The Future of the Global Muslim Population (original) (raw)
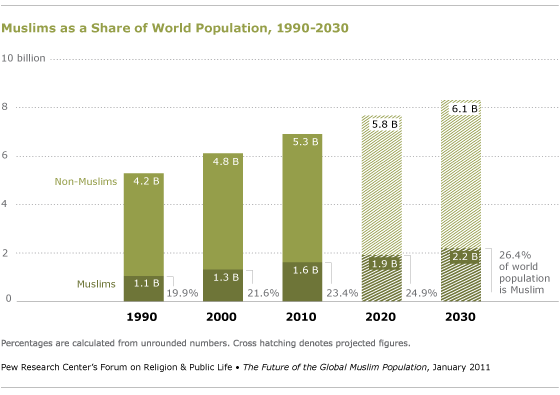
The world’s Muslim population is expected to increase by about 35% in the next 20 years, rising from 1.6 billion in 2010 to 2.2 billion by 2030, according to new population projections by the Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion & Public Life.
Globally, the Muslim population is forecast to grow at about twice the rate of the non-Muslim population over the next two decades – an average annual growth rate of 1.5% for Muslims, compared with 0.7% for non-Muslims. If current trends continue, Muslims will make up 26.4% of the world’s total projected population of 8.3 billion in 2030, up from 23.4% of the estimated 2010 world population of 6.9 billion.
While the global Muslim population is expected to grow at a faster rate than the non-Muslim population, the Muslim population nevertheless is expected to grow at a slower pace in the next two decades than it did in the previous two decades. From 1990 to 2010, the global Muslim population increased at an average annual rate of 2.2%, compared with the projected rate of 1.5% for the period from 2010 to 2030.
These are among the key findings of a comprehensive report on the size, distribution and growth of the global Muslim population. The report by the Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life seeks to provide up-to-date estimates of the number of Muslims around the world in 2010 and to project the growth of the Muslim population from 2010 to 2030. The projections are based both on past demographic trends and on assumptions about how these trends will play out in future years. Making these projections inevitably entails a host of uncertainties, including political ones. Changes in the political climate in the United States or European nations, for example, could dramatically affect the patterns of Muslim migration.

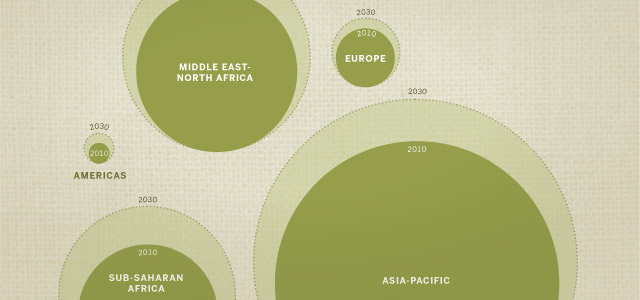
If current trends continue, however, 79 countries will have a million or more Muslim inhabitants in 2030, up from 72 countries today.1 A majority of the world’s Muslims (about 60%) will continue to live in the Asia-Pacific region, while about 20% will live in the Middle East and North Africa, as is the case today. But Pakistan is expected to surpass Indonesia as the country with the single largest Muslim population. The portion of the world’s Muslims living in sub-Saharan Africa is projected to rise; in 20 years, for example, more Muslims are likely to live in Nigeria than in Egypt. Muslims will remain relatively small minorities in Europe and the Americas, but they are expected to constitute a growing share of the total population in these regions.

In the United States, for example, the population projections show the number of Muslims more than doubling over the next two decades, rising from 2.6 million in 2010 to 6.2 million in 2030, in large part because of immigration and higher-than-average fertility among Muslims. The Muslim share of the U.S. population (adults and children) is projected to grow from 0.8% in 2010 to 1.7% in 2030, making Muslims roughly as numerous as Jews or Episcopalians are in the United States today. Although several European countries will have substantially higher percentages of Muslims, the United States is projected to have a larger number of Muslims by 2030 than any European countries other than Russia and France. (See the Americas section for more details.)
In Europe as a whole, the Muslim share of the population is expected to grow by nearly one-third over the next 20 years, rising from 6% of the region’s inhabitants in 2010 to 8% in 2030. In absolute numbers, Europe’s Muslim population is projected to grow from 44.1 million in 2010 to 58.2 million in 2030. The greatest increases – driven primarily by continued migration – are likely to occur in Western and Northern Europe, where Muslims will be approaching double-digit percentages of the population in several countries. In the United Kingdom, for example, Muslims are expected to comprise 8.2% of the population in 2030, up from an estimated 4.6% today. In Austria, Muslims are projected to reach 9.3% of the population in 2030, up from 5.7% today; in Sweden, 9.9% (up from 4.9% today); in Belgium, 10.2% (up from 6% today); and in France, 10.3% (up from 7.5% today). (See the Europe section.)
Several factors account for the faster projected growth among Muslims than non-Muslims worldwide. Generally, Muslim populations tend to have higher fertility rates (more children per woman) than non-Muslim populations. In addition, a larger share of the Muslim population is in, or soon will enter, the prime reproductive years (ages 15-29). Also, improved health and economic conditions in Muslim-majority countries have led to greater-than-average declines in infant and child mortality rates, and life expectancy is rising even faster in Muslim-majority countries than in other less-developed countries. (See the section on Main Factors Driving Population Growth for more details. For a list of Muslim-majority countries and definitions for the terms less- and more-developed, see the section on Muslim- Majority Countries.)
Growing, But at a Slower Rate
The growth of the global Muslim population, however, should not obscure another important demographic trend: the rate of growth among Muslims has been slowing in recent decades and is likely to continue to decline over the next 20 years, as the graph below shows. From 1990 to 2000, the Muslim population grew at an average annual rate of 2.3%. The growth rate dipped to 2.1% from 2000 to 2010, and it is projected to drop to 1.7% from 2010 to 2020 and 1.4% from 2020 to 2030 (or 1.5% annually over the 20-year period from 2010 to 2030, as previously noted).
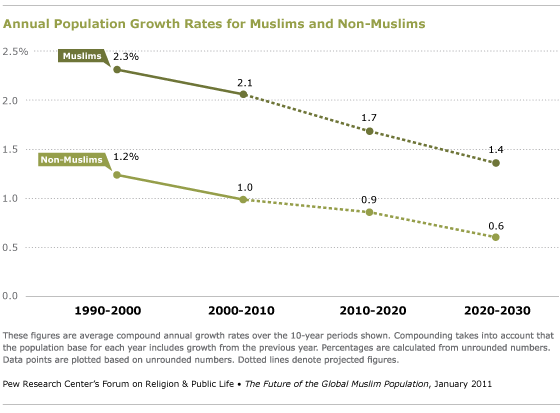
The declining growth rate is due primarily to falling fertility rates in many Muslim-majority countries, including such populous nations as Indonesia and Bangladesh. Fertility is dropping as more women in these countries obtain a secondary education, living standards rise and people move from rural areas to cities and towns. (See the Related Factors section for more details.)

The slowdown in Muslim population growth is most pronounced in the Asia- Pacific region, the Middle East-North Africa and Europe, and less sharp in sub-Saharan Africa. The only region where Muslim population growth is accelerating through 2020 is the Americas, largely because of immigration. (For details, see the charts on population growth in the sections of this report on Asia-Pacific, Middle-East-North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Europe and the Americas.)
Falling birth rates eventually will lead to significant shifts in the age structure of Muslim populations. While the worldwide Muslim population today is relatively young, the so-called Muslim “youth bulge” – the high percentage of Muslims in their teens and 20s – peaked around the year 2000 and is now declining. (See the Age Structure section for more details.)
In 1990, more than two-thirds of the total population of Muslim-majority countries was under age 30. Today, people under 30 make up about 60% of the population of these countries, and by 2030 they are projected to fall to about 50%.
At the same time, many Muslim-majority countries will have aging populations; between 2010 and 2030, the share of people age 30 and older in these countries is expected to rise from 40% to 50%, and the share of people age 60 and older is expected nearly to double, from 7% to 12%.
Muslim-majority countries, however, are not the only ones with aging populations. As birth rates drop and people live longer all around the globe, the population of the entire world is aging. As a result, the global Muslim population will remain comparatively youthful for decades to come. The median age in Muslim-majority countries, for example, rose from 19 in 1990 to 24 in 2010 and is expected to climb to 30 by 2030. But it will still be lower than the median age in North America, Europe and other more-developed regions, which rose from 34 to 40 between 1990 and 2010 and is projected to be 44 in 2030. By that year, nearly three-in-ten of the world’s youth and young adults – 29.1% of people ages 15-29 – are projected to be Muslims, up from 25.8% in 2010 and 20.0% in 1990.
Other key findings of the study include:
Worldwide
- Sunni Muslims will continue to make up an overwhelming majority of Muslims in 2030 (87- 90%). The portion of the world’s Muslims who are Shia may decline slightly, largely because of relatively low fertility in Iran, where more than a third of the world’s Shia Muslims live.
- As of 2010, about three-quarters of the world’s Muslims (74.1%) live in the 49 countries in which Muslims make up a majority of the population. More than a fifth of all Muslims (23.3%) live in non-Muslim-majority countries in the developing world. About 3% of the world’s Muslims live in more-developed regions, such as Europe, North America, Australia, New Zealand and Japan.
- Fertility rates in Muslim-majority countries are closely related to women’s education levels. In the eight Muslim-majority countries where girls generally receive the fewest years of schooling, the average fertility rate (5.0 children per woman) is more than double the average rate (2.3 children per woman) in the nine Muslim-majority countries where girls generally receive the most years of schooling. One exception is the Palestinian territories, where the average fertility rate (4.5 children per woman) is relatively high even though a girl born there today can expect to receive 14 years of formal education.
- Fewer than half (47.8%) of married women ages 15-49 in Muslim-majority countries use some form of birth control. By comparison, in non-Muslim-majority, less-developed countries nearly two-thirds (63.3%) of all married women in that age group use some form of birth control.
Asia-Pacific

- Nearly three-in-ten people living in the Asia-Pacific region in 2030 (27.3%) will be Muslim, up from about a quarter in 2010 (24.8%) and roughly a fifth in 1990 (21.6%).
- Muslims make up only about 2% of the population in China, but because the country is so populous, its Muslim population is expected to be the 19th largest in the world in 2030.
Middle East-North Africa

- The Middle East-North Africa will continue to have the highest percentage of Muslim-majority countries. Of the 20 countries and territories in this region, all but Israel are projected to be at least 50% Muslim in 2030, and 17 are expected to have a population that is more than 75% Muslim in 2030, with Israel, Lebanon and Sudan (as currently demarcated) being the only exceptions.
- Nearly a quarter (23.2%) of Israel’s population is expected to be Muslim in 2030, up from 17.7% in 2010 and 14.1% in 1990. During the past 20 years, the Muslim population in Israel has more than doubled, growing from 0.6 million in 1990 to 1.3 million in 2010. The Muslim population in Israel (including Jerusalem but not the West Bank and Gaza) is expected to reach 2.1 million by 2030.
- Egypt, Algeria and Morocco currently have the largest Muslim populations in the Middle East-North Africa. By 2030, however, Iraq is expected to have the second-largest Muslim population in the region – exceeded only by Egypt – largely because Iraq has a higher fertility rate than Algeria or Morocco.
Sub-Saharan Africa

- The Muslim population in sub-Saharan Africa is projected to grow by nearly 60% in the next 20 years, from 242.5 million in 2010 to 385.9 million in 2030. Because the region’s non- Muslim population also is growing at a rapid pace, Muslims are expected to make up only a slightly larger share of the region’s population in 2030 (31.0%) than they do in 2010 (29.6%).
- Various surveys give differing figures for the size of religious groups in Nigeria, which appears to have roughly equal numbers of Muslims and Christians in 2010. By 2030, Nigeria is expected to have a slight Muslim majority (51.5%).
Europe

- In 2030, Muslims are projected to make up more than 10% of the total population in 10 European countries: Kosovo (93.5%), Albania (83.2%), Bosnia-Herzegovina (42.7%), Republic of Macedonia (40.3%), Montenegro (21.5%), Bulgaria (15.7%), Russia (14.4%), Georgia (11.5%), France (10.3%) and Belgium (10.2%).
- Russia will continue to have the largest Muslim population (in absolute numbers) in Europe in 2030. Its Muslim population is expected to rise from 16.4 million in 2010 to 18.6 million in 2030. The growth rate for the Muslim population in Russia is projected to be 0.6% annually over the next two decades. By contrast, Russia’s non-Muslim population is expected to shrink by an average of 0.6% annually over the same period.
- France had an expected net influx of 66,000 Muslim immigrants in 2010, primarily from North Africa. Muslims comprised an estimated two-thirds (68.5%) of all new immigrants to France in the past year. Spain was expected to see a net gain of 70,000 Muslim immigrants in 2010, but they account for a much smaller portion of all new immigrants to Spain (13.1%). The U.K.’s net inflow of Muslim immigrants in the past year (nearly 64,000) was forecast to be nearly as large as France’s. More than a quarter (28.1%) of all new immigrants to the U.K. in 2010 are estimated to be Muslim.
The Americas

- The number of Muslims in Canada is expected to nearly triple in the next 20 years, from about 940,000 in 2010 to nearly 2.7 million in 2030. Muslims are expected to make up 6.6% of Canada’s total population in 2030, up from 2.8% today. Argentina is expected to have the third-largest Muslim population in the Americas, after the U.S. and Canada. Argentina, with about 1 million Muslims in 2010, is now in second place, behind the U.S.
- Children under age 15 make up a relatively small portion of the U.S. Muslim population today. Only 13.1% of Muslims are in the 0-14 age group. This reflects the fact that a large proportion of Muslims in the U.S. are newer immigrants who arrived as adults. But by 2030, many of these immigrants are expected to start families. If current trends continue, the number of U.S. Muslims under age 15 will more than triple, from fewer than 500,000 in 2010 to 1.8 million in2030. The number of Muslim children ages 0-4 living in the U.S. is expected to increase from fewer than 200,000 in 2010 to more than 650,000 in 2030.
- About two-thirds of the Muslims in the U.S. today (64.5%) are first-generation immigrants (foreign-born), while slightly more than a third (35.5%) were born in the U.S. By 2030, however, more than four-in-ten of the Muslims in the U.S. (44.9%) are expected to be native-born.
- The top countries of origin for Muslim immigrants to the U.S. in 2009 were Pakistan and Bangladesh. They are expected to remain the top countries of origin for Muslim immigrants to the U.S. in 2030.
About the Report
This report makes demographic projections. Projections are not the same as predictions. Rather, they are estimates built on current population data and assumptions about demographic trends; they are what will happen if the current data are accurate and the trends play out as expected. But many things – immigration laws, economic conditions, natural disasters, armed conflicts, scientific discoveries, social movements and political upheavals, to name just a few – can shift demographic trends in unforeseen ways, which is why this report adheres to a modest time frame, looking just 20 years down the road. Even so, there is no guarantee that Muslim populations will grow at precisely the rates anticipated in this report and not be affected by unforeseen events, such as political decisions on immigration quotas or national campaigns to encourage larger or smaller families.
The projections presented in this report are the medium figures in a range of three scenarios – high, medium and low – generated from models commonly used by demographers around the world to forecast changes in population size and composition. The models follow what is known as the cohort-component method, which starts with a baseline population (in this case, the current number of Muslims in each country) divided into groups, or cohorts, by age and sex. Each cohort is projected into the future by adding likely gains – new births and immigrants – and subtracting likely losses – deaths and emigrants. These calculations were made by the Pew Forum’s demographers, who collaborated with researchers at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) in Austria on the projections for the United States and European countries. (For more details, see Appendix A: Methodology.)
The current population data that underpin this report were culled from the best sources available on Muslims in each of the 232 countries and territories for which the U.N. Population Division provides general population estimates. Many of these baseline statistics were published in the Pew Forum’s 2009 report, Mapping the Global Muslim Population, which acquired and analyzed about 1,500 sources of data – including census reports, large-scale demographic studies and general population surveys – to estimate the number of Muslims in every country and territory. (For a list of sources, see Appendix B: Data Sources by Country.) All of those estimates have been updated for 2010, and some have been substantially revised. (To find the current estimate and projections for a particular region or country, see Muslim Population by Country, 1990-2030.) Since many countries are conducting national censuses in 2010-11, more data is likely to emerge over the next few years, but a cut-off must be made at some point; this report is based on information available as of mid-2010. To the extent possible, the report provides data for decennial years – 1990, 2000, 2010, 2020 and 2030. In some cases, however, the time periods vary because data is available only for certain years or in five-year increments (e.g., 2010-15 or 2030-35).
The definition of Muslim in this report is very broad. The goal is to count all groups and individuals who self-identify as Muslims. This includes Muslims who may be secular or nonobservant. No attempt is made in this report to measure how religious Muslims are or to forecast levels of religiosity (or secularism) in the decades ahead.2
The main factors, or inputs, in the population projections are:
- Births (fertility rates)
- Deaths (mortality rates)
- Migration (emigration and immigration), and
- The age structure of the population (the number of people in various age groups)
Related factors – which are not direct inputs into the projections but which underlie vital assumptions about the way Muslim fertility rates are changing and Muslim populations are shifting – include:
- Education (particularly of women)
- Economic well-being (standards of living)
- Contraception and family planning
- Urbanization (movement from rural areas into cities and towns), and
- Religious conversion
To fully understand the projections, one must understand these factors, which the next section of the report will discuss in more detail.
Readers can also explore an online, interactive feature that allows them to select a region or one of the 232 countries and territories – as well as a decade from 1990-2030 – and see the size of the Muslim population in that place and time.
Footnotes
1 The seven countries projected to rise above 1 million Muslims by 2030 are: Belgium, Canada, Congo, Djibouti, Guinea Bissau,Netherlands and Togo. (return to text)
2 In other reports, the Pew Forum and the Pew Research Center have used large-scale public opinion surveys to measure the beliefs and practices of many religious groups, including Muslims in several countries. See, for example,Tolerance and Tension: Islam and Christianity in Sub-Saharan Africa, 2010, and Muslim Americans: Middle Class and Mostly Mainstream, 2007. (return to text)
Photo Credits:
Asia-Pacific: Lindsay Hebberd/CORBIS Middle East-North Africa: Alaa Al-Shemaree/epa/Corbis Sub-Saharan Africa: Paul Almasy/CORBIS Europe: Pascal Le Segretain/CORBIS SYGMA Americas: John Van Hasselt/Sygma/Corbis