Advanced Topics in the Arithmetic of Elliptic Curves. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 151. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-94328-5.
- Joseph H. Silverman; John Tate (1992). Rational Points on Elliptic Curves. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-97825-9.
- John Tate (1974). "The arithmetic of elliptic curves". Inventiones Mathematicae. 23 (3–4): 179–206. Bibcode:1974InMat..23..179T. doi:10.1007/BF01389745. S2CID 120008651.
- Lawrence Washington (2003). Elliptic Curves: Number Theory and Cryptography. Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 1-58488-365-0.
- LMFDB: Database of Elliptic Curves over Q
- "Elliptic curve", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Elliptic Curves". MathWorld.
- The Arithmetic of elliptic curves from PlanetMath
- Interactive elliptic curve over R and over Zp – web application that requires HTML5 capable browser.
This article incorporates material from Isogeny on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.















![{\displaystyle Z(E(\mathbf {F} _{p}),T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\#\left[E({\mathbf {F} }_{p^{n}})\right]{\frac {T^{n}}{n}}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a5e3238b8c26886b9bb7ee84530036d9c50133ef)









![{\displaystyle Z(E(K),T)=\exp \left(\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\#\left[E(K_{n})\right]{T^{n} \over n}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/608830007ce25cbc3a81ef246adff37a4bf9572e)

















![{\displaystyle z\mapsto \left[1:\wp (z):{\tfrac {1}{2}}\wp '(z)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c351bf351c830acec700d97d49f2eeff421f8644)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}g_{2}'&={\frac {\sqrt[{3}]{4}}{3}}\left(\lambda ^{2}-\lambda +1\right)\[4pt]g_{3}'&={\frac {1}{27}}(\lambda +1)\left(2\lambda ^{2}-5\lambda +2\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1bf4038a9f1589968852c135e3541865cfb05136)









![{\displaystyle f\circ {\hat {f}}=[n].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b0902791fd7c1ef2cfbe31dfc7c8aadb95904acb)


