Mask2Former (original) (raw)
Overview
The Mask2Former model was proposed in Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation by Bowen Cheng, Ishan Misra, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov, Rohit Girdhar. Mask2Former is a unified framework for panoptic, instance and semantic segmentation and features significant performance and efficiency improvements over MaskFormer.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Image segmentation groups pixels with different semantics, e.g., category or instance membership. Each choice of semantics defines a task. While only the semantics of each task differ, current research focuses on designing specialized architectures for each task. We present Masked-attention Mask Transformer (Mask2Former), a new architecture capable of addressing any image segmentation task (panoptic, instance or semantic). Its key components include masked attention, which extracts localized features by constraining cross-attention within predicted mask regions. In addition to reducing the research effort by at least three times, it outperforms the best specialized architectures by a significant margin on four popular datasets. Most notably, Mask2Former sets a new state-of-the-art for panoptic segmentation (57.8 PQ on COCO), instance segmentation (50.1 AP on COCO) and semantic segmentation (57.7 mIoU on ADE20K).
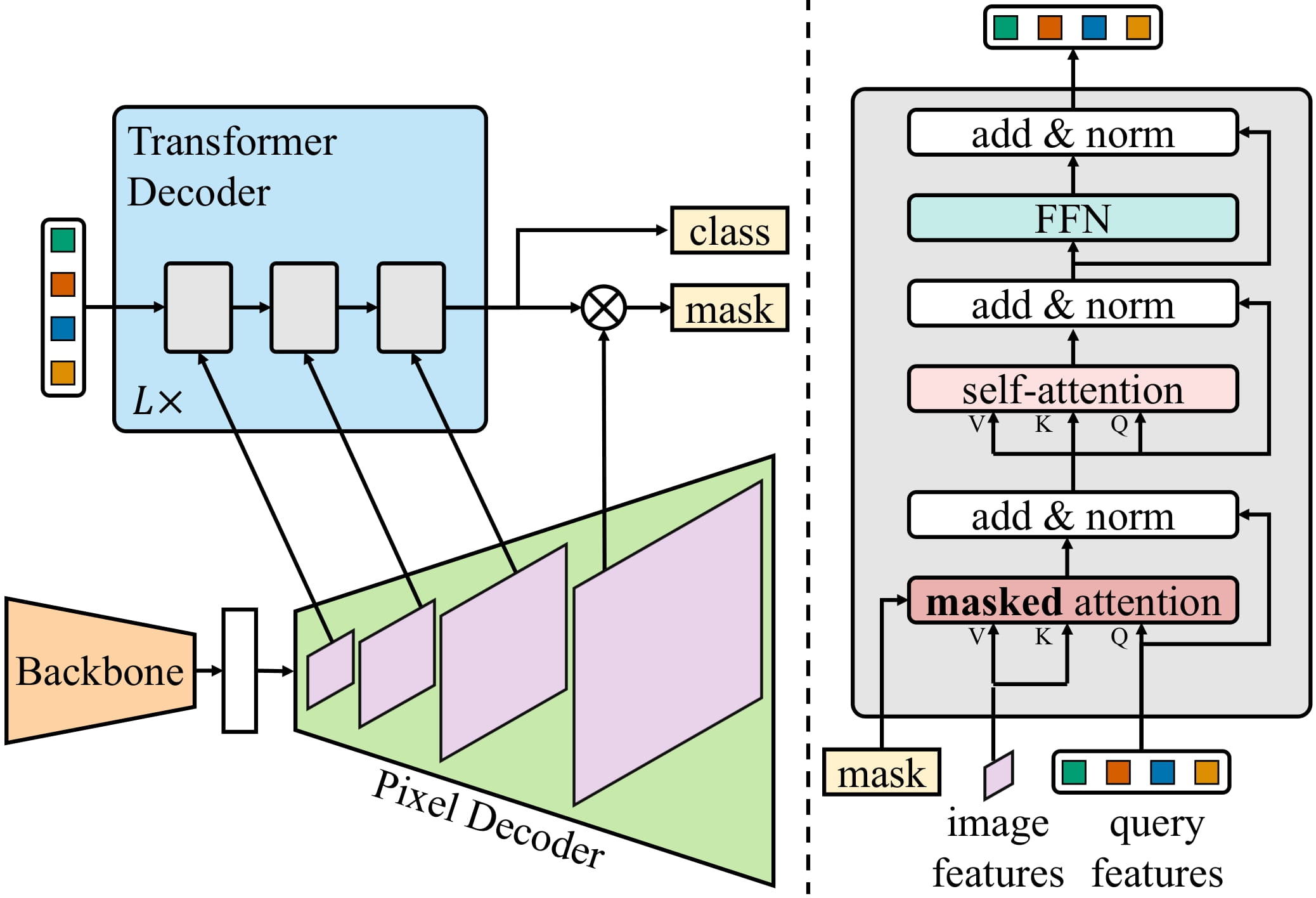 Mask2Former architecture. Taken from the original paper.
Mask2Former architecture. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by Shivalika Singh and Alara Dirik. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips
- Mask2Former uses the same preprocessing and postprocessing steps as MaskFormer. Use Mask2FormerImageProcessor or AutoImageProcessor to prepare images and optional targets for the model.
- To get the final segmentation, depending on the task, you can call post_process_semantic_segmentation() or post_process_instance_segmentation() or post_process_panoptic_segmentation(). All three tasks can be solved using Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation output, panoptic segmentation accepts an optional
label_ids_to_fuseargument to fuse instances of the target object/s (e.g. sky) together.
Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with Mask2Former.
- Demo notebooks regarding inference + fine-tuning Mask2Former on custom data can be found here.
- Scripts for finetuning
Mask2Formerwith Trainer or Accelerate can be found here.
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we will review it. The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
Mask2FormerConfig
class transformers.Mask2FormerConfig
( backbone_config: typing.Optional[typing.Dict] = None feature_size: int = 256 mask_feature_size: int = 256 hidden_dim: int = 256 encoder_feedforward_dim: int = 1024 activation_function: str = 'relu' encoder_layers: int = 6 decoder_layers: int = 10 num_attention_heads: int = 8 dropout: float = 0.0 dim_feedforward: int = 2048 pre_norm: bool = False enforce_input_projection: bool = False common_stride: int = 4 ignore_value: int = 255 num_queries: int = 100 no_object_weight: float = 0.1 class_weight: float = 2.0 mask_weight: float = 5.0 dice_weight: float = 5.0 train_num_points: int = 12544 oversample_ratio: float = 3.0 importance_sample_ratio: float = 0.75 init_std: float = 0.02 init_xavier_std: float = 1.0 use_auxiliary_loss: bool = True feature_strides: typing.List[int] = [4, 8, 16, 32] output_auxiliary_logits: typing.Optional[bool] = None backbone: typing.Optional[str] = None use_pretrained_backbone: bool = False use_timm_backbone: bool = False backbone_kwargs: typing.Optional[typing.Dict] = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- backbone_config (
PretrainedConfigordict, optional, defaults toSwinConfig()) — The configuration of the backbone model. If unset, the configuration corresponding toswin-base-patch4-window12-384will be used. - backbone (
str, optional) — Name of backbone to use whenbackbone_configisNone. Ifuse_pretrained_backboneisTrue, this will load the corresponding pretrained weights from the timm or transformers library. Ifuse_pretrained_backboneisFalse, this loads the backbone’s config and uses that to initialize the backbone with random weights. - use_pretrained_backbone (
bool, optional,False) — Whether to use pretrained weights for the backbone. - use_timm_backbone (
bool, optional,False) — Whether to loadbackbonefrom the timm library. IfFalse, the backbone is loaded from the transformers library. - backbone_kwargs (
dict, optional) — Keyword arguments to be passed to AutoBackbone when loading from a checkpoint e.g.{'out_indices': (0, 1, 2, 3)}. Cannot be specified ifbackbone_configis set. - feature_size (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — The features (channels) of the resulting feature maps. - mask_feature_size (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — The masks’ features size, this value will also be used to specify the Feature Pyramid Network features’ size. - hidden_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers. - encoder_feedforward_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 1024) — Dimension of feedforward network for deformable detr encoder used as part of pixel decoder. - encoder_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 6) — Number of layers in the deformable detr encoder used as part of pixel decoder. - decoder_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 10) — Number of layers in the Transformer decoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer. - dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder. - dim_feedforward (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Feature dimension in feedforward network for transformer decoder. - pre_norm (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use pre-LayerNorm or not for transformer decoder. - enforce_input_projection (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to add an input projection 1x1 convolution even if the input channels and hidden dim are identical in the Transformer decoder. - common_stride (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — Parameter used for determining number of FPN levels used as part of pixel decoder. - ignore_value (
int, optional, defaults to 255) — Category id to be ignored during training. - num_queries (
int, optional, defaults to 100) — Number of queries for the decoder. - no_object_weight (
int, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The weight to apply to the null (no object) class. - class_weight (
int, optional, defaults to 2.0) — The weight for the cross entropy loss. - mask_weight (
int, optional, defaults to 5.0) — The weight for the mask loss. - dice_weight (
int, optional, defaults to 5.0) — The weight for the dice loss. - train_num_points (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to 12544) — Number of points used for sampling during loss calculation. - oversample_ratio (
float, optional, defaults to 3.0) — Oversampling parameter used for calculating no. of sampled points - importance_sample_ratio (
float, optional, defaults to 0.75) — Ratio of points that are sampled via importance sampling. - init_std (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - init_xavier_std (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — The scaling factor used for the Xavier initialization gain in the HM Attention map module. - use_auxiliary_loss (
boolean``, *optional*, defaults toTrue) -- IfTrue - feature_strides (
List[int], optional, defaults to[4, 8, 16, 32]) — Feature strides corresponding to features generated from backbone network. - output_auxiliary_logits (
bool, optional) — Should the model output itsauxiliary_logitsor not.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a Mask2FormerModel. It is used to instantiate a Mask2Former model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the Mask2Formerfacebook/mask2former-swin-small-coco-instancearchitecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Currently, Mask2Former only supports the Swin Transformer as backbone.
Examples:
from transformers import Mask2FormerConfig, Mask2FormerModel
configuration = Mask2FormerConfig()
model = Mask2FormerModel(configuration)
configuration = model.config
Instantiate a Mask2FormerConfig (or a derived class) from a pre-trained backbone model configuration.
MaskFormer specific outputs
class transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerModelOutput
( encoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None encoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None pixel_decoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None transformer_decoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None transformer_decoder_intermediate_states: typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor] = None masks_queries_logits: typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor] = None attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
Parameters
- encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width), optional) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the encoder model (backbone). Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the encoder model at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width), optional) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the pixel decoder model. - pixel_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), , optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the pixel decoder model at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)) — Final output of the transformer decoder(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). - transformer_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the transformer decoder at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - transformer_decoder_intermediate_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of shape(num_queries, 1, hidden_size)) — Intermediate decoder activations, i.e. the output of each decoder layer, each of them gone through a layernorm. - masks_queries_logits (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of shape(batch_size, num_queries, height, width)) — Mask Predictions from each layer in the transformer decoder. - attentions (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Self attentions weights from transformer decoder.
Class for outputs of Mask2FormerModel. This class returns all the needed hidden states to compute the logits.
class transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput
( loss: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None class_queries_logits: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None masks_queries_logits: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None auxiliary_logits: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Dict[str, torch.FloatTensor]]] = None encoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None encoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None pixel_decoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None transformer_decoder_hidden_states: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None attentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
Parameters
- loss (
torch.Tensor, optional) — The computed loss, returned when labels are present. - class_queries_logits (
torch.FloatTensor) — A tensor of shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_labels + 1)representing the proposed classes for each query. Note the+ 1is needed because we incorporate the null class. - masks_queries_logits (
torch.FloatTensor) — A tensor of shape(batch_size, num_queries, height, width)representing the proposed masks for each query. - auxiliary_logits (
List[Dict(str, torch.FloatTensor)], optional) — List of class and mask predictions from each layer of the transformer decoder. - encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the encoder model (backbone). - encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the encoder model at the output of each stage. - pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the pixel decoder model. - pixel_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the pixel decoder model at the output of each stage. - transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)) — Final output of the transformer decoder(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). - transformer_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the transformer decoder at the output of each stage. - attentions (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Self and Cross Attentions weights from transformer decoder.
Class for outputs of Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput.
This output can be directly passed to post_process_semantic_segmentation() orpost_process_instance_segmentation() orpost_process_panoptic_segmentation() to compute final segmentation maps. Please, see [`~Mask2FormerImageProcessor] for details regarding usage.
Mask2FormerModel
class transformers.Mask2FormerModel
( config: Mask2FormerConfig )
Parameters
- config (Mask2FormerConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out thefrom_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Mask2Former Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: Tensor pixel_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using{image_processor_class}. See{image_processor_class}.__call__for details ({processor_class}uses{image_processor_class}for processing images). - pixel_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding pixel values. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for pixels that are real (i.e. not masked),
- 0 for pixels that are padding (i.e. masked).
What are attention masks?
- output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
A transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerModelOutput or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (Mask2FormerConfig) and inputs.
- encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width), optional) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the encoder model (backbone). Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the encoder model at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width), optional) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the pixel decoder model. - pixel_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), , optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the pixel decoder model at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)) — Final output of the transformer decoder(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). - transformer_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the transformer decoder at the output of each stage. Returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed. - transformer_decoder_intermediate_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of shape(num_queries, 1, hidden_size)) — Intermediate decoder activations, i.e. the output of each decoder layer, each of them gone through a layernorm. - masks_queries_logits (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)of shape(batch_size, num_queries, height, width)) Mask Predictions from each layer in the transformer decoder. - attentions (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Self attentions weights from transformer decoder.
The Mask2FormerModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation
class transformers.Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation
( config: Mask2FormerConfig )
Parameters
- config (Mask2FormerConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out thefrom_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The Mask2Former Model with heads on top for instance/semantic/panoptic segmentation.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: Tensor mask_labels: typing.Optional[typing.List[torch.Tensor]] = None class_labels: typing.Optional[typing.List[torch.Tensor]] = None pixel_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_auxiliary_logits: typing.Optional[bool] = None output_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using{image_processor_class}. See{image_processor_class}.__call__for details ({processor_class}uses{image_processor_class}for processing images). - mask_labels (
List[torch.Tensor], optional) — List of mask labels of shape(num_labels, height, width)to be fed to a model - class_labels (
List[torch.Tensor], optional) — list of target class labels of shape(num_labels, height, width)to be fed to a model. They identify the labels ofmask_labels, e.g. the label ofmask_labels[i][j]ifclass_labels[i][j]. - pixel_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding pixel values. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 for pixels that are real (i.e. not masked),
- 0 for pixels that are padding (i.e. masked).
What are attention masks?
- output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_auxiliary_logits (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to output auxiliary logits. - output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
A transformers.models.mask2former.modeling_mask2former.Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput or a tuple oftorch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (Mask2FormerConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.Tensor, optional) — The computed loss, returned when labels are present. - class_queries_logits (
torch.FloatTensor) — A tensor of shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_labels + 1)representing the proposed classes for each query. Note the+ 1is needed because we incorporate the null class. - masks_queries_logits (
torch.FloatTensor) — A tensor of shape(batch_size, num_queries, height, width)representing the proposed masks for each query. - auxiliary_logits (
List[Dict(str, torch.FloatTensor)], optional) — List of class and mask predictions from each layer of the transformer decoder. - encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the encoder model (backbone). - encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the encoder model at the output of each stage. - pixel_decoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Last hidden states (final feature map) of the last stage of the pixel decoder model. - pixel_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the pixel decoder model at the output of each stage. - transformer_decoder_last_hidden_state (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor)) — Final output of the transformer decoder(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). - transformer_decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the transformer decoder at the output of each stage. - attentions (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor)), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftuple(torch.FloatTensor)(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Self and Cross Attentions weights from transformer decoder.
The Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Instance segmentation example:
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation from PIL import Image import requests import torch
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/mask2former-swin-small-coco-instance") model = Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation.from_pretrained( ... "facebook/mask2former-swin-small-coco-instance" ... )
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad(): ... outputs = model(**inputs)
class_queries_logits = outputs.class_queries_logits masks_queries_logits = outputs.masks_queries_logits
pred_instance_map = image_processor.post_process_instance_segmentation( ... outputs, target_sizes=[(image.height, image.width)] ... )[0] print(pred_instance_map.shape) torch.Size([480, 640])
Semantic segmentation example:
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation from PIL import Image import requests import torch
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/mask2former-swin-small-ade-semantic") model = Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation.from_pretrained("facebook/mask2former-swin-small-ade-semantic")
url = ( ... "https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/fixtures_ade20k/resolve/main/ADE_val_00000001.jpg" ... ) image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad(): ... outputs = model(**inputs)
class_queries_logits = outputs.class_queries_logits masks_queries_logits = outputs.masks_queries_logits
pred_semantic_map = image_processor.post_process_semantic_segmentation( ... outputs, target_sizes=[(image.height, image.width)] ... )[0] print(pred_semantic_map.shape) torch.Size([512, 683])
Panoptic segmentation example:
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation from PIL import Image import requests import torch
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/mask2former-swin-small-cityscapes-panoptic") model = Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation.from_pretrained( ... "facebook/mask2former-swin-small-cityscapes-panoptic" ... )
url = "https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/Inference-API/Sample-results-on-the-Cityscapes-dataset-The-above-images-show-how-our-method-can-handle.png" image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw) inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad(): ... outputs = model(**inputs)
class_queries_logits = outputs.class_queries_logits masks_queries_logits = outputs.masks_queries_logits
pred_panoptic_map = image_processor.post_process_panoptic_segmentation( ... outputs, target_sizes=[(image.height, image.width)] ... )[0]["segmentation"] print(pred_panoptic_map.shape) torch.Size([338, 676])
Mask2FormerImageProcessor
class transformers.Mask2FormerImageProcessor
( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None size_divisor: int = 32 resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2> do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: float = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None ignore_index: typing.Optional[int] = None do_reduce_labels: bool = False num_labels: typing.Optional[int] = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the input to a certainsize. - size (
int, optional, defaults to 800) — Resize the input to the given size. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. If size is a sequence like(width, height), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int, smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number. i.e, ifheight > width, then image will be rescaled to(size * height / width, size). - size_divisor (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — Some backbones need images divisible by a certain number. If not passed, it defaults to the value used in Swin Transformer. - resample (
int, optional, defaults toResampling.BILINEAR) — An optional resampling filter. This can be one ofPIL.Image.Resampling.NEAREST,PIL.Image.Resampling.BOX,PIL.Image.Resampling.BILINEAR,PIL.Image.Resampling.HAMMING,PIL.Image.Resampling.BICUBICorPIL.Image.Resampling.LANCZOS. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the input to a certainscale. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults to1/ 255) — Rescale the input by the given factor. Only has an effect ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not to normalize the input with mean and standard deviation. - image_mean (
int, optional, defaults to[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) — The sequence of means for each channel, to be used when normalizing images. Defaults to the ImageNet mean. - image_std (
int, optional, defaults to[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) — The sequence of standard deviations for each channel, to be used when normalizing images. Defaults to the ImageNet std. - ignore_index (
int, optional) — Label to be assigned to background pixels in segmentation maps. If provided, segmentation map pixels denoted with 0 (background) will be replaced withignore_index. - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to decrement all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced byignore_index. - num_labels (
int, optional) — The number of labels in the segmentation map.
Constructs a Mask2Former image processor. The image processor can be used to prepare image(s) and optional targets for the model.
This image processor inherits from BaseImageProcessor which contains most of the main methods. Users should refer to this superclass for more information regarding those methods.
preprocess
( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] segmentation_maps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor'], NoneType] = None instance_id_to_semantic_id: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[int, int]] = None do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str, int]] = None size_divisor: typing.Optional[int] = None resample: Resampling = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None ignore_index: typing.Optional[int] = None do_reduce_labels: typing.Optional[bool] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None )
encode_inputs
( pixel_values_list: typing.List[typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']]] segmentation_maps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] = None instance_id_to_semantic_id: typing.Union[typing.List[typing.Dict[int, int]], typing.Dict[int, int], NoneType] = None ignore_index: typing.Optional[int] = None do_reduce_labels: bool = False return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None ) → BatchFeature
Parameters
- pixel_values_list (
List[ImageInput]) — List of images (pixel values) to be padded. Each image should be a tensor of shape(channels, height, width). - segmentation_maps (
ImageInput, optional) — The corresponding semantic segmentation maps with the pixel-wise annotations.
(bool, optional, defaults toTrue): Whether or not to pad images up to the largest image in a batch and create a pixel mask.
If left to the default, will return a pixel mask that is:- 1 for pixels that are real (i.e. not masked),
- 0 for pixels that are padding (i.e. masked).
- instance_id_to_semantic_id (
List[Dict[int, int]]orDict[int, int], optional) — A mapping between object instance ids and class ids. If passed,segmentation_mapsis treated as an instance segmentation map where each pixel represents an instance id. Can be provided as a single dictionary with a global/dataset-level mapping or as a list of dictionaries (one per image), to map instance ids in each image separately. - return_tensors (
stror TensorType, optional) — If set, will return tensors instead of NumPy arrays. If set to'pt', return PyTorchtorch.Tensorobjects. - input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format of the input image. If not provided, it will be inferred.
A BatchFeature with the following fields:
- pixel_values — Pixel values to be fed to a model.
- pixel_mask — Pixel mask to be fed to a model (when
=Trueor ifpixel_maskis inself.model_input_names). - mask_labels — Optional list of mask labels of shape
(labels, height, width)to be fed to a model (whenannotationsare provided). - class_labels — Optional list of class labels of shape
(labels)to be fed to a model (whenannotationsare provided). They identify the labels ofmask_labels, e.g. the label ofmask_labels[i][j]ifclass_labels[i][j].
Pad images up to the largest image in a batch and create a corresponding pixel_mask.
Mask2Former addresses semantic segmentation with a mask classification paradigm, thus input segmentation maps will be converted to lists of binary masks and their respective labels. Let’s see an example, assumingsegmentation_maps = [[2,6,7,9]], the output will contain mask_labels = [[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]] (four binary masks) and class_labels = [2,6,7,9], the labels for each mask.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
( outputs target_sizes: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Tuple[int, int]]] = None ) → List[torch.Tensor]
Parameters
- outputs (Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
List[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — List of length (batch_size), where each list item (Tuple[int, int]]) corresponds to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If left to None, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
List[torch.Tensor]
A list of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is specified). Each entry of eachtorch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
post_process_instance_segmentation
( outputs threshold: float = 0.5 mask_threshold: float = 0.5 overlap_mask_area_threshold: float = 0.8 target_sizes: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Tuple[int, int]]] = None return_coco_annotation: typing.Optional[bool] = False return_binary_maps: typing.Optional[bool] = False ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — The probability score threshold to keep predicted instance masks. - mask_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — Threshold to use when turning the predicted masks into binary values. - overlap_mask_area_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.8) — The overlap mask area threshold to merge or discard small disconnected parts within each binary instance mask. - target_sizes (
List[Tuple], optional) — List of length (batch_size), where each list item (Tuple[int, int]]) corresponds to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If left to None, predictions will not be resized. - return_coco_annotation (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — If set toTrue, segmentation maps are returned in COCO run-length encoding (RLE) format. - return_binary_maps (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — If set toTrue, segmentation maps are returned as a concatenated tensor of binary segmentation maps (one per detected instance).
A list of dictionaries, one per image, each dictionary containing two keys:
- segmentation — A tensor of shape
(height, width)where each pixel represents asegment_id, orList[List]run-length encoding (RLE) of the segmentation map if return_coco_annotation is set toTrue, or a tensor of shape(num_instances, height, width)if return_binary_maps is set toTrue. Set toNoneif no mask if found abovethreshold. - segments_info — A dictionary that contains additional information on each segment.
- id — An integer representing the
segment_id. - label_id — An integer representing the label / semantic class id corresponding to
segment_id. - score — Prediction score of segment with
segment_id.
- id — An integer representing the
Converts the output of Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput into instance segmentation predictions. Only supports PyTorch. If instances could overlap, set either return_coco_annotation or return_binary_maps to True to get the correct segmentation result.
post_process_panoptic_segmentation
( outputs threshold: float = 0.5 mask_threshold: float = 0.5 overlap_mask_area_threshold: float = 0.8 label_ids_to_fuse: typing.Optional[typing.Set[int]] = None target_sizes: typing.Optional[typing.List[typing.Tuple[int, int]]] = None ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
- outputs (
Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput) — The outputs from Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentation. - threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — The probability score threshold to keep predicted instance masks. - mask_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — Threshold to use when turning the predicted masks into binary values. - overlap_mask_area_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 0.8) — The overlap mask area threshold to merge or discard small disconnected parts within each binary instance mask. - label_ids_to_fuse (
Set[int], optional) — The labels in this state will have all their instances be fused together. For instance we could say there can only be one sky in an image, but several persons, so the label ID for sky would be in that set, but not the one for person. - target_sizes (
List[Tuple], optional) — List of length (batch_size), where each list item (Tuple[int, int]]) corresponds to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction in batch. If left to None, predictions will not be resized.
A list of dictionaries, one per image, each dictionary containing two keys:
- segmentation — a tensor of shape
(height, width)where each pixel represents asegment_id, set toNoneif no mask if found abovethreshold. Iftarget_sizesis specified, segmentation is resized to the correspondingtarget_sizesentry. - segments_info — A dictionary that contains additional information on each segment.
- id — an integer representing the
segment_id. - label_id — An integer representing the label / semantic class id corresponding to
segment_id. - was_fused — a boolean,
Trueiflabel_idwas inlabel_ids_to_fuse,Falseotherwise. Multiple instances of the same class / label were fused and assigned a singlesegment_id. - score — Prediction score of segment with
segment_id.
- id — an integer representing the
Converts the output of Mask2FormerForUniversalSegmentationOutput into image panoptic segmentation predictions. Only supports PyTorch.
