Females and Fragile X: Full Mutation and Premutation | Info Series (original) (raw)
-
- Fragile X 101
* Fragile X 101
* Prevalence
* Signs and Symptoms
* Genetics and Inheritance
* Testing and Diagnosis - Fragile X Syndrome
* Fragile X Syndrome
* Newly Diagnosed
* Fragile X & Autism - Associated Conditions
* Premutation
* FXPOI
* FXTAS
* New Developments - Xtraordinary Individuals
- 31 Shareable Fragile X Facts
- Fragile X Info SeriesFact sheets by topic
- Fragile X MasterClass™️
- Knowledge CenterFrequently asked questions.
- Fragile X 101
-
- Resources for Families
- FXS Strategies by Topic
* Adulthood
* Autism
* Behavior
* COVID-19
* Daily Living
* Females
* Medications
* Physical & Medical Concerns
* Puberty & Sexuality
* School & Education - FXS Resources by Age
- Premutation Topics
* The Fragile X Premutation
* FXTAS Resources
* FXPOI Resources
* Reproductive Resources - Newly Diagnosed
- ResearchLearn and participate
* Research 101What is research?
* STX209 Reconsent ProjectEnrollment is open
* International Fragile X Premutation Registry — For ParticipantsEnroll now
* Participate in ResearchMyFXResearch Portal
* Original Research Articles
* FORWARD-MARCHDatabase and registry
* Research ResultsNew and archives - Find a Fragile X Clinic
* U.S. Fragile X Syndrome Clinics
* FXTAS-Specific Clinics
* International Clinics & Organizations - Find a Contact Near You
- Knowledge CenterOur Fragile X library
- Webinars & Videos
- Printable Resources
- Treatment Recommendations
-
- Resources for Professionals
- NFXF MasterClass™️ for Professionals
- Research Readiness ProgramResearch facilitation for researchers
- NFXF Data Repository
- International Fragile X Premutation Registry — Research Requests
- FORWARD-MARCHRegistry & Database
- NFXF-Led PFDD Meeting for Fragile X SyndromePatient-focused drug development
- Marketing Your Research Opportunities
- Treatment Recommendations
- Fragile X Clinics
* U.S. FXS Clinics
* FXTAS-Specific Clinics
* International Clinics & Organizations - NFXF RESEARCH AWARDS
* Randi J. Hagerman Summer Scholar Research Awards
* Junior Investigator Awards
Get
Involved-
- Fragile X 101
* Fragile X 101
* Prevalence
* Signs & Symptoms
* Genetics and Inheritance
* Testing and Diagnosis - Fragile X Syndrome
* Fragile X Syndrome
* Fragile X & Autism - Associated Conditions
* Premutation
* FXPOI
* FXTAS
* New Developments - Xtraordinary Individuals
- 31 Shareable Fragile X Facts
- Fragile X Info Series
- FRAGILE X MASTERCLASS
- Knowledge Center
- Fragile X 101
-
- Resources for Families
- FXS Strategies by Topic
* Adulthood
* Autism
* Behavior
* Daily Living
* Females
* Medications
* Physical & Medical Concerns
* Fragile X and Puberty & Sexuality
* School & Education - FXS Resources by Age
- Premutation Topics
* The Fragile X Premutation
* FXTAS Resources
* FXPOI Resources
* Reproductive Resources - Newly Diagnosed
- Research
* Research 101: What is Research?
* STX209 Reconsent Project
* International Fragile X Premutation Registry — For Participants
* Participate in Research
* Original Research Articles
* FORWARD-MARCH
* Research Results Roundup - Find a Clinic Near You
- Find a Contact Near Your
- Knowledge Center
- Webinars & Videos
- Printable Resources
- Treatment Recommendations
-
- Resources for Professionals
- NFXF MasterClass™️ for Professionals
- Research Readiness Program
- NFXF Data Repository
- International Fragile X Premutation Registry — Research Requests
- FORWARD-MARCH Registry & Database
- NFXF-Led Patient-Focused Drug Development Meeting
- Marketing Your Research Opportunities
- Treatment Recommendations
- Find a Clinic Near You
- NFXF Research Awards
* Randi J. Hagerman Summer Scholars
* Junior Investigator Awards
Fragile X Info Series: Females and Fragile X
Fragile X Info Series: Females and Fragile XDany Petraska2023-10-12T13:27:48-04:00
Fragile X Info Series
Females and
Fragile X
Females and Fragile X, including physical, cognitive, behavioral, and emotional issues associated with the mutation, and the differences when compared to males.
overview of fragile x syndrome and associated disorders
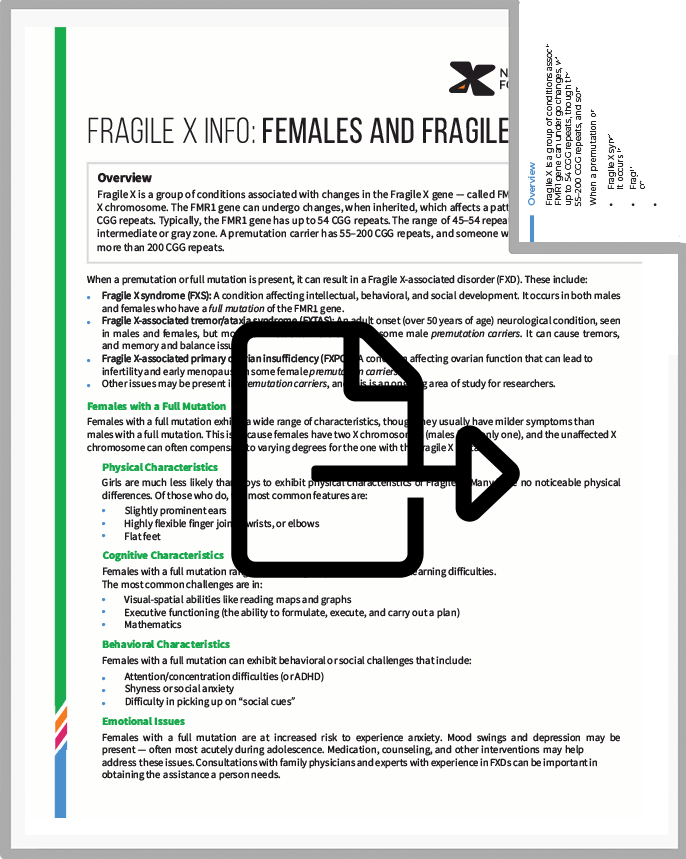
Fragile X is a group of conditions associated with changes in the Fragile X gene — called FMRl — located on the X chromosome. The FMRl gene can undergo changes, when inherited, which affects a pattern of DNA called CGG repeats. Typically, the FMRl gene has up to 54 CGG repeats. The range of 45–54 repeats is called the intermediate or “gray zone.” A premutation carrier has 55–200 CGG repeats, and someone with a full mutation has more than 200 CGG repeats.
When a premutation or full mutation is present, it can result in a Fragile X-associated disorder (FXD). These include:
FXS is a condition affecting intellectual, behavioral, and social development. It occurs in both males and females who have a full mutation of the FMRl gene.
FRAGILE X-ASSOCIATED TREMOR/ATAXIA SYNDROME
FXTAS is an adult onset (over 50 years of age) neurological condition, seen in males and females, but more common and more severe in some male premutation carriers. It can cause tremors, memory, and balance issues.
FRAGILE X-ASSOCIATED PRIMARY OVARIAN INSUFFICIENCY
FXPOI is a condition affecting ovarian function that can lead to infertility and early menopause in some female premutation carriers.
Genetic counseling is recommended for any woman with a Fragile X premutation or full mutation. This can allow for discussion of pregnancy issues, and reproductive options including prenatal testing, use of egg donor or IVF, and other options.
Testing to determine whether a full mutation or premutation exists is recommended for any adult woman who may be at risk of being a premutation carrier. This includes women with a personal or family history of intellectual disability, FXS, FXTAS, or infertility.
OTHER PREMUTATION CONDITIONS
Females With a Full Mutation
Females with a full mutation exhibit a wide range of characteristics, though they usually have milder symptoms than males with a full mutation, and may not even know their status. This is because females have two X chromosomes (males have only one), and the unaffected X chromosome can often compensate to varying degrees for the one with the Fragile X mutation.
Women with a full mutation are not at risk for FXPOI and have no associated infertility.
Girls are much less likely than boys to exhibit physical characteristics of Fragile X. Many have no noticeable physical differences. Of those who do, the most common features are:
- Slightly prominent ears
- Highly flexible finger joints, wrists, or elbows
- Flat feet
COGNITIVE CHARACTERISTICS
Females with a full mutation range from having very mild to moderate learning difficulties. The most common challenges are in:
- Visual-spatial abilities like reading maps and graphs
- Executive functioning (the ability to formulate, execute, and carry out a plan)
- Mathematics
BEHAVIORAL CHARACTERISTICS
Females with a full mutation can exhibit behavioral or social challenges that include:
- Attention/concentration difficulties (or ADHD)
- Shyness or social anxiety
- Difficulty in picking up on “social cues”
Females with a full mutation are at increased risk to experience anxiety.
Mood swings and depression may be present — often most acutely during adolescence. Medication, counseling, and other interventions may help address these issues.
Consultations with family physicians and experts with experience in FXDs can be important in obtaining the assistance a person needs.
A small percentage of females who have the full mutation will have no apparent signs of the condition — physical, cognitive, behavioral, or emotional. These females are often identified only after another family member has been diagnosed.
Females with Premutation
Females with a premutation are at risk to have a child, male or female, with Fragile X syndrome. The magnitude of this risk is related to the number of CGG repeats identified in her FMRl gene. The larger the number, the higher the risk for expansion from a premutation to a full mutation if it is passed on.
Some women with a premutation have reported increased general anxiety, shyness, and social anxiety. In addition, there is evidence that women with the premutation are at increased risk for depression.
FXPOI
Approximately 20%-25% of women with a premutation experience FXPOI, which is characterized by infertility, decreased ovarian function, early menopause, or irregular cycles. (Note: Women with a full mutation are not at risk for FXPOI and have no associated infertility.)
FXTAS
FXTAS is another medical effect of the premutation. It is more common in male carriers, but has been reported in about 5%-8% of female carriers over the age of 50.
The Unique Challenges for Females with Fragile X Syndrome
By Marcia Braden
The more we learn, the more effective our interventions and support structures become in assisting them to live personally fulfilling lives.
What Defines a Carrier?
By Brenda Finucane
Why is there so much variability among male and female Fragile X carriers? There are a number of factors involved. Because the Fragile X gene is X-linked, gender plays a big role in determining who might show symptoms.
DOWNLOAD THIS PAGE AS A PDF
Females and Fragile X
Characteristics of females with full mutation and premutation Fragile X.
How We Can Help
The NFXF is dedicated to serving the entire Fragile X community to live their best lives by providing the knowledge, resources, and tools, until, and even after more effective treatments and a cure are achieved. Learn more with Fragile X 101.
If you have questions please reach out to us at treatment@fragilex.org or call (800) 688-8765.