Andrei Rybin - Academia.edu (original) (raw)
Papers by Andrei Rybin
Solitons of the Korteweg-de Vries equation on the background of a known solution
Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, 1985
The authors consider for the example of the KdV equation, the application of a Darboux transforma... more The authors consider for the example of the KdV equation, the application of a Darboux transformation to the finding of solitons on the background of a ''seed'' solution of arbitrary form. A study is made of the problem of finding the phase shifts of such solitons when they interact in pairs and also when a soliton interacts with a solution that decreases with respect to x.
Non-adiabatic manipulation of slow-light solitons
New Journal of Physics, 2005
... AV Rybin 1 ,4 , IP Vadeiko 2 and AR Bishop 3. ... In this paper, we provide an exact analytic... more ... AV Rybin 1 ,4 , IP Vadeiko 2 and AR Bishop 3. ... In this paper, we provide an exact analytical solution of the Maxwell-Bloch system of equations describing a Λ-type model in the strongly nonlinear non-adiabatic regime of the dynamics. ...
Application of the Darboux transformation to inverse problems with variable spectral parameters
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 1991
ABSTRACT
Solitons ofq-deformed quantum lattices and the quantum soliton
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 2001
We use the classical N-soliton solution of a q-deformed lattice, the Maxwell-Bloch (MB) lattice, ... more We use the classical N-soliton solution of a q-deformed lattice, the Maxwell-Bloch (MB) lattice, which we reported recently (Rybin A V, Varzugin G G, Timonen J and Bullough R K Year 2001 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 34 157) in order, ultimately, to fully comprehend the `quantum soliton'. This object may be the source of a new information technology (Abram
Nonexponential dynamics and competition between quasi-trapped states in an N-atomic micromaser
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters, 2000
Transient processes are examined for the reduced density matrix (RDM) of the quantum mode of a mi... more Transient processes are examined for the reduced density matrix (RDM) of the quantum mode of a micromaser pumped by clusters of N two-level atoms. The RDM dynamics consists of the fast and slow stages. The hierarchy of time scales is explained by the fact that the spectrum of the operator of RDM evolution contains groups of eigenvalues concentrated near zero
Darboux transformations and coherent interaction of the light pulse with two-level media
Inverse Problems, 1988
Applications of the Darboux transformation method to study the reduced Maxwell-Bloch (RMB) system... more Applications of the Darboux transformation method to study the reduced Maxwell-Bloch (RMB) system and of the self-induced transparency (SIT) equations are considered. Both systems describe the propagation of ultrashort optical pulses in a two-level medium to a reasonable approximation. The main result of the present work is the construction of multisoliton solutions on an arbitrary background for RMB and SIT
Journal of Soviet Mathematics, 1991
GENERAL SOLUTION OF THE REDUCED MAXWELL-BLOCH SYSTEM A. V. Rybin UDC 517.9 A scheme of constructi... more GENERAL SOLUTION OF THE REDUCED MAXWELL-BLOCH SYSTEM A. V. Rybin UDC 517.9 A scheme of constructing the general solution of the reduced Maxwell-Block system is provided on the basis of the formalism of the Riemann matrix problem.
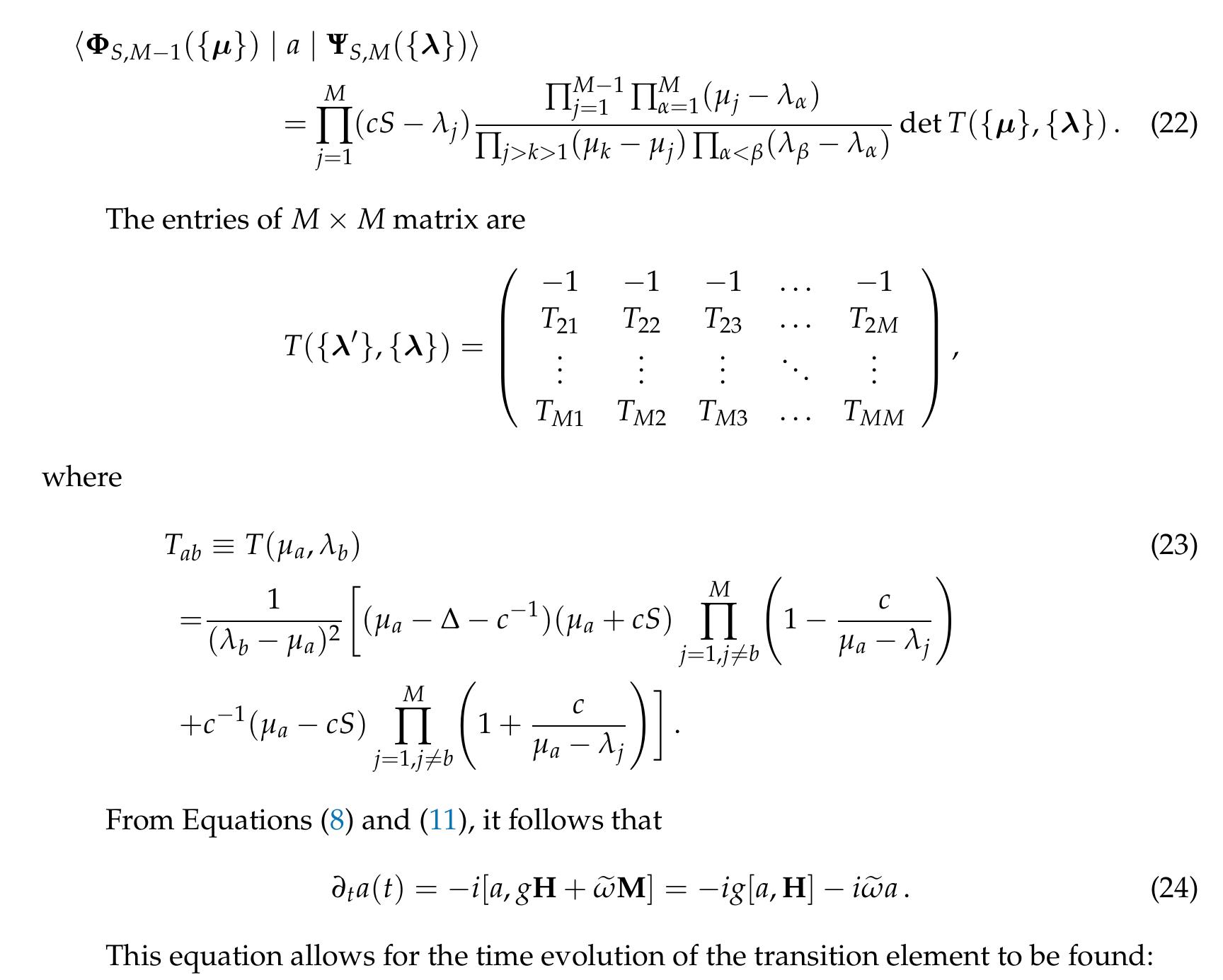
Symmetry
We study the quantum dynamics of the opened three-level su(1, 1) bosonic model. The effective non... more We study the quantum dynamics of the opened three-level su(1, 1) bosonic model. The effective non-Hermitian Hamiltonians describing the system of the Lindblad equation in the short time limit are constructed. The obtained non-Hermitian Hamiltonians are exactly solvable by the Algebraic Bethe Ansatz. This approach allows representing biorthogonal and nonorthogonal bases of the system. We analyze the biorthogonal expectation values of a number of particles in the zero mode and represent it in the determinantal form. The time-dependent density matrix satisfying the Lindblad master equation is found in terms of the nonorthogonal basis.
Symmetry, 2021
In this communication we study dynamics of the open quantum bosonic system governed by the genera... more In this communication we study dynamics of the open quantum bosonic system governed by the generalized Lindblad equation with both dynamical and environment induced intermode couplings taken into account. By using the method of characteristics we deduce the analytical expression for the normally ordered characteristic function. Analytical results for one-point correlation functions describing temporal evolution of the covariance matrix are obtained.
Symmetry, 2021
In this Communication, we consider a generalised Tavis–Cummings model when the damping process is... more In this Communication, we consider a generalised Tavis–Cummings model when the damping process is taken into account. We show that the quantum dynamics governed by a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian is exactly solvable using the Quantum Inverse Scattering Method, and the Algebraic Bethe Ansatz. The leakage of photons is described by a Lindblad-type master equation. The non-Hermitian Hamiltonian is diagonalised by state vectors, which are elementary symmetric functions parametrised by the solutions of the Bethe equations. The time evolution of the photon annihilation operator is defined via a corresponding determinant representation.
Materials, 2020
Heavy metal ions are not subject to biodegradation and could cause the environmental pollution of... more Heavy metal ions are not subject to biodegradation and could cause the environmental pollution of natural resources and water. Many of the heavy metals are highly toxic and dangerous to human health, even at a minimum amount. This work considered an optical method for detecting heavy metal ions using colloidal luminescent semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). Over the past decade, QDs have been used in the development of sensitive fluorescence sensors for ions of heavy metal. In this work, we combined the fluorescent properties of AgInS2/ZnS ternary QDs and the magnetism of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in a matrix of porous calcium carbonate microspheres for the detection of toxic ions of heavy metal: Co2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+. We demonstrate a relationship between the level of quenching of the photoluminescence of sensors under exposure to the heavy metal ions and the concentration of these ions, allowing their detection in aqueous solutions at concentrations of Co2+, Ni2+...
Entropy, 2021
In this paper, we consider the thermal bath Lindblad master equation to describe the quantum nonu... more In this paper, we consider the thermal bath Lindblad master equation to describe the quantum nonunitary dynamics of quantum states in a multi-mode bosonic system. For the two-mode bosonic system interacting with an environment, we analyse how both the coupling between the modes and the coupling with the environment characterised by the frequency and the relaxation rate vectors affect dynamics of the entanglement. We discuss how the revivals of entanglement can be induced by the dynamic coupling between the different modes. For the system, initially prepared in a two-mode squeezed state, we find the logarithmic negativity as defined by the magnitude and orientation of the frequency and the relaxation rate vectors. We show that, in the regime of finite-time disentanglement, reorientation of the relaxation rate vector may significantly increase the time of disentanglement.
Materials, 2019
Graphene-quantum dot nanocomposites attract significant attention for novel optoelectronic device... more Graphene-quantum dot nanocomposites attract significant attention for novel optoelectronic devices, such as ultrafast photodetectors and third-generation solar cells. Combining the remarkable optical properties of quantum dots (QDs) with the exceptional electrical properties of graphene derivatives opens a vast perspective for further growth in solar cell efficiency. Here, we applied (3-mercaptopropyl) trimethoxysilane functionalized reduced graphene oxide (f-rGO) to improve the QDs-based solar cell active layer. The different strategies of f-rGO embedding are explored. When f-rGO interlayers are inserted between PbS QD layers, the solar cells demonstrate a higher current density and a better fill factor. A combined study of the morphological and electrical parameters of the solar cells shows that the improved efficiency is associated with better layer homogeneity, lower trap-state densities, higher charge carrier concentrations, and the blocking of the minor charge carriers.
Physical Review E, 2000
We analyse a generalised Gross-Pitaevskii equation involving a paraboloidal trap potential in D s... more We analyse a generalised Gross-Pitaevskii equation involving a paraboloidal trap potential in D space dimensions and generalised to a nonlinearity of order 2n + 1. For attractive coupling constants collapse of the particle density occurs for Dn ≥ 2 and typically to a δ-function centered at the origin of the trap. By introducing a new dynamical variable for the spherically symmetric solutions we show that all such solutions are self-similar close to the center of the trap. Exact self-similar solutions occur if, and only if, Dn = 2, and for this case of Dn = 2 we exhibit an exact but rather special D = 1 analytical selfsimilar solution collapsing to a δ-function which however recovers and collapses periodically, while the ordinary G-P equation in 2 space dimensions also has a special solution with periodic δ-function collapses and revivals of the density. The relevance of these various results to attractive Bose-Einstein condensation in spherically symmetric traps is discussed.
We investigate propagation of slow-light solitons in atomic media described by the nonlinear Λmod... more We investigate propagation of slow-light solitons in atomic media described by the nonlinear Λmodel. Under a physical assumption, appropriate to the slow light propagation, we reduce the Λ-scheme to a simplified nonlinear model, which is also relevant to 2D dilatonic gravity. Exact solutions describing various regimes of stopping slow-light solitons can then be readily derived.
We provide an exact analytic description of decelerating, stopping and re-accelerating optical so... more We provide an exact analytic description of decelerating, stopping and re-accelerating optical solitons in atomic media. By virtue of this solution we describe in detail how spatially localized optical memory bits can be written down, read and moved along the atomic medium in a prescribed manner. Dynamical control over the solitons is realized via a background laser field whose intensity controls the velocity of the slow light in a similar way as in the linear theory of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). We solve the nonlinear model when the controlling field and the solitons interact in an inseparable nonlinear superposition process. This allows us to access results beyond the limits of the linear theory of EIT.
A generic mechanism of collapse in the Gross-Pitaevskii equation with attractive interparticle in... more A generic mechanism of collapse in the Gross-Pitaevskii equation with attractive interparticle interactions is gained by reformulating this equation as Newton's equation of motion for a system of particles with a constraint. 'Quantum pressure' effects give rise to formation of a potential barrier around the emerging singularity, which prevents a fraction of the particles from falling into the singularity. For
We study the dynamics of the reduced density matrix(RDM) of the field in the micromaser. The reso... more We study the dynamics of the reduced density matrix(RDM) of the field in the micromaser. The resonator is pumped by N-atomic clusters of two-level atoms. At each given instant there is only one cluster in the cavity. We find the conditions of the independent evolution of the matrix elements of RDM belonging to a (sub)diagonal of the RDM, i.e. conditions
Теоретическая и математическая физика, 2003
Physical Review A, 2003
An algebraic method is introduced for an analytical solution of the eigenvalue problem of the Tav... more An algebraic method is introduced for an analytical solution of the eigenvalue problem of the Tavis-Cummings (TC) Hamiltonian, based on polynomially deformed su(2), i.e. sun(2), algebras. In this method the eigenvalue problem is solved in terms of a specific perturbation theory, developed here up to third order. Generalization to the N-atom case of the Rabi frequency and dressed states is also provided. A remarkable enhancement of spontaneous emission of N atoms in a resonator is found to result from collective effects.
Solitons of the Korteweg-de Vries equation on the background of a known solution
Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, 1985
The authors consider for the example of the KdV equation, the application of a Darboux transforma... more The authors consider for the example of the KdV equation, the application of a Darboux transformation to the finding of solitons on the background of a ''seed'' solution of arbitrary form. A study is made of the problem of finding the phase shifts of such solitons when they interact in pairs and also when a soliton interacts with a solution that decreases with respect to x.
Non-adiabatic manipulation of slow-light solitons
New Journal of Physics, 2005
... AV Rybin 1 ,4 , IP Vadeiko 2 and AR Bishop 3. ... In this paper, we provide an exact analytic... more ... AV Rybin 1 ,4 , IP Vadeiko 2 and AR Bishop 3. ... In this paper, we provide an exact analytical solution of the Maxwell-Bloch system of equations describing a Λ-type model in the strongly nonlinear non-adiabatic regime of the dynamics. ...
Application of the Darboux transformation to inverse problems with variable spectral parameters
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 1991
ABSTRACT
Solitons ofq-deformed quantum lattices and the quantum soliton
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 2001
We use the classical N-soliton solution of a q-deformed lattice, the Maxwell-Bloch (MB) lattice, ... more We use the classical N-soliton solution of a q-deformed lattice, the Maxwell-Bloch (MB) lattice, which we reported recently (Rybin A V, Varzugin G G, Timonen J and Bullough R K Year 2001 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 34 157) in order, ultimately, to fully comprehend the `quantum soliton'. This object may be the source of a new information technology (Abram
Nonexponential dynamics and competition between quasi-trapped states in an N-atomic micromaser
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters, 2000
Transient processes are examined for the reduced density matrix (RDM) of the quantum mode of a mi... more Transient processes are examined for the reduced density matrix (RDM) of the quantum mode of a micromaser pumped by clusters of N two-level atoms. The RDM dynamics consists of the fast and slow stages. The hierarchy of time scales is explained by the fact that the spectrum of the operator of RDM evolution contains groups of eigenvalues concentrated near zero
Darboux transformations and coherent interaction of the light pulse with two-level media
Inverse Problems, 1988
Applications of the Darboux transformation method to study the reduced Maxwell-Bloch (RMB) system... more Applications of the Darboux transformation method to study the reduced Maxwell-Bloch (RMB) system and of the self-induced transparency (SIT) equations are considered. Both systems describe the propagation of ultrashort optical pulses in a two-level medium to a reasonable approximation. The main result of the present work is the construction of multisoliton solutions on an arbitrary background for RMB and SIT
Journal of Soviet Mathematics, 1991
GENERAL SOLUTION OF THE REDUCED MAXWELL-BLOCH SYSTEM A. V. Rybin UDC 517.9 A scheme of constructi... more GENERAL SOLUTION OF THE REDUCED MAXWELL-BLOCH SYSTEM A. V. Rybin UDC 517.9 A scheme of constructing the general solution of the reduced Maxwell-Block system is provided on the basis of the formalism of the Riemann matrix problem.
Symmetry
We study the quantum dynamics of the opened three-level su(1, 1) bosonic model. The effective non... more We study the quantum dynamics of the opened three-level su(1, 1) bosonic model. The effective non-Hermitian Hamiltonians describing the system of the Lindblad equation in the short time limit are constructed. The obtained non-Hermitian Hamiltonians are exactly solvable by the Algebraic Bethe Ansatz. This approach allows representing biorthogonal and nonorthogonal bases of the system. We analyze the biorthogonal expectation values of a number of particles in the zero mode and represent it in the determinantal form. The time-dependent density matrix satisfying the Lindblad master equation is found in terms of the nonorthogonal basis.
Symmetry, 2021
In this communication we study dynamics of the open quantum bosonic system governed by the genera... more In this communication we study dynamics of the open quantum bosonic system governed by the generalized Lindblad equation with both dynamical and environment induced intermode couplings taken into account. By using the method of characteristics we deduce the analytical expression for the normally ordered characteristic function. Analytical results for one-point correlation functions describing temporal evolution of the covariance matrix are obtained.
Symmetry, 2021
In this Communication, we consider a generalised Tavis–Cummings model when the damping process is... more In this Communication, we consider a generalised Tavis–Cummings model when the damping process is taken into account. We show that the quantum dynamics governed by a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian is exactly solvable using the Quantum Inverse Scattering Method, and the Algebraic Bethe Ansatz. The leakage of photons is described by a Lindblad-type master equation. The non-Hermitian Hamiltonian is diagonalised by state vectors, which are elementary symmetric functions parametrised by the solutions of the Bethe equations. The time evolution of the photon annihilation operator is defined via a corresponding determinant representation.
Materials, 2020
Heavy metal ions are not subject to biodegradation and could cause the environmental pollution of... more Heavy metal ions are not subject to biodegradation and could cause the environmental pollution of natural resources and water. Many of the heavy metals are highly toxic and dangerous to human health, even at a minimum amount. This work considered an optical method for detecting heavy metal ions using colloidal luminescent semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). Over the past decade, QDs have been used in the development of sensitive fluorescence sensors for ions of heavy metal. In this work, we combined the fluorescent properties of AgInS2/ZnS ternary QDs and the magnetism of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in a matrix of porous calcium carbonate microspheres for the detection of toxic ions of heavy metal: Co2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+. We demonstrate a relationship between the level of quenching of the photoluminescence of sensors under exposure to the heavy metal ions and the concentration of these ions, allowing their detection in aqueous solutions at concentrations of Co2+, Ni2+...
Entropy, 2021
In this paper, we consider the thermal bath Lindblad master equation to describe the quantum nonu... more In this paper, we consider the thermal bath Lindblad master equation to describe the quantum nonunitary dynamics of quantum states in a multi-mode bosonic system. For the two-mode bosonic system interacting with an environment, we analyse how both the coupling between the modes and the coupling with the environment characterised by the frequency and the relaxation rate vectors affect dynamics of the entanglement. We discuss how the revivals of entanglement can be induced by the dynamic coupling between the different modes. For the system, initially prepared in a two-mode squeezed state, we find the logarithmic negativity as defined by the magnitude and orientation of the frequency and the relaxation rate vectors. We show that, in the regime of finite-time disentanglement, reorientation of the relaxation rate vector may significantly increase the time of disentanglement.
Materials, 2019
Graphene-quantum dot nanocomposites attract significant attention for novel optoelectronic device... more Graphene-quantum dot nanocomposites attract significant attention for novel optoelectronic devices, such as ultrafast photodetectors and third-generation solar cells. Combining the remarkable optical properties of quantum dots (QDs) with the exceptional electrical properties of graphene derivatives opens a vast perspective for further growth in solar cell efficiency. Here, we applied (3-mercaptopropyl) trimethoxysilane functionalized reduced graphene oxide (f-rGO) to improve the QDs-based solar cell active layer. The different strategies of f-rGO embedding are explored. When f-rGO interlayers are inserted between PbS QD layers, the solar cells demonstrate a higher current density and a better fill factor. A combined study of the morphological and electrical parameters of the solar cells shows that the improved efficiency is associated with better layer homogeneity, lower trap-state densities, higher charge carrier concentrations, and the blocking of the minor charge carriers.
Physical Review E, 2000
We analyse a generalised Gross-Pitaevskii equation involving a paraboloidal trap potential in D s... more We analyse a generalised Gross-Pitaevskii equation involving a paraboloidal trap potential in D space dimensions and generalised to a nonlinearity of order 2n + 1. For attractive coupling constants collapse of the particle density occurs for Dn ≥ 2 and typically to a δ-function centered at the origin of the trap. By introducing a new dynamical variable for the spherically symmetric solutions we show that all such solutions are self-similar close to the center of the trap. Exact self-similar solutions occur if, and only if, Dn = 2, and for this case of Dn = 2 we exhibit an exact but rather special D = 1 analytical selfsimilar solution collapsing to a δ-function which however recovers and collapses periodically, while the ordinary G-P equation in 2 space dimensions also has a special solution with periodic δ-function collapses and revivals of the density. The relevance of these various results to attractive Bose-Einstein condensation in spherically symmetric traps is discussed.
We investigate propagation of slow-light solitons in atomic media described by the nonlinear Λmod... more We investigate propagation of slow-light solitons in atomic media described by the nonlinear Λmodel. Under a physical assumption, appropriate to the slow light propagation, we reduce the Λ-scheme to a simplified nonlinear model, which is also relevant to 2D dilatonic gravity. Exact solutions describing various regimes of stopping slow-light solitons can then be readily derived.
We provide an exact analytic description of decelerating, stopping and re-accelerating optical so... more We provide an exact analytic description of decelerating, stopping and re-accelerating optical solitons in atomic media. By virtue of this solution we describe in detail how spatially localized optical memory bits can be written down, read and moved along the atomic medium in a prescribed manner. Dynamical control over the solitons is realized via a background laser field whose intensity controls the velocity of the slow light in a similar way as in the linear theory of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). We solve the nonlinear model when the controlling field and the solitons interact in an inseparable nonlinear superposition process. This allows us to access results beyond the limits of the linear theory of EIT.
A generic mechanism of collapse in the Gross-Pitaevskii equation with attractive interparticle in... more A generic mechanism of collapse in the Gross-Pitaevskii equation with attractive interparticle interactions is gained by reformulating this equation as Newton's equation of motion for a system of particles with a constraint. 'Quantum pressure' effects give rise to formation of a potential barrier around the emerging singularity, which prevents a fraction of the particles from falling into the singularity. For
We study the dynamics of the reduced density matrix(RDM) of the field in the micromaser. The reso... more We study the dynamics of the reduced density matrix(RDM) of the field in the micromaser. The resonator is pumped by N-atomic clusters of two-level atoms. At each given instant there is only one cluster in the cavity. We find the conditions of the independent evolution of the matrix elements of RDM belonging to a (sub)diagonal of the RDM, i.e. conditions
Теоретическая и математическая физика, 2003
Physical Review A, 2003
An algebraic method is introduced for an analytical solution of the eigenvalue problem of the Tav... more An algebraic method is introduced for an analytical solution of the eigenvalue problem of the Tavis-Cummings (TC) Hamiltonian, based on polynomially deformed su(2), i.e. sun(2), algebras. In this method the eigenvalue problem is solved in terms of a specific perturbation theory, developed here up to third order. Generalization to the N-atom case of the Rabi frequency and dressed states is also provided. A remarkable enhancement of spontaneous emission of N atoms in a resonator is found to result from collective effects.