GPTBigCode (original) (raw)


Overview
The GPTBigCode model was proposed in SantaCoder: don’t reach for the stars! by BigCode. The listed authors are: Loubna Ben Allal, Raymond Li, Denis Kocetkov, Chenghao Mou, Christopher Akiki, Carlos Munoz Ferrandis, Niklas Muennighoff, Mayank Mishra, Alex Gu, Manan Dey, Logesh Kumar Umapathi, Carolyn Jane Anderson, Yangtian Zi, Joel Lamy Poirier, Hailey Schoelkopf, Sergey Troshin, Dmitry Abulkhanov, Manuel Romero, Michael Lappert, Francesco De Toni, Bernardo García del Río, Qian Liu, Shamik Bose, Urvashi Bhattacharyya, Terry Yue Zhuo, Ian Yu, Paulo Villegas, Marco Zocca, Sourab Mangrulkar, David Lansky, Huu Nguyen, Danish Contractor, Luis Villa, Jia Li, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Yacine Jernite, Sean Hughes, Daniel Fried, Arjun Guha, Harm de Vries, Leandro von Werra.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
The BigCode project is an open-scientific collaboration working on the responsible development of large language models for code. This tech report describes the progress of the collaboration until December 2022, outlining the current state of the Personally Identifiable Information (PII) redaction pipeline, the experiments conducted to de-risk the model architecture, and the experiments investigating better preprocessing methods for the training data. We train 1.1B parameter models on the Java, JavaScript, and Python subsets of The Stack and evaluate them on the MultiPL-E text-to-code benchmark. We find that more aggressive filtering of near-duplicates can further boost performance and, surprisingly, that selecting files from repositories with 5+ GitHub stars deteriorates performance significantly. Our best model outperforms previous open-source multilingual code generation models (InCoder-6.7B and CodeGen-Multi-2.7B) in both left-to-right generation and infilling on the Java, JavaScript, and Python portions of MultiPL-E, despite being a substantially smaller model. All models are released under an OpenRAIL license at this https URL.
The model is an optimized GPT2 model with support for Multi-Query Attention.
Implementation details
The main differences compared to GPT2.
- Added support for Multi-Query Attention.
- Use
gelu_pytorch_tanhinstead of classicgelu. - Avoid unnecessary synchronizations (this has since been added to GPT2 in #20061, but wasn’t in the reference codebase).
- Use Linear layers instead of Conv1D (good speedup but makes the checkpoints incompatible).
- Merge
_attnand_upcast_and_reordered_attn. Always merge the matmul with scaling. Renamereorder_and_upcast_attn->attention_softmax_in_fp32 - Cache the attention mask value to avoid recreating it every time.
- Use jit to fuse the attention fp32 casting, masking, softmax, and scaling.
- Combine the attention and causal masks into a single one, pre-computed for the whole model instead of every layer.
- Merge the key and value caches into one (this changes the format of layer_past/ present, does it risk creating problems?)
- Use the memory layout (self.num_heads, 3, self.head_dim) instead of
(3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)for the QKV tensor with MHA. (prevents an overhead with the merged key and values, but makes the checkpoints incompatible with the original openai-community/gpt2 model).
You can read more about the optimizations in the original pull request
Combining Starcoder and Flash Attention 2
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2 to include the sliding window attention feature.
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
Make also sure that you have a hardware that is compatible with Flash-Attention 2. Read more about it in the official documentation of flash-attn repository. Make also sure to load your model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16“)
To load and run a model using Flash Attention 2, refer to the snippet below:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer device = "cuda"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2") tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder")
prompt = "def hello_world():"
model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to(device) model.to(device)
generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=30, do_sample=False) tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0] 'def hello_world():\n print("hello world")\n\nif name == "main":\n print("hello world")\n<|endoftext|>'
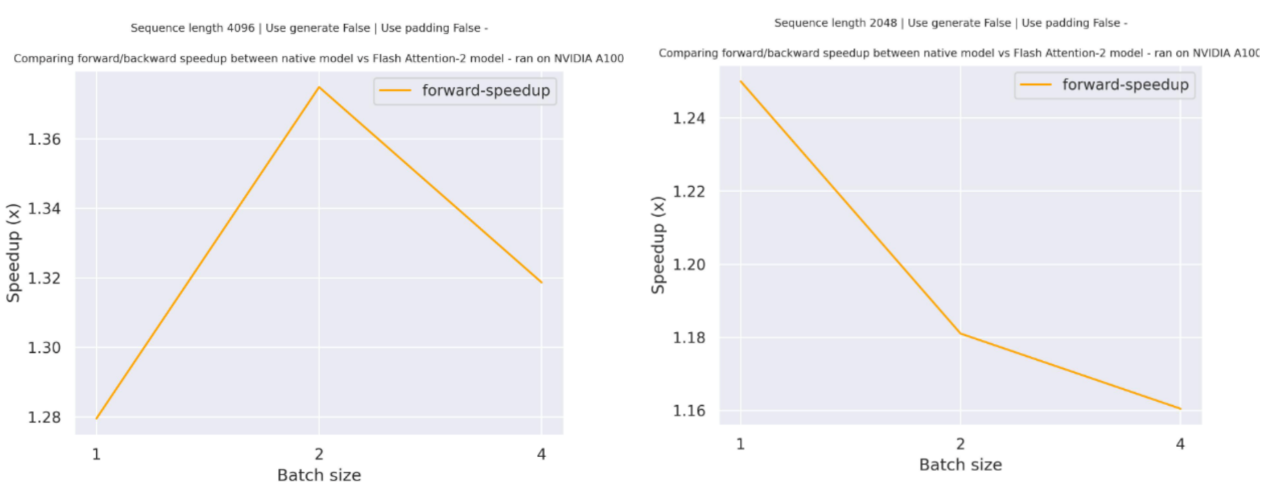
Expected speedups
Below is a expected speedup diagram that compares pure inference time between the native implementation in transformers using bigcode/starcoder checkpoint and the Flash Attention 2 version of the model using two different sequence lengths.
GPTBigCodeConfig
class transformers.GPTBigCodeConfig
( vocab_size = 50257 n_positions = 1024 n_embd = 768 n_layer = 12 n_head = 12 n_inner = None activation_function = 'gelu_pytorch_tanh' resid_pdrop = 0.1 embd_pdrop = 0.1 attn_pdrop = 0.1 layer_norm_epsilon = 1e-05 initializer_range = 0.02 scale_attn_weights = True use_cache = True bos_token_id = 50256 eos_token_id = 50256 attention_softmax_in_fp32 = True scale_attention_softmax_in_fp32 = True multi_query = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 50257) — Vocabulary size of the GPT-2 model. Defines the number of different tokens that can be represented by theinputs_idspassed when calling GPTBigCodeModel. - n_positions (
int, optional, defaults to 1024) — The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048). - n_embd (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the embeddings and hidden states. - n_layer (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - n_head (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - n_inner (
int, optional, defaults to None) — Dimensionality of the inner feed-forward layers.Nonewill set it to 4 times n_embd - activation_function (
str, optional, defaults to"gelu_pytorch_tanh") — Activation function, to be selected in the list["relu", "silu", "gelu", "tanh", "gelu_new", "gelu_pytorch_tanh"]. - resid_pdrop (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler. - embd_pdrop (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout ratio for the embeddings. - attn_pdrop (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout ratio for the attention. - layer_norm_epsilon (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — The epsilon to use in the layer normalization layers. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - scale_attn_weights (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Scale attention weights by dividing by sqrt(hidden_size).. - use_cache (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not the model should return the last key/values attentions (not used by all models). - attention_softmax_in_fp32 (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to call the fused softmax in float32. - scale_attention_softmax_in_fp32 (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to scale the attention softmax in float32. - attention_type (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use Multi-Query Attion (True) or Multi-Head Attention (False).
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a GPTBigCodeModel. It is used to instantiate a GPTBigCode model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the GPTBigCodegpt_bigcode architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
from transformers import GPTBigCodeConfig, GPTBigCodeModel
configuration = GPTBigCodeConfig()
model = GPTBigCodeModel(configuration)
configuration = model.config
GPTBigCodeModel
class transformers.GPTBigCodeModel
( config )
Parameters
- config (GPTBigCodeConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare GPT_BIGCODE Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.List[torch.Tensor]] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None encoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None encoder_attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, onlyinput_idsthat do not have their past calculated should be passed asinput_ids.
Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() andPreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
What are input IDs? - past_key_values (
Tuple[torch.Tensor]of lengthconfig.n_layers) — Contains precomputed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) as computed by the model (seepast_key_valuesoutput below). Can be used to speed up sequential decoding. Theinput_idswhich have their past given to this model should not be passed asinput_idsas they have already been computed. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used,attention_maskneeds to contain the masking strategy that was used forpast_key_values. In other words, theattention_maskalways has to have the length:len(past_key_values) + len(input_ids)
What are attention masks?
- token_type_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
What are token type IDs?
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].
What are position IDs? - head_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, optionally only the lastinputs_embedshave to be input (seepast_key_values). - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (GPTBigCodeConfig) and inputs.
- last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used only the last hidden-state of the sequences of shape(batch_size, 1, hidden_size)is output. - past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenuse_cache=Trueis passed or whenconfig.use_cache=True) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple having 2 tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)) and optionally ifconfig.is_encoder_decoder=True2 additional tensors of shape(batch_size, num_heads, encoder_sequence_length, embed_size_per_head).
Contains pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and optionally ifconfig.is_encoder_decoder=Truein the cross-attention blocks) that can be used (seepast_key_valuesinput) to speed up sequential decoding. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads. - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueandconfig.add_cross_attention=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Attentions weights of the decoder’s cross-attention layer, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the cross-attention heads.
The GPTBigCodeModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTBigCodeModel import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder") model = GPTBigCodeModel.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder")
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt") outputs = model(**inputs)
last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
GPTBigCodeForCausalLM
class transformers.GPTBigCodeForCausalLM
( config )
Parameters
- config (GPTBigCodeConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The GPT_BIGCODE Model transformer with a language modeling head on top (linear layer with weights tied to the input embeddings).
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor]]] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None encoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None encoder_attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None **kwargs ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, onlyinput_idsthat do not have their past calculated should be passed asinput_ids.
Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() andPreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
What are input IDs? - past_key_values (
Tuple[torch.Tensor]of lengthconfig.n_layers) — Contains precomputed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) as computed by the model (seepast_key_valuesoutput below). Can be used to speed up sequential decoding. Theinput_idswhich have their past given to this model should not be passed asinput_idsas they have already been computed. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used,attention_maskneeds to contain the masking strategy that was used forpast_key_values. In other words, theattention_maskalways has to have the length:len(past_key_values) + len(input_ids)
What are attention masks?
- token_type_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
What are token type IDs?
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].
What are position IDs? - head_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, optionally only the lastinputs_embedshave to be input (seepast_key_values). - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Labels for language modeling. Note that the labels are shifted inside the model, i.e. you can setlabels = input_idsIndices are selected in[-100, 0, ..., config.vocab_size]All labels set to-100are ignored (masked), the loss is only computed for labels in[0, ..., config.vocab_size]
A transformers.modeling_outputs.CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (GPTBigCodeConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Language modeling loss (for next-token prediction). - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax). - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads. - cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).
Cross attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the cross-attention heads. - past_key_values (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenuse_cache=Trueis passed or whenconfig.use_cache=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensortuples of lengthconfig.n_layers, with each tuple containing the cached key, value states of the self-attention and the cross-attention layers if model is used in encoder-decoder setting. Only relevant ifconfig.is_decoder = True.
Contains pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) that can be used (seepast_key_valuesinput) to speed up sequential decoding.
The GPTBigCodeForCausalLM forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
import torch from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPTBigCodeForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder") model = GPTBigCodeForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/gpt_bigcode-santacoder")
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt") outputs = model(**inputs, labels=inputs["input_ids"]) loss = outputs.loss logits = outputs.logits
GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification
class transformers.GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification
( config )
Parameters
- config (GPTBigCodeConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The GPTBigCode Model transformer with a sequence classification head on top (linear layer).
GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification uses the last token in order to do the classification, as other causal models (e.g. GPT-1) do.
Since it does classification on the last token, it requires to know the position of the last token. If apad_token_id is defined in the configuration, it finds the last token that is not a padding token in each row. If no pad_token_id is defined, it simply takes the last value in each row of the batch. Since it cannot guess the padding tokens when inputs_embeds are passed instead of input_ids, it does the same (take the last value in each row of the batch).
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor]]] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, onlyinput_idsthat do not have their past calculated should be passed asinput_ids.
Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() andPreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
What are input IDs? - past_key_values (
Tuple[torch.Tensor]of lengthconfig.n_layers) — Contains precomputed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) as computed by the model (seepast_key_valuesoutput below). Can be used to speed up sequential decoding. Theinput_idswhich have their past given to this model should not be passed asinput_idsas they have already been computed. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used,attention_maskneeds to contain the masking strategy that was used forpast_key_values. In other words, theattention_maskalways has to have the length:len(past_key_values) + len(input_ids)
What are attention masks?
- token_type_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
What are token type IDs?
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].
What are position IDs? - head_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, optionally only the lastinputs_embedshave to be input (seepast_key_values). - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
The GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
GPTBigCodeForTokenClassification
class transformers.GPTBigCodeForTokenClassification
( config )
Parameters
- config (GPTBigCodeConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
GPT_BIGCODE Model with a token classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the hidden-states output) e.g. for Named-Entity-Recognition (NER) tasks.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None past_key_values: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[typing.Tuple[torch.Tensor]]] = None attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None token_type_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None position_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None head_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None use_cache: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None )
Parameters
- input_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length)) —input_ids_length=sequence_lengthifpast_key_valuesisNoneelsepast_key_values[0][0].shape[-2](sequence_lengthof input past key value states). Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, onlyinput_idsthat do not have their past calculated should be passed asinput_ids.
Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() andPreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
What are input IDs? - past_key_values (
Tuple[torch.Tensor]of lengthconfig.n_layers) — Contains precomputed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) as computed by the model (seepast_key_valuesoutput below). Can be used to speed up sequential decoding. Theinput_idswhich have their past given to this model should not be passed asinput_idsas they have already been computed. - attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for tokens that are not masked,
- 0 for tokens that are masked.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used,attention_maskneeds to contain the masking strategy that was used forpast_key_values. In other words, theattention_maskalways has to have the length:len(past_key_values) + len(input_ids)
What are attention masks?
- token_type_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, input_ids_length), optional) — Segment token indices to indicate first and second portions of the inputs. Indices are selected in[0, 1]:- 0 corresponds to a sentence A token,
- 1 corresponds to a sentence B token.
What are token type IDs?
- position_ids (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].
What are position IDs? - head_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- inputs_embeds (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passinginput_idsyou can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This is useful if you want more control over how to convertinput_idsindices into associated vectors than the model’s internal embedding lookup matrix.
Ifpast_key_valuesis used, optionally only the lastinputs_embedshave to be input (seepast_key_values). - use_cache (
bool, optional) — If set toTrue,past_key_valueskey value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (seepast_key_values). - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
The GPTBigCodeForTokenClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
